Summary
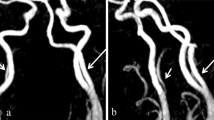
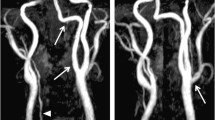
The persistent hypoglossal artery is an anomaly of great interest which probably becomes clinically significant only when it is associated with occlusive cerebrovascular disease or some other life-threatening vascular abnormality such as intracranial aneurysm on the same side in the carotid-middle cerebral artery territory. In the case reported here it was apparently of no clinical importance in spite of associated atherosclerosis and thrombosis.
Zusammenfassung
Die A. hypoglossica primitiva ist eine sehr interessante Anomalie, die nur klinische Bedeutung bekommt, wenn sie vergesellschaftet ist mit arteriellen Hirngefäßverschlüssen oder mit anderen lebensbedrohenden Gefäßanomalien, wie Aneurysmen des Carotis-Media-Gebietes derselben Seite. In dem hier berichteten Fall war sie offenbar nicht von klinischer Bedeutung, trotz gleichzeitiger Atherosklerose und Thrombose anderer Gefäßterritorien.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Begg, A. C.: Radiographic demonstration of the “hypoglossal artery”. Clin. Radiol.12 (1961) 187–189.
Blain, J. G., J. Logothetis: The persistent hypoglossal artery. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat.29 (1966) 346–349.
Bruetman, M. E., W. S. Fields: Persistent hypoglossal artery. Arch. Neurol.8 (1963) 369–372.
Fields, W. S.: The significance of persistent trigeminal artery. Radiol.91, (1968) 1096–1101.
Gaist, G., G. Piazza: Arteria trigeminale ed arteria dell ‘ipoglosso’. Tre casi con documentazione angiografica di circolo cerebrale di tipo embrionario. Arch. Neurochir.4 (1947) 135–146.
Gerlach, J., H. P. Jenson, H. Spuler, G. Viehweger: Traumatic carotico-cavernous fistula combined with persisting primitive hypoglossal artery. J. Neurosurg.20 (1963) 885–887.
Jackson, F. E.: Syncopy associated with persistent hypoglossal artery. J. Neurosurg.21 (1964) 139–141.
Lecuire, J., P. Buffard, A. Goutelle, J. P. Dechaume, D. Michel, G. Rambaud, J. P. Gentil, D. Verger: Considerations anatomiques, cliniques et radiologiques a propos d'une artère hypoglosse. J. Radiol. Electol.46 (1965) 217–222.
Lie, T. A.: Congenital Anomalies of the Carotid Arteries. Excerpta Medica Foundation, Amsterdam 1968.
Morris, E. D., D. B. Moffat: Abnormal origin of the basilar artery from the cervical part of the internal carotid and its embryological significance. Anat. Rec.125 (1956) 701–708.
Padget, D. H.: The development of the cranial arteries in the human embryo. Contributions to Embryology.32 (1948) 207–260.
Udvarhelyi, G. B., M. Lai: Subarachnoid haemorrhage due to rupture of an aneurysm on a persistent left hypoglossal artery. Brit. J. Radiol.36 (1963) 843–847.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Professor K. J. Zülch on the occasion of his 70th birthday.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fields, W.S. Persistent hypoglossal artery in association with advanced atherosclerosis. Neurosurg. Rev. 3, 37–41 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01644417
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01644417