Summary
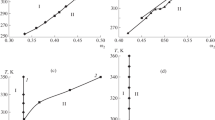
Structural and thermodynamic characteristics of liquid-crystalline solutions of four cellulose derivatives in a range of solvents were studied. Basic observations were made on these systems using polarized light microscopy, small angle light scattering, dilute solution and concentrated solution viscosities. The polymers studied include hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC), cellulose acetate butyrate (CAB), ethyl cellulose (EC), and cellulose triacetate (CT). The formation of the liquid crystalline phase was shown to strongly depend on polymer concentration, solvent type and temperature. The critical volume fraction of polymer required to form the liquid crystal phase varied significantly as the solvent changed. The critical volume fraction decreased with increasing solvent acidity and polymer intrinsic viscosity in a given solvent. The breadth of the two phase region seems to decrease with increasing acidity. The liquid crystalline phase was in most cases determined to be cholesteric. In all cases positively birefringent cellulose derivatives form negative spherulitic domains. In one case, the negativity birefringent system (cellulose triacetate) formed positively birefringent spherulitic liquid crystalline domains. This is interpreted to mean the structure organizes itself by a tangential alignment of polymer chains within the domain. SALS measurements appear to detect domains and in some cases cholesteristic pitch.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robinson, C., Trans. Faraday Soc.52, 571 (1956), Tetrahedron13, 219 (1961).
Samulski E. T., A. V. Tobolsky, in: Liquid Crystals and Plastic Crystals edited by G. Gray and P. Winsor, Wiley, NY (1974).
Onogi, Y., J. L. White, J. F. Fellers, J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys.18, 663 (1980).
Kwolek, S. L., U. S. Patent, 3, 671, 542 (1972).
Hancock, T. A., J. E. Spruiell, J. L. White, J. Appl. Polym. Sci.21, 1227 (1977).
Morgan, P. W., Macromolecules10, 1381 (1977).
Kwolek, S. L., P. W. Morgan, J. R. Shaefgen, L. W. Gulrich, Macromolecules10, 1390 (1977).
Bair, T. I., P. W. Morgan, F. L. Killian, Macromolecules10, 1396 (1977).
Panar, M., L. F. Beste, Macromolecules10, 1401 (1977).
White, J. L., J. F. Fellers, Appl. Polym. Symp.33, 137 (1978).
Jackson, W. J., H. F. Kuhfuss, J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem.14, 2043 (1976).
Pletcher, T. C., U. S. Patent, 3, 991, 013 (1976), andJ. J. Kleinschuster, U.S. Patent, 3, 991, 014 (1976).
Werbowyj, R. S., D. G. Gray, Mol. Cryst, Liq. Cryst.34, (Letters) 97 (1976).
Werbowyj, R. S., D. G. Gray, Macromolecules13, 69 (1980).
Panar, M., O. B. Willcox, Offenlegungsschrift, 2705381, German Federal Republic (1977).
Aharoni, S. M., Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst.56, (Letters) 237 (1980).
Chanzy, H., M. Dube, R. H. Marchessault, J. Polym. Sci., Polym. Letters17, 219 (1979).
Onogi, Y., J. L. White, J. F. Fellers, J. Non-Newt. Fluid Mech.7, 121 (1980).
Aoki, H., J. L. White, J. F. Fellers, J. Appl. Polym. Sci.23, 2293 (1979).
Aoki, H., Y. Onogi, J. L. White, J. F. Fellers, Polym. Eng. Sci.20, 221 (1980).
Flory, P. J., Proc. Roy. Soc.A234, 73 (1956).
Bender, B. W., J. Appl. Polym. Sci.9, 2887 (1965).
Molau, G. E., W. M. Witbrodt, V. E. Meyer, J. Appl. Polym. Sci.13, 2735 (1969).
Wirick, M. G., M. H. Waldman, J. Appl. Polym. Sci.14, 579 (1970).
Denbigh, K., The Principles of Chemical Equilibrium, 3rd Edition, Cambridge University Press (1971).
Stein, R. S., M. B. Rhodes, J. Appl. Phys.31, 1873 (1960).
Samuels, R. J., J. Polym. Sci. A-2,9, 2165 (1971).
Hashimoto, T., A. Todo, H. Kawai, J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys.11, 149, (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 5 figures and 4 tables
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bheda, J., Fellers, J.F. & White, J.L. Phase behavior and structure of liquid crystalline solutions of cellulose derivatives. Colloid & Polymer Sci 258, 1335–1342 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01668781
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01668781