Abstract
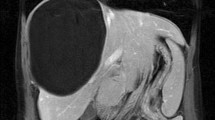
A series of 39 consecutive patients with proven hepatic hydatid disease have been followed from the time of presentation to Westmead Hospital with 6 monthly ultrasound examinations. In the 32 patients having surgery in this unit, it has been found that the standard operation—evacuation of the cyst in the plane of the laminated membrane, suture of bile duct openings, and omentoplasty—achieved good local control of liver cysts. Further cysts, mainly in the retroperitoneal area, were identified with increasing frequency as time passed. The recurrence rate reached 22% by 30 months. Recurrence was not seen after that time. The longest period of follow-up was 7 years. Not all recurrences required surgical treatment. Small asymptomatic cysts have been simply observed, and some shrink without further treatment. Multivariate analysis showed that the single main determinant of recurrence was evidence of previous cyst rupture before operation.
Résumé
Trente neuf patients ayant un kyste hydatique du foie ont été revus tous les 6 mois à l'échographie à l'Hôpital de Westmead (Australie). Sur 32 patients opérés, l'intervention standard (périkystectomie avec suture des fistules biliaires et épliplooplastie) a donné de bons résultats localement. Cependant, au cours de l'évolution, oh a décelé, avec une fréquence croissante, des kystes rétropéritonéaux. Le taux de récidives était de 22% à 30 mois. Ce taux s'est ensuite stabilisé. La survie maximale était de 7 ans. La chirurgie n'était pas toujours nécessaire en cas de récidive. Les plus petits kystes ont été simplement surveillés, et certains ont diminué de volume sans traitement complémentaire. L'analyse multifactorielle a montré que le facteur principal de récidive était la rupture préopératoire.
Resumen
Una serie de 39 pacientes consecutivos con enfermedad hidatídica del hígado ha sido seguida, desde el momento de su presentación al Westmead Hospital, mediante exámenes ultrasonográficos efectuados cada 6 meses. En 32 pacientes sometidos a cirugía en esta institución, se ha encontrado que la operación estándar, que es la evacuatión del quiste en el plano de la membrana laminada, con sutura de los orificios de los canales biliares, y omentoplastia, logró un buen control local de los quistes hepáticos. La presencia de otros quistes, principalmente en el área retroperitoneal, fue detectada con creciente frecuencia con el transcurso del tiempo. La tasa de recurrencia llegó a 22% a los 30 meses, y no se observaron recurrencias después de transcurrido este lapso. El mayor período de seguimiento fue 7 años. No todas las recurrencias requirieron tratamiento quirúrgico. Pequeños quistes asintomáticos han sido observados simplemente y algunos han disminuído de tamaño sin tratamiento adicional. El análisis multivariado demostró que el factor determinante más importante en cuanto a recurrencia es la evidencia de ruptura previa del quiste antes de la operación.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen, Z., Stone, R.M., Langer, B.: Surgical treatment of hydatid disease of the liver. Can. J. Surg.19:416, 1976
Langer, J.C., Rose, D.B., Keystone, J.S., Taylor, B.R., Langer, B.: Diagnosis and management of hydatid disease of the liver. A 15 year North American experience. Ann. Surg.199:412, 1983
Sayek, I., Yalin, R., Sanac, Y.: Surgical treatment of hydatid disease of the liver. Arch. Surg.115:847, 1980
Pissiotis, C.A., Wander, J.V., Condon, R.E.: Surgical treatment of hydatid disease. Prevention of complications and recurrences. Arch. Surg.104:454, 1972
Belli, L., Aseni, P., Rondinara, G.F., Bertini, M.: Improved results with pericystectomy in normothermic ischemia for hepatic hydatidosis. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet.163:128, 1986
Gharbi, H.A., Hassine, W., Bauner, M.W., Dupuch, K.: Ultrasound examination of the hydatid liver. Radiology139:459, 1981
Scherer, U., Weinzierl, M., Sturm, R., Schildberg, F.-W., Zrenner, M., Lissner, J.: Computed tomography in hydatid disease of the liver. A report on 13 cases. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr.2:612, 1978
Beggs, I., Walmsley, K., Cowie, A.G.A.: The radiological appearances of the liver after surgical removal of hydatid cyst. Clin. Radiol.34:565, 1983
Kalovidouris, A., Gouliamos, A., Demou, L., Vassilopoulos, P., Vlachos, L., Papavassilious, K.: Postsurgical evaluation of hydatid disease with CT: Diagnostic pitfalls. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr.8:1114, 1984
Chaimoff, C., Lubin, E., Dintsman, M.: The postoperative appearance of the liver on scanning following omentopexy of the hydatid cyst. Int. Surg.65:331, 1980
Barros, J.L.: Hydatid disease of the liver. Am. J. Surg.135:597, 1978
Mohaghian, H., Saidi, F.: Postoperative recurrence of hydatid disease. Br. J. Surg.65:237, 1978
Little, J.M.: Hydatid disease at Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, 1964–1974. Med. J. Aust.1:903, 1976
Little, J.M., Deane, S.A.: Hydatid disease. In Liver Surgery, S. Bengmark, L.H. Blumgart, editors, Edinburgh, Churchill Livingstone, 1986, pp. 118–129
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Little, J.M., Hollands, M.J. & Ekberg, H. Recurrence of hydatid disease. World J. Surg. 12, 700–703 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01655892
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01655892