Summary
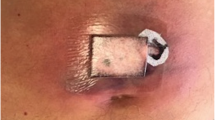
A patient with acute leukaemia developed a maxillary sinusitis and septicaemia withBranhamella catarrhalis during the period of bone marrow hypoplasia. One blood culture also grewStaphylococcus aureus. In the same period, the patient developed tender red skin lesions and disseminated intra-vascular coagulation. The patient recovered when therapy with high dosages of amoxicillin was instituted. At the same time, however, the bone marrow recovered.
Zusammenfassung
Bei einem Patienten mit akuter Leukämie trat während der Phase der Knochenmarksdepression eine Sinusitis maxillaris und Septikämie durchBranhamella catarrhalis auf. In einer Blutkultur wuchs auchStaphylococcus aureus. In der gleichen Phase entwickelten sich bei dem Patienten weiche gerötete Hautläsionen und eine disseminierte intravasale Gerinnung. Unter hohen Dosen Amoxicillin erholte sich der Patient, gleichzeitig regenerierte auch das Knochenmark.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Coffey, J. D. Otitis media in the practice of pediatrics. Pediatrics 38 (1966) 25–32.
Brorson, J. E., Axelsson, A., Holm, S. E. Studies onBranhamella catarrhalis (Neisseria catarrhalis) with special reference to maxillary sinusitis. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 8 (1976) 151–155.
McNeely, D. J., Kitchens, C. S., Kluge, R. M. FatalNeisseria (Branhamella) catarrhalis pneumonia in an immunodeficient host. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 14 (1976) 399–402.
Pfister, L. E., Gallagher, M. V., Potterfield, T. G., van Brown, D. W. Neisseria catarrhalis bacteremia with meningitis. JAMA 193 (1965) 399–401.
Doern, G. V., Miller, M. J., Winn, R. E. Branhamella (Neisseria) catarrhalis systemic disease in humans. Arch. Intern. Med. 141 (1981) 1690–1692.
Feigin, R. D., San Joaquin, V., Middelkamp, J. N. Purpura fulminans associated withNeisseria catarrhalis septicaemia and meningitis. Pediatrics 44 (1969) 120–123.
Srinivasan, G., Raff, M. J., Templeton, W. C., Givens, S. J., Grave, R. C., Melo, J. C. Branhamella catarrhalis pneumonia. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 123 (1981) 553–555.
Pollock, A. A., Holzman, R. S. Neisseria catarrhalis endocarditis. Ann. Intern. Med. 85 (1976) 206–207.
Douer, D., Danziger, Y., Pinkhas, J. Neisseria catarrhalis endocarditis. Ann. Intern. Med. 86 (1977) 116–119.
Guiot, H. F. L., van den Broek, P. J., van der Meer, J. W. M., van Furth, R. Selective antimicrobial modulation of the intestinal flora of patients with acute non-lymphocytic leukaemia: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Infect. Dis. 147 (1983) 615–623.
Willemze, R., Fibbe, W. E., Zwaan, F. E. Experience with intermediate and high dose cytosine arabinoside in refractory acute leukaemia. Onkologie 6 (1983) 200–204.
Dekker, A. W., Rozenberg-Arska, M., Sixma, J. J., Verhoef, J. Prevention of infection by trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole plus amphotericin B in patients with acute non-lymphocytic leukaemia. Ann. Intern. Med. 95 (1981) 555–559.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henny, F.C., Mulder, C.J.J., van der Meer, J.W.M. et al. Branhamella catarrhalis septicaemia in a granulocytopenic patient. Infection 12, 208–209 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01640902
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01640902