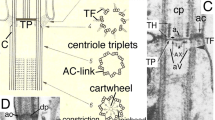
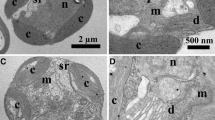
Summary
The ultrastructural features, biogenesis and functions of several selected protist extrusive organelles are discussed. Most of the review focuses on some common extrusive organelles that were not considered by Hausmann and several types which have been described since that review of 16 years ago. For convenience, extrusomes are categorized as projectile or mucocyst extrusomes. The projectile extrusomes are further subdivided into non-penetrating and cell penetrating extrusomes. This review is restricted to projectile extrusomes such as ejectisomes, the microsporidian invasion apparatus, and the gun cell of oomycetes. Mucocysts include the apicomplexan rhoptries, the K2 bodies of oomycetes, and the spermatial vesicles and adhesive vesicles of red algae. The possible phylogenetic importance of some extrusive organelles is briefly considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adoutte A (1988) Exocytosis: biogenesis, transport and secretion of trichocysts. In: Görtz H-D (ed) Paramecium. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 325–362
Allen RD (1988) Cytology. In: Görtz H-D (ed) Paramecium. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 4–40
Allman GJ (1855) On the occurrence among the infusoria of peculiar organs resembling thread cells. Q J Microsc Sci 3: 177–179
Andersen RA (1992) Diversity of eukaryotic algae. Biodivers Conserv 1: 267–292
Azvedo C (1987) Fine structure of the microsporidianAbelspora portulacalensis gen. n. sp. n. (Microsporida) parasite of the hepatopancreas ofCarcinus maenas (Crustacea, Decapoda). J Invertebr Pathol 49: 83–92
Bannister LH, Mitchell GH (1989) The fine structure of secretion byPlasmodium knowlesi merozoites during red cell invasion. J Protozool 36: 362–367
Barron GL (1980) A newHaptoglossa attacking rotifers by rapid injection of an infective sporidium. Mycologia 72: 1186–1194
Bauer LS, Pankratz HS (1993)Nosema scripta n.sp. (Microsporidia: Nosematidae), a microsporidian parasite of the cottonwood leaf beetle,Chrysomela scripta (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). J Protozool 40: 135–141
Beard BB, Butler JF, Becnel JJ (1990)Nolleria pulicis n.gen., n.sp. (Microsporidia: Chytridiopsidae), a microsporidian parasite of the cat flea,Ctenocephalides felis (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). J Protozool 37: 90–99
Becnel JJ, Hazard EI, Fukuda T (1986) Fine structure and development ofPilosporella chapmani (Microspora: Telohaniidae) in the mosquito,Aedes triseriatus (Say). J Protozool 33: 60–66
Benwitz G (1984) Die Entladung der Haptocysten vonEphelota gemmipara (Suctoria, Ciliata). Z Zellforsch 39 c: 812–817
Broadwater ST, Scott JL, West JA (1991) Spermatial appendages ofSpyridia filamentosa (Ceramiaceae, Rhodophyta). Phycologia 30: 189–195
Brugerolle G (1985) Des trichocytes chez bodonidés, un caractère phylogénétique supplémantaire entre Kinetoplastida et Euglenida. Protistologica 21: 339–348
Bryan RT, Cali A, Owen RL, Spencer KC (1990) Microsporidia. Opportunistic pathogens in patients with AIDS. Prog Clin Parasitol 2: 1–26
Cali A (1991) General microsporidian features and recent findings on AIDS isolates. J Protozool 38: 625–630
—, Owen RL (1988) Microsporidiosis. In: Balows A, Hauser WJ, Lennette EH (eds) The laboratory diagnosis of infectious diseases: principles and practice, vol 1. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 929–950
— — (1990) Intracellular development ofEnterocytozoon, a unique microsporidian found in the intestine of AIDS patients. J Protozool 37: 145–155
—, Kotler DP, Orenstein JM (1993)Septata intestinalis n.g, n.sp., and intestinal microsporidian associated with chronic diarrhea and dissemination in AIDS patients. J Protozool 40: 101–112
—, Orenstein JM, Kotler DP, Owen RL (1991) A comparison of two microsporidian parasites in enterocytes of AIDS patients with chronic diarrhea. J Protozool 38: 96S-98S
Canning EU (1990) Phylum Microspora. In: Margulis L, Corliss JO, Melkonian M, Chapman DJ (eds) Handbook of Protoctista. Jones and Bartlett, Boston, pp 53–72
—, Hollister WS (1992) Human infections with microsporidia. Rev Med Microbiol 3: 35–42
—, Lom J (1986) The microsporidia of vertebrates. Academic Press, New York
Cooper JA, Ingram LT, Fardoulys CA, Stenzel D, Schofield L, Saul LJ (1988) The 140/105 kilodalton protein complex in the rhoptries ofPlasmodium falciparum consists of discrete polypeptides. Mol Biochem Parasitol 29: 251–260
Corliss JO (1972) The ciliate protozoa and other organisms: some unresolved questions of major phylogenetic significance. Am Zool 12: 739–753
— (1979) The ciliated protozoa: characterization, classification and guide to the literature, 2nd edn. Pergamon, London
— (1988) The quest for the ancestor of the Ciliophora: a brief review of the continuing problem. BioSystems 7: 338–349
—, Lom J (1985) An annotated glossary of protozoological terms. In: Lee JJ, Hutner SH Bovee EC (eds) An illustrated guide to the Protozoa. Society of Protozoologists, Lawrence, KS, pp 576–602
Didier PJ, Didier ES, Orenstein JM, Shadduck JA (1991) Fine structure of a new human microsporidia,Encephalitozoon hellem, in culture. J Protozool 38: 502–507
Dodge JD, Gruet C (1987) Dinoflagellate ultrastructure and complex organelles. In: Taylor FJR (ed) The biology of dinoflagellates. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 93–142
Douglas SE, Murphy CA, Spencer DF, Gray MW (1991) Cryptomonad algae are evolutionary chimaeras of two phylogenetically distinct unicellular eukaryotes. Nature 350: 148–151
Dragesco J (1984) Organites sous-cuticulaires éjectables: éjectisomes (trichocystes). In: Grasse P-P (ed) Traité de Zoologie, vol 2, fasc 1. Masson, Paris, pp 181–199
Ellis J (1969) Observations on a particular manner of increase in the animalcula of vegetable infusions. Philos Trans Soc Lond [Biol] 59: 138–152
Eperon S, Vigues B, Peck RK (1993) Immunological characterization of trichocyst proteins in the ciliatePseudomicrothorax dubius. J Eukar Microbiol 40: 81–91
Etzion Z, Murray MC, Perkins ME (1991) Isolation and characterization of rhoptries ofPlasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol 47: 51–62
Fetter R, Neushul M (1981) Studies on the development and released spermatia in the red algaTiffaniella snyderae (Rhodophyta). J Phycol 17: 141–159
Friedberg DN, Stenson SM, Orenstein JM, Charles N (1990) Microsporidial keratoconjunctivities in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Ophthalmol 108: 504–508
Frixione E, Ruiz L, Santillan M, de Vargas LV, Tajero JM (1992) Dynamics of polar filament discharge and sporoplasm expulsion by microsporidian spores. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 22: 38–50
Garofalo RS, Satir BH (1984)Paramecium secretory granule content: quantitative studies on in vitro expansion and its regulation by calcium and pH. J Cell Biol 99: 2193–2199
Glas-Albrecht R, Plattner H (1990) High yield isolation procedure for intact secretory organelles (trichocysts) from differentParamecium tetraurelia strains. Eur J Cell Biol 53: 164–172
Grim JN, Staehelin LA (1984) The ejectisomes of the flagellateChilomonas paramecium: visualization by freeze-fracture and isolation techniques. J Protozool 3: 259–267
Harrison FW, Corliss JO (eds) (1991) Protozoa. Wiley-Liss, New York [Harrison FW (ed) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates, vol 1]
Hausmann K (1978) Extrusive organelles in protists. Int Rev Cytol 52: 197–276
—, Fok AK, Allen RD (1988) Immunocytochemical analysis of trichocyst structure and development inParamecium. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res 99: 213–225
Heywood P, Rothschild LJ (1987) Reconciliation of evolution and nomenclature among the higher taxa of protists. Biol J Linn Soc 30: 91–98
Hibberd DJ (1970) Observations on the cytology and ultrastructure ofOchromonas tuberculatus sp.nov. (Chrysophyceae), with special reference to the discobolocysts. Br Phycol J 5: 119–143
Hilenski LL, Walne PL (1983) Ultrastructure of mucocysts inPeranema trichophorum (Euglenophyceae). J Protozool 30: 491–496
Hovasse R, Mignot JP (1975) Trichocystes et organites analogues chez les protistes. Ann Biol 14: 397–422
Jensen JB, Edgar SA (1976) Possible secretory function of the rhoptries ofEimeria magna during penetration of cultured cells. J Parasitol 62: 988–992
Kimata I, Tanabe K (1978) Secretion byToxoplasma gondii of an antigen that appears to become associated with parasitophorous vacuole membrane upon invasion of the host cell. J Cell Sci 88: 231–239
Krüger F (1936) Die Trichocysten der Ciliaten im Dunkelfeldabbild. Zoologica 34: 1–82
Kugrens P (1980) Electron microscopic observations on the differentiation and release of spermatia in the marine red algaPolysiphonia hendryi (Ceramiales, Rhodomelaceae). Amer J Bot 67: 519–528
—, Delivopoulos SG (1986) Ultrastructure of the carposporophyte and carposporogenesis in the parasitic red algaPlocamiocolax pulvinata Setch (Gigartinales, Plocamiaceae). J Phycol 22: 8–21
—, Lee RE (1991) Organization of cryptoprotists. In: Patterson DJ, Larsen J (eds) The biology of free-living heterotrophic flagellates. Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp 219–233 (Systematics Association special volume 45)
Larsson JIR (1986) Ultrastructure, function and classification of microsporidia. Prog Protistol 1: 325–390
— (1992) The light and electron microscopic cytology ofIancekia adpophila n.sp. (Microspora, Tuzetiidae), a microsporidian parasite ofPtychoptera paludosa (Diptera, Ptychopteridae). J Protozool 39: 432–440
— (1993) Description ofChytridiopsis trichopterae n.sp. (Microspora, Chytridiopsidae), a microsporidan parasite of the caddis flyPolycentrophus flavomaculatus (Trichoptera, Polycentropodidae), with comments on relationships between families Chytridiopsidae and Metchnikovellidae. J Protozool 40: 37–48
Lee JJ, Hutner SH, Bovee EC (eds) (1985) An illustrated guide to the Protozoa. Society of Protozoologists, Lawrence, KS
Lee RE, Kugrens P (1991)Katablepharis ovalis, a colorless flagellate with interesting cytological characteristics. J Phycol 27: 505–513
— — (1992) Relationship between the flagellates and the ciliates. Microbiol Rev 56: 529–542
Lehnen LP, Powell MJ (1988) Cytochemical localization of carbohydrates in zoospores ofSaprolegnia ferax. Mycologia 80: 423–432
— — (1989) The role of kinetosome associated organelles in the attachment of secondary zoospores ofSaprolegnia ferax to substrates. Protoplasma 149: 163–174
— — (1991) Formation of K2 bodies in primary cysts ofSaprolegnia ferax. Mycologia 8: 163–179
Leitch GJ, Qing H, Wallace S, Visvesvara GS (1993) Inhibition of the spore polar filament extrusion of the microsporidium,Encephalocytozoon hellem, isolated from an AIDS patient. J Eukar Microbiol 40: 711–717
Leriche MA, Dubremetz JF (1991) Characterization of the protein contents of rhoptries by subcellular fractionation and monoclonal antibodies. Mol Biochem Parasitol 45: 249–260
Levine ND (1982) Apicomplexa. In: Parker SP (ed) Synopsis and classification of living organisms. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 570–587
— (1985) Phylum II. Apicomplexa Levine, 1970. In: Lee JJ, Hutner SH, Bovee EC (eds) An illustrated guide to the Protozoa. Society of Protozoologists, Lawrence, KS, pp 322–374
— (1988) The protozoan Phylum Apicomplexa, vol I. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Lima O, Gulik-Krzywicki T, Sperling L (1989)Paramecium trichocysts isolated with their membranes are stable in the presence of millimolar Ca2+. J Cell Sci 93: 557–564
Lom J (1990) Phylum Myxozoa. In: Margulis L, Corliss JO, Melkonian M, Chapman DJ (eds), Handbook of Protoctista. Jones and Bartlett, Boston, pp 36–52
—, Dyková I, Lhotáková S (1982) Fine structure ofSphaerospora renicola Dyková & Lom, 1982. A myxosporean from carp kidney and comments on the origin of pansporoblasts. Protistologica 19: 489–502
Lumpert CJ, Kersken H, Plattner H (1990) Cell surface complexes (corticles) isolated fromParamecium tetraurelia cells as a model system for analyzing exocytosis in vitro in conjunction with microinjection studies. Biochem J 269: 639–645
Lynn DH, Corliss JO (1991) Phylum Ciliophora. In: Harrison FW, Corliss JO (eds) Protozoa. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 333–467 [Harrison FW (ed) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates, vol 1]
Magruder WH (1984) Specialized appendages on spermatia from the red algaAglaothamnion neglectum (Ceramiales, Ceramiaceae) specifically bind with trichogynes. J Phycol 20: 436–440
Manton I (1968) Tubular trichocysts in a species ofPyramimonas parkeae. Oesterr Bot Z 116: 378–397
Margulis L, Corliss JO, Melkonian M, Chapman DJ (eds) (1990) Handbook of Protoctista. Jones and Bartlett, Boston
Mine I, Tatewaki M (1994) Attachment and fusion of gametes during fertilization ofPalmaria sp. (Rhodophyta). J Phycol 30: 55–66
Mitchell MJ, Cali A (1993) Ultrastructural study of the development ofVairimorpha necatrix (Kramer 1965) (Protozoa, Microsporida) in larvae of the corn earworm,Heliothis zea (Boddie) (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae) with emphasis on sporogony. J Eukar Microbiol 40: 701–710
Moestrup Ø (1984) Further studies onNephroselmis and its allies (Prasinophyceae). II.Mamiella gen.nov., Mamiellaceae fam.nov., Mamiellales ord.nov. Nord J Bot 4: 109–121
Moore CB, Brooks WM (1992) An ultrastructural study ofVairimorpha necatrix (Microspora, Microsporida) with particular reference to episporontal inclusions during octosporogony. J Protozool 39: 392–398
Morrall S, Greenwood AD (1980) A comparison of the periodic structures of the trichocysts of the Cryptophyceae and Prasinophyceae. BioSystems 12: 71–84
Navdeep SJ, Rozario C, Ridley RG, Perkins ME (1993) Biogenesis of rhoptry organelles inPlasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol 57: 269–280
Neill PJG, Smith JH, Box ED (1989) Pathogenesis ofSarcocystis falculata (Apicomplexa∶Sarcocystidae) in the budgerigar (Melopsittacus undulatus). IV. Ultrastructure of developing, mature and degenerating sarcocysts. J Protozool 36: 430–437
Nichols BA, Chiappino ML (1987) Cytoskeleton ofToxoplasma gondii. J Protozool 34: 217–226
— —, O'Conner GR (1983) Secretion from the rhoptries ofToxoplasma gondii during host-cell invasion. J Ultrastruct Res 83: 85–98
Orenstein JM (1991) Microsporidiosis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Parasitol 77: 843–864
Ossorio PN, Schwartzman JD, Boothroyd JC (1992) AToxoplasma gondii protein associated with host cell penetration has unusual discharged symmetry. Mol Biochem Parasitol 50: 1–16
Parker SP (ed) (1982) Synopsis and classification of living organisms, vols. 1, 2. McGraw-Hill, New York
Perkins FO (1991) “Sporozoa”∶Apicomplexa, Microsporidia, Paramyxea, Myxosporidia and Actinosporidia. In: Harrison FW, Corliss JO (eds) Protozoan. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 261–331 [Harrison FW (ed) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates, vol 1]
Perkins ME (1992) Rhoptry organelles of apicomplexan parasites. Parasitol Today 8: 28–32
Peterson JB (1991) Small GTP-binding proteins associated with secretory vesicles ofParamecium. J Protozool 38: 495–501
—, Heuser JE, Nelson DL (1987) Dissociation and reassociation of trichocyst proteins: biochemical and ultrastructural studies. J Cell Sci 87: 3–25
Pueschel CM (1979) Ultrastructure of tetrasporogenesis inPalmaria palmata (Rhodophyta). J Phycol 15: 409–424
Pitelka DR (1963) Electron microscopic structure of Protozoa. Pergamon, London
Pleshinger J, Weidner E (1985) The microsporidian spore invasion tube. IV. Discharge activation begins with pH triggered Ca2+ influx. J Cell Biol 100: 1834–1838
Powell MJ, Lehnen LP, Bortnick RN (1985) Microbody-like organelles as taxonomic markers among oomycetes. BioSystems 18: 321–334
Preparata RM, Meyer EB, Preparata FB, Simon EM, Vossbrink CR, Nanney DL (1989) Ciliate evolution: the ribosomal phylogenies of tetrahymenine cillates. J Mol Evol 28: 427–441
Raikov IB (1993) The orthonematocyst, a new type of extrusome found inRemanella rugosa andRemanella brunnea (Ciliophora: Karyorelictida). Eur J Protistol 29: 81–87
Robb J, Barron GL (1982) Nature's ballistic missile. Science 218: 1221–1222
—, Lee B (1986 a) Developmental sequence of the attack apparatus ofHaptoglossa mirabilis. Protoplasma 135: 102–111
— — (1986 b) Ultrastructure of mature and fired gun cells ofHaptoglossa mirabilis. Can J Bot 64: 1935–1947
Roger N, Dubremetz JF, Delplace P, Fortier B, Tronchin B, Vernes A (1988) Characterization of 225-kilodalton rhoptry protein ofPlasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol 27: 135–142
Safer LD, Schwartzman JD (1991) A soluble phospholipase ofToxoplasma gondii associated with host cell penetration. J Protozool 38: 454–460
Sam-Yellowe TY (1992) Molecular factors responsible for host cell recognition and invasion inPlasmodium falciparum. J Protozool 39: 181–189
—, Ndengele MM (1993) Monoclonal antibody epitope mapping ofPlasmodium falciparum rhoptry proteins. Exp Parasitol 76: 46–58
—, Perkins ME (1981) Interaction of the 140/130/110 kDa rhoptry protein complex ofPlasmodium falciparum with the erythrocyte membrane and liposomes. Exp Parasitol 73: 161–171
— — (1990) Binding ofPlasmodium falciparum rhoptry proteins to mouse erythrocytes and their possible role in invasion. Mol Biochem Parasitol 39: 91–100
— — (1991) Interaction of the 140/130/110 kDa rhoptry protein complex ofPlasmodium falciparum with erythrocyte membrane and liposomes. Exp Parasitol 73: 161–171
—, Shio H, Perkins ME (1988) Secretion ofPlasmodium falciparum rhoptry protein into the plasma membrane of host erythrocytes. J Cell Biol 106: 1507–1513
Scarborough-Bull A, Weidner E (1985) Some properties of dischargedGlugea hertwigi (Microsporidia) sporoplasms. J Protozool 32: 284–289
Shadduck JA (1989) Human microsporidiosis in AIDS. Rev Infect Dis 11: 203–207
—, Meccoli RA, Davis R, Font RL (1989) First isolation of a microsporidian from a human patient. Infect Dis 162: 773–776
Sprague V (1982 a) Microspora. In: Parker SP (ed) Synopsis and classification of living organisms. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 589–594
Sprague V (1982 b) Myxozoa. In: Parker SP (ed) Synopsis and classification of living organisms. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 595–597
Stewart MJ, Schulman S, Vanderberg JP (1986) Rhoptry secretion of membranous whorls byPlasmodium falciparum merozoites. Am J Tropical Med 35: 37–44
Supamattaya K, Fischer-Scherl T, Hoffman RW, Boonyaratpalin S (1991)Sphaerospora epinepheli n.sp. (Myxosporea: Sphaerosporidae) observed in grouper (Epinephelus malabaricus). J Protozool 38: 448–454
— — — — (1993) Light and electron microscopic observations on presporogonic and sporogonic stages ofSphaerospora epinepheli (Myxosporea) in grouper (Epinephelus malabaricus). J Protozool 40: 71–80
Taylor FJR (1976) Flagellate phylogeny: a study in conflicts. J Protozool 23: 28–30
— (1978) Problems in the development of an explicit hypothetical phylogeny of the lower eukaryotes. BioSystems 10: 67–69
— (1987) The biology of dinoflagellates. Blackwell, Oxford
— (1990) Dinoflagellate. In: Margulis L, Corliss JO, Melkonian M, Chapman DJ (eds) Handbook of Protoctista. Jones and Bartlett, Boston, pp 419–437
Terada S, Reddy R, Jeffers LJ, Cali A, Schiff ER (1987) Microsporidian hepatitis in a patient with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med 107: 61–62
Tönniges G (1914) Die Trichocysten vonFrontonia leucas und ihr chromidialer Ursprung. Arch Protistenk 32: 298–378
Vavra (1976) Structure of the microsporidia. In: Bulla LA Jr, Cheng TC (eds) Comparative pathobiology, vol 1, biology of microsporidia. Plenum, New York, pp 1–85
Vesk M, Lucas IAN (1986) The rhabdosome: a new type of organelle in the dinoflagellateDinophysis. Protoplasma 134: 62–64
Vickerman K, Brugerolle G, Mignot J-P (1991) Mastigophora. In: Harrison FW, Corliss JO (eds) Protozoa. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 13–159 [Harrison FW (ed) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates, vol 1]
Visvesvra GS, Leitch GJ, Moura H, Wallace S, Weber R, Bryan RT (1991) Culture, electron microscopy and immunoblot studies on a microsporidian parasite isolated from the urine of a patient with AIDS. J Protozool 38: 105S-113S
Vørs N (1992) Ultrastructure and autecology of the marine, heterotrophic flagellateLeucocryptos marina (Braarud) Butcher 1967 (Katablepharidaceae/Kathablepharidaceae), with a discussion of the generaLeucocryptos andKatablepharis/Kathablepharis. Eur J Protistol 28: 369–389
Vossbrinck CR, Maddox JV, Friedman S, Debrunner-Vossbrinck BA, Woese CR (1987) Ribosomal RNA sequence suggests microsporidia are extremely ancient eukaryotes. Nature 326: 411–414
Weidner E (1972) Ultrastructural study of microsporidian invasion into cells. Z Parasitenk 40: 227–242
— (1976) The microsporidian spore invasion tube. The ultrastructure, isolation and characterization of the protein comprising the tube. J Cell Biol 71: 23–34
— (1982) The microsporidian invasion tube. III. Tube extrusion and assembly. J Cell Biol 93: 976–979
— (1984) Microsporidian spore discharge and the transfer of polaroplast organelle membrane into plasma membrane. J Protozool 31: 208–213
—, Byrd W (1982) The microsporidian spore invasion tube. II. Role of calcium in the activation of invasion tube discharge. J Cell Biol 93: 970–975
—, Byre A, Scarborough J, Pleshinger J, Sibley D (1984) Microsporidian spore discharge and the transfer of the polaroplast organelle membrane into plasma membrane. J Protozool 31: 195–198
West JA, Calumpong HP (1989) On the reproductive biology ofSpyridia filamentosa (Wulfen) Harvey (Rhodophyta) in culture. Bot Mar 32: 379–387
Westfall JA, Bradbury PC, Townsend JW (1983) Ultrastructure of the dinoflagellatePolykrikos. I. Development of the nematocysttaeniocyst complex and morphology of the site for extrusion. J Cell Sci 63: 245–261
Yamamoto T, Sanders JE (1979) Light and electron microscopic observations of sporogenesis in the myxosporidianCeratomyxa shasta (Noble, 1950). J Fish Dis 2: 411–428
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kugrens, P., Lee, R.E. & Corliss, J.O. Ultrastructure, biogenesis, and functions of extrusive organelles in selected non-ciliate protists. Protoplasma 181, 164–190 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01666394
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01666394