Summary
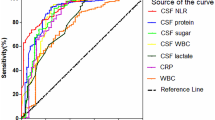
The lactate, lysozyme, C-reactive protein and serum amyloid-A protein concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid were measured in 11 patients with bacterial meningitis, 27 patients with aseptic meningitis and in 31 control patients. The mean concentration of each parameter was significantly higher (p≦0.0001) in patients with bacterial meningitis than in those with aseptic meningitis or those without meningitis. The reliability of these tests in the differential diagnosis of bacterial and aseptic meningitis was compared with leucocyte counts in cerebrospinal fluid, Gram staining for bacteria, and protein and glucose levels. The cerebrospinal fluid lactate level proved to be more sensitive than lysozyme, C-reactive protein or serum amyloid-A protein and had a high degree of specificity.
Zusammenfassung
Bei 11 Patienten mit bakterieller Meningitis, 27 Patienten mit aseptischer Meningitis und 31 Kontrollpatienten wurden die Konzentrationen von Laktat, Lysozym, C-reaktivem Protein und Serum-Amyloid-A-Protein im Liquor cerebrospinalis gemessen. Für jeden Parameter war die Konzentration bei Patienten mit bakterieller Meningitis im Mittel signifikant höher (p≦0,001) als bei Patienten mit aseptischer Meningitis oder Patienten ohne Meningitis. Die Verläßlichkeit dieser Tests für die Differentialdiagnose zwischen bakterieller und aseptischer Meningitis wurde mit derjenigen von Leukozytenzählung im Liquor, Bakteriennachweis durch Gramfärbung, Eiweiß- und Glukosespiegel im Liquor, verglichen. Dabei zeigte sich, daß der Laktatspiegel im Liquor empfindlicher ist als der Spiegel von Lysozym, C-reaktivem Protein oder Serum-Amyloid-A-Protein, und daß er einen hohen Grad an Spezifität besitzt.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Coonrod, J. D., Rytel, M. W. Determination of aetiology of bacterial meningitis by counter-immunoelectrophoresis. Lancet I (1972) 1154–1157.
Fikrig, S. M., Berkovich, S., Emmett, S. M., Gordon, S. Nitroblue tetrazolium dye test and differential diagnosis of meningitis. J. Pediatr. 82 (1973) 855–857.
Nachum, R., Lipsey, A., Siegel, S. E. Rapid detection of gramnegative bacterial meningitis by the limulus lysate test. N. Engl. J. Med. 289 (1973) 931–934.
Leinonen, M., Käyhty, H. Comparison of counter-current immunoelectrophoresis, latex agglutination, and radioimmunoassay in detection of soluble capsular polysaccharide antigens ofHaemophilus influenzae type B andNeisseria meningitidis of groups A or C. J. Clin. Pathol. 31 (1978) 1172–1176.
Killian, J. A. Lactic acid of normal and pathological spinal fluids. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 23 (1926) 255–257.
Brook, I., Bricknell, K. S., Overturf, G. D., Finegold, S. M. Measurement of lactic acid in cerebrospinal fluid in patients with infections of the central nervous system. J. Infect. Dis. 137 (1978) 384–390.
Gästrin, B., Briem, H., Rombo, L. Rapid diagnosis of meningitis with use of selected clinical data and gas-liquid chromatographic determination of lactate concentration in cerebrospinal fluid. J. Infect. Dis. 139 (1979) 529–533.
Curtis, G. D. W., Slack, M. P. E., Tompkins, D. S. Cerebrospinal fluid lactate and the diagnosis of meningitis. J. Infect. 3 (1981) 159–165.
D'Souza, E., Mandal, B. K., Hooper, J., Parker, L. Lactic-acid concentration in cerebrospinal fluid and differential diagnosis of meningitis. Lancet II (1978) 579–580.
Bland, R. D., Lister, R. C., Ries, J. P. Cerebrospinal fluid lactic acid level and pH in meningitis. Am. J. Dis. Child. 128 (1974) 151–156.
Lauwers, S. Lactic-acid concentration in cerebrospinal fluid and differential diagnosis of meningitis. Lancet II (1978) 163.
Gould, I. M., Irwin, W. J., Wadhwani, P. R. The use of cerebrospinal fluid lactate determination in the diagnosis of meningitis. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 12 (1980) 185–188.
Rutledge, J., Benjamin, D., Hood, L., Smith, A. Is the CSF lactate measurement useful in the management of children with suspected bacterial meningitis? J. Pediatr. 98 (1981) 20–24.
Klockars, M., Reitamo, S., Weber, T., Kerttula, Y. Cerebrospinal fluid lysozyme in bacterial and viral meningitis. Acta Med. Scand. 203 (1978) 71–74.
Corrall, C. J., Pepple, J. M., Moxon, E. R., Hughes, W. T. C-reactive protein in spinal fluid of children with meningitis. J. Pediatr. 99 (1981) 365–369.
Laurell, C. B. Electroimmunoassay. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 29 Suppl. 124 (1972) 21–37.
Gorevic, P. D., Rosenthal, C. J., Franklin, E. C. Amyloid-related serum component (SAA) — Studies in acute infections, medullary thyroid carcinoma and postsurgery. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 6 (1976) 83–93.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pönkä, A., Ojala, K., Teppo, A.M. et al. The differential diagnosis of bacterial and aseptic meningitis using cerebrospinal fluid laboratory tests. Infection 11, 129–131 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01641290
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01641290