Summary
The digestion ofSaccharomyces cerevisiae byAcanthamoeba castellanii, at different times after feeding, has been examined by cytochemical techniques at electron microscope level and by measurement of yeast viability. The measurement of viability, combined with cytochemistry is presented as a novel method of examining the progress of digestion. Particular attention has been given to the temporal development of digestion.
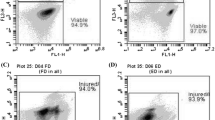
Vacuoles, probably primary lysosomes, have been identified containing acid phosphatase activity within minutes of feeding and these accumulate around and fuse with phagocytic vacuoles. Acid phosphatase levels in the digestive vacuoles appeared highest at 20 to 40 minutes. Yeast digestion was observed and yeast viability began to decline at this time. Mixing of autophagic and heterophagic material was also observed. At least half of the yeast population was still viable after 90 minutes.
Our method (p-nitrophenyl phosphate) of enzyme localization has demonstrated plasma membrane associated acid phosphatase activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beadle, D. J., Dawson, A. L., Amos, S., 1976: The demonstration of acid phosphatase in cultured 3T3 mouse cells. Histochemistry48, 161–166.
Bowen, I. D., Davies, P., 1971: The fine structural distribution of acid phosphatase in the digestive glandArion hortensis (Fer.). Protoplasma73, 73–81.
Bowen, I. D., Ryder, T. A., 1974: Cell autolysis and deletion in the planarianPolycelis tenuis Iijima. Cell and Tissue Research154, 265–274.
— —, 1976: Use of the p-nitrophenyl phosphate method for the demonstration of acid phosphatase during starvation and cell autolysis in the planarianPolycelis tenuis Iijima. Histochem. J.8, 319–329.
— —,Dark, C., 1976: The effects of starvation on the planarian wormPolycelis tenuis. Cell and Tissue Research169, 193–269.
Bowers, B., Korn, E. D., 1969: The fine structure ofAcanthamoeba castellanii (Neff strain) II. Encystment. J. Cell Biol.41, 786–805.
Brown, R. C., Bass, H., Coombs, J. P., 1975: Carbohydrate binding proteins involved in phagocytosis byAcanthamoeba. Nature254, 434–435.
Goodall, R. J., Thompson, J. E., 1971: A scanning electron microscopic study of phagocytosis. Exp. Cell Res.64, 1–8.
Griffiths, A. J., Bowen, S. M., 1969: Lysosomal activity and its control in encystingHartmannella castellanii, J. gen. Microbiol.59, 239–245.
Muller, M., 1969: Lysosomal hydrolases inAcanthamoeba sp. J. Protozool.16, 428–431.
Novikoff, A. B., Essner, E., Quintana, N., 1964: The golgi apparatus and lysosomes. Fed. Proc.23, 1010–1022.
Oates, P. J., Touster, O., 1976:In vitro fusion ofAcanthamoeba phagolysomes. 1. Demonstration and quantitation of vacuole fusion inAcanthamoeba homogenates. J. Cell Biol.68, 319–338.
Ryter, A., Bowers, B., 1976: Localization of acid phosphatase inAcanthamoeba castellanii with light and electron microscopy during growth and after phagocytosis. J. Ultrastruct. Res.57, 309–321.
Ugolev, A. M., 1960: Parietal (contact) digestion. Bull. exp. Biol. Med.49, 12–17.
Wetzel, M. G., Korn, E. D., 1969: Phagocytosis of latex heads byAcanthamoeba castellanii (Neff). III. Isolation of the phagocytic vesicles and their membranes. J. Cell Biol.43, 90–104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bowen, I.D., Coakley, W.T. & James, C.J. The digestion ofSaccharomyces cerevisiae byAcanthamoeba castellanii . Protoplasma 98, 63–71 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01676662
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01676662