Summary
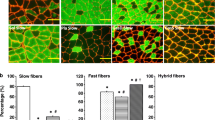
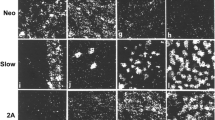
Changes in myosin synthesis during the postnatal development of the fast extensor digitorum longus (EDL) and the slow soleus muscles of the kitten were examined using immunocytochemical techniques supplemented by pyrophosphate gel electrophoresis and gel electrophoresis-derived enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (GEDELISA) of myosin isoforms. The antibodies used were monoclonals against heavy chains of slow and fast myosins and a polyclonal against foetal/embryonic myosin. In both muscles in the newborn kitten, there was a population of more mature fibres which stained strongly for slow but weakly for foetal/embryonic myosin. These fibres were considered to be primary fibres. They formed 4.8% of EDL fibres and 26% of soleus fibres at birth, and continued to express slow myosin in adult muscles. The less mature secondary fibres stained strongly for foetal/embryonic myosin, and these could be divided into two subpopulations; fast secondaries in which foetal/embryonic myosin was replaced by fast myosin, and slow secondaries in which the myosin was replaced by slow myosin. At 50 days the EDL had a large population of fast secondaries (83% of total fibres) and a small population of slow secondaries which gradually transformed into fast fibres with maturity. The vast majority of secondary fibres in the soleus were slow secondaries, in which slow myosin synthesis persisted in adult life. There was a restricted zone of fast secondaries in the soleus, and these gradually transformed into slow fibres in adult life. It is proposed that the emergence of primary fibres and the two populations of secondary fibres is myogenically determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashmore, C. R., Robinson, D. W., Rattray, P. &Doerr, L. (1972) Biphasic development of muscle fibres in the foetal lamb.Expl Neurol. 37, 241–255.
Bagust, J., Lewis, D. M. &Westerman, R. A. (1973) Polyneural innervation of kitten skeletal muscle,J. Physiol. (Lond.) 229, 241–255.
Bárány, M. (1967) ATPase activity of myosin correlated with speed of muscle shortening.J. Gen. Physiol. 50, 197–218.
Bárány, M. &Close, I. (1971) The transformation of myosin in cross-innervated rat muscles.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 213, 455–474.
Brooke, M. H. &Kaiser, K. K. (1969) Some comments on the histochemical characterization of muscle adenosine triphosphatase.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 17, 431–432.
Brooke, M. H. &Kaiser, K. K. (1970) Three ‘myosin adenosine triphosphatase’ systems: the nature of their pH liability and sulfhydryl dependence.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 18, 670–672.
Brooke, M. H., Williamson, E. &Kaiser, K. K. (1971) The behaviour of four fibre types in developing and reinnervated muscle.Arch. Neurol. 25, 360–366.
Buller, A. J., Eccles, J. C. &Eccles, R. M. (1960a) Differentiation of fast and slow muscles in the cat hindlimb.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 150, 399–416.
Buller A. J., Eccles, J. C. &Eccles, R. M. (1960b) Interactions between motoneurones and muscles in respect of the characteristic speeds of their responses.J. Physiol (Lond.) 150, 417–439.
Burke, R. E. &Tsairis, P. (1974) The correlation of physiological properties with histochemical characteristics in single muscle units.Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 228, 145–158.
Butler-Browne, G. S., Bugaisky, L. B., Cuenoud, S., Schwartz, K. &Whalen, R. G. (1982) Denervation of newborn rat muscles does not block the appearance of adult fast myosin heavy chain.Nature (Lond.) 299, 830–833.
Butler-Browne, G. S. &Whalen, R. G. (1984) Myosin transitions occurring during postnatal development of the rat soleus muscle.Devl. Biol. 102, 324–334.
Close. R. (1964) Dynamic properties of fast and slow skeletal muscles of the rat during development.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 173, 74–95.
Close, R. &Hoh, J. F. Y. (1967) Force:velocity properties of kitten muscles.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 192, 815–822.
Crow, M. T. &Stockdale, F. E. (1986) Myosin expression and specialization among the earliest muscle fibres of the developing avian limb.Devl. Biol. 113, 238–254.
D'Albis, A., Janmot, C. &Bechet, J-J. (1985) Myosin switches in skeletal muscle development of an urodelan amphibian,Pleurodeles waltli. Comparison with a mammalian, Mus musculus.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 128, 94–100.
Davies, A. (1972) Postnatal changes in the histochemical fibre types of porcine skeletal muscle.J. Anat. 113, 213–240.
Dhoot, G. K. (1986) Selective synthesis and degradation of slow skeletal myosin heavy chains in developing muscle fibres.Muscle Nerve 9, 155–164.
Draeger, A., Weeds, A. G. &Fitzsimons, R. B. (1987) Primary, secondary and tertiary myotubes in developing skeletal muscle: a new approach to the analysis of human myogenesis.J. Neurol. Sci. 81, 19–43.
Dubowitz, V. (1965) Enzyme histochemistry of skeletal muscle.J. Neurol. Nerosurg. Psychiat. 28, 516–524.
Eccles, J. C., Eccles, R. M. &Lundberg, A. (1958) The action potentials of the alpha motoneurones supplying fast and slow muscles.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 142, 275–291.
Fitzsimons, R. B. &Hoh, J. F. Y. (1981) Embryonic and foetal myosins in human skeletal muscle.J. Neurol. Sci. 52, 367–384.
Gallego, R., Huizar, P., Kudo, N. &Kuno, M. (1978) Disparity of motoneurone and muscle differentiation following spinal transection in the kitten.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 281, 253–265.
Gauthier, G. F., Lowey, S. &Hobbs, A. W. (1978) Fast and slow myosin in developing muscle fibres.Nature (Lond.) 274, 25–29.
Harris, A. J. (1981) Embryonic growth and innervation of rat skeletal muscles. I. Neural regulation of muscle fibre numbers.Philos. Trans. Roy. Soc. B 293, 257–277.
Haslasz, P. &Martin, P. R. (1984) A microcomputer based system for semi-automatic analysis of histological sections.Proc. Roy. Micr. Soc. 19, 312P.
Hennig, R. &Lømo, T. (1984) Firing patterns of motor units in normal rats.Nature (Lond.) 314, 164–166.
Hoh, J. F. Y. (1978) Light chain distribution of chicken skeletal muscle myosin isoenzymes.FEBS Lett. 90, 297–300.
Hoh, J. F. Y. &Hughes, S. (1988) Myogenic and neurogenic regulation of myosin gene expression in cat jaw-closing muscles regenerating in fast and slow limb muscle beds.J. Musc. Res. Cell Motility 9, 59–72.
Hoh, J. F. Y., Hughes, S., Chow, C., Hale, P. T. &Fitzsimons, R. B. (1988) Immunocytochemical and electrophoretic analyses of changes in myosin gene expression in cat posterior temporalis muscle during postnatal development.J. Musc. Res. Cell Motility 9, 48–58.
Hoh, J. F. Y., Kwan, B. T. S., Dunlop, C. &Kim, B. H. (1980) Effects of nerve cross-union and cordotomy on myosin isoenzymes in fast-twitch and slow-twitch muscles of the rat. InPlasticity of Muscle (edited byPette, D.), pp. 339–352. Berlin. New York: Walter de Gruyter & Co.
Hoh, J. F. Y., Mcgrath, P. A. &White, R. I. (1976) Electrophoretic analysis of mutiple forms of myosin in fast-twitch and slow-twitch muscles of the chick.Biochem. J. 157, 87–95.
Hoh, J. F. Y. &Yeoh, G. P. S. (1979) Rabbit skeletal myosin isoenzymes from foetal, fast-twitch and slow-twitch muscles.Nature (Lond.) 280, 321–323.
Hoh, J. F. Y., Yeoh, G. P. S., Thomas, M. A. W. &Higginbottom, L. (1979) Structural differences in the heavy chains of rat ventricular myosin isoenzymes.FEBS Lett. 97, 330–334.
Howald, H. (1982) Training-induced morphological and functional changes in skeletal muscle.Int. J. Sports Med. 3, 1–12.
Hugh, G. &Hoh, J. F. Y. (1987) Immunocytochemical analysis of myosin isoenzymes in denervated rat fast and slow muscles.Proc. Aust. Physiol. Pharm. Soc. 18, 45P.
Hughes, S. &Hoh, J. F. Y. (1985) Myotubes grown in tissue culture from juvenile cat jaw and limb muscles express a slow myosin epitope.Proc. Aust. Physiol. Pharm. Soc. 16, 260P.
Jolesz, F. &Sréter, F. A. (1981) Development, innervation, and activity-pattern induced changes in skeletal muscle.Ann. Rev. Physiol. 43, 531–552.
Jones, S. P., Ridge, R. M. A. P. &Rowlerson, A. (1987a) The non-selective innervation of muscle fibres and mixed composition of motor units in a muscle of neonatal rat.J. Physiol (Lond.) 386, 377–394.
Jones, S. P., Ridge, R. M. A. P. &Rowlerson, A. (1987b) Rat muscle during post-natal development: evidence in favour of no interconversion between fast-and slow-twitch fibres.J. Physiol (Lond.) 386, 395–406.
Karpati, G. &Engel, W. K. (1967) Neuronal trophic function.Arch. Neurol. 17, 542–545.
Kelly, A. M. &Zacks, S. I. (1969) The histogenesis of rat intercostal muscle.J. Cell Biol. 42, 135–153.
Kugelberg, E. (1976) Adaptive transformation of rat soleus motor units during growth.J. Neurol. Sci. 27, 269–289.
Lowey, S. (1985) Myosin isozymes in developing chicken muscle.Advances in Experimental Med. & Biol. 182, 269–280.
Lutz, H., Ermini, M., Jenny, E., Bruggmann, S., Joris, F. &Weber, E. (1978) The size of the fibre populations in rabbit skeletal muscles as revealed by indirect immunofluorescence with anti-myosin sera.Histochemistry 57, 223–235.
Lyons, G. E., Haselgrove, J., Kelly, A. M. &Rubinstein, N. A. (1983) Myosin transitions in developing fast and slow muscles of the rat hindlimb.Differentiation 25, 168–175.
Maier, A. &Eldred, E. (1974) Postnatal growth of the extra-and intrafusal fibres in the soleus and medial gastrocnemius muscles of the cat.Amer. J. Anat. 141, 161–177.
Maxwell, L. C., Barclay, J. K., Mohrman, D. E. &Faulkner, J. A. (1977) Physiological characteristics of skeletal muscles of dogs and cats.Amer. J. Physiol. 233, C14-C18.
Mclennan, I. S. (1983) Neural dependence and independence of myotube production in chicken hindlimb muscles.Devl. Biol. 98, 287–294.
Miller, J. B. &Stockdale, F. E. (1986) Developmental origins of skeletal muscle fibres: clonal analysis of myogenic cell lineages based on expression of fast and slow myosin heavy chains.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 83, 3860–3864
Narusawa, M., Fitzsimons, R. B., Izumo, S., Nadal-Ginard, B., Rubinstein, N. A. &Kelly, A. M. (1987) Slow myosin in developing rat skeletal muscle.J. Cell Biol. 104, 447–459.
Navarrete, R. &Vrbová, G. (1983) Changes in activity patterns in slow and fast muscles during postnatal development.Dev. Brain Res. 8, 11–19.
Nystrom, B. (1968) Histochemistry of developing cat muscles.Acta Neurologica Scand. 44, 405–439.
Periasamy, M., Wieczorek, D. F. &Nadal-Ginard, B. (1984) Characterization of developmentally regulated perinatal myosin heavy-chain gene expressed in skeletal muscle.J. Biol. Chem. 259, 13573–13578.
Periasamy, M., Wydro, R. M., Strehler-Page, A-M., Strehler, E. E. &Nadal-Ginard, B. (1985) Characterization of cDNA and genomic sequences corresponding to an embryonic myosin heavy chain.J. Biol. Chem. 260, 15856–15862.
Pette, D. &Vrbová, G. (1985) Invited review: neural control of phenotypic expression in mammalian muscle fibres.Muscle Nerve 8, 676–689.
Phillips, W. D. &Bennett, M. R. (1984) Differentiation of fibre types in wing muscles during embryonic development: effect of neural tube removal.Devl. Biol. 106, 457–468.
Redfern, P. A.(1970) Neuromuscular transmission in new-born rats.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 209. 701–709.
Rossmanith, G. H., Hoh, J. F. Y., Kirman, A. &Kwan, L. J. (1986) Influence of V1 and V3 isomyosins on the mechanical behaviour of rat papillary muscle as studied by pseudo-random binary noise modulated length perturbations.J. Musc. Res. Cell Motility 7, 307–319.
Rowlerson, A. (1979) Differentiation of muscle fibre types in foetal and young rats studied with a labelled antibody to slow myosin.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 301, 19P.
Rubinstein, N. A. &Kelly, A. M. (1981) Development of muscle fibre specialization in the rat hindlimb.J. Cell Biol. 90, 128–144.
Salviati, G., Biasia, E. &Aloisi, M. (1986) Synthesis of fast myosin induced by fast ectopic innervation of rat soleus muscle is restricted to the ectopic endplate region.Nature (Lond.) 322, 637–639.
Swynghedauw, B. (1986) Developmental and functional adaptation of contractile proteins in cardiac and skeletal muscles.Physiol. Rev. 66, 710–771.
Syrovy, I. &Gutmann, E. (1977) Differentiation of myosin in soleus and extensor digitorum longus muscle in different animal species during development.Pflügers Arch. 369, 85–89.
Thompson, W. J., Sutton, L. A. &Riley, D. A. (1984) Fibre type composition of single motor units during synapse elimination in neonatal rat soleus muscle.Nature (Lond.) 309, 709–711.
Thornell, L.-E., Billeter, R., Butler-Browne, G. S., Eriksson, P.-O., Ringqvist, M. &Whalen, R. G. (1984) Development of fibre types in human foetal muscle.J. Neurol. Sci. 66, 107–115.
Tomanek, R. J. (1975) A histochemical study of postnatal differentiation of skeletal muscle with reference to functional overload.Devl. Biol. 42, 305–314.
Weydert, A., Barton, P., Harris, A. J., Pinset, C. &Buckingham, M. (1987) Developmental pattern of mouse skeletal myosin heavy chain gene transcriptsin vivo andin vitro.Cell 49, 121–129.
Whalen, R. G., Sell, S. M., Butler-Browne, G. S., Schwartz, K., Bouveret, P. &Pinset-Harstrom, I. (1981) Three myosin heavy-chain isozymes appear sequentially in rat muscle development.Nature (Lond.) 292, 805–809.
White, N. K., Bonner, P. H., Nelson, D. R. &Hauschka, S. D. (1975) Clonal analysis of vertebrate myogenesis. IV. Medium-dependent classification of colony forming cells.Devl. Biol. 44, 346–361.
Young, R. B., Moriarity, D. M. &Mcgee, C. E. (1986) Structural analysis of myosin genes using recombinant DNA techniques.J. Anim. Sci. 63, 259–268.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoh, J.F.Y., Hughes, S., Hale, P.T. et al. Immunocytochemical and electrophoretic analyses of changes in myosin gene expression in cat limb fast and slow muscles during postnatal development. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 9, 30–47 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01682146
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01682146