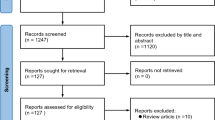
Summary
In a double blind, randomized study, sulfamethoxazole was compared alone and in combination with trimethoprim as commonly used in therapeutic regimes for the treatment of uncomplicated acute urinary tract infections in outpatients. The cure rate of sulfamethoxazole alone was 92.2%, and for sulfamethoxazole plus trimethoprim 97.6%. The rate of side-effects for the former was 5%, for the latter 21.8%. If the failure rate plus the rate of occurrence of rash, which necessitated discontinuing the drug, are combined, it appears that 8.8% of the patients were at a disadvantage receiving sulfamethoxazole compared to 9.7% for the combination of sulfamethoxazole plus trimethoprim. When considering the cure rate and rate of side-effects together, therefore, the position of sulfamethoxazole alone as a suitable drug in this type of infection is defended.
Zusammenfassung
In einer randomisierten Doppelblindstudie wurde Sulfamethoxazol allein und in Kombination mit Trimethoprim, wie es allgemein in Therapieschemata für die Behandlung der unkomplizierten Harnwegsinfektionen gebraucht wird, untersucht. Die Heilungsrate von Sulfamethoxazol allein betrug 92,9% und von Sulfamethoxazol plus Trimethoprim 97,6%. Die Rate an Nebenwirkungen für das erstere betrug 5%, für das letztere 21,8%. Wenn die Versagerraten mit der Rate an Exanthemen kombiniert werden, die ein Absetzen des Medikamentes erforderlich machten, dann sieht es so aus, daß 8,8% der Patienten nachteilige Erfahrungen machten, die Sulfamethoxazol erhielten, verglichen mit 9,7% von denen, die die Kombination von Sulfamethoxazol plus Trimethoprim erhielten. Wenn die Heilungsrate und Nebenwirkungsrate zusammen betrachtet werden, ist die Bedeutung des Sulfamethoxazol allein als geeignetes Medikament für diese Art von Infektionen belegt.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Gleckman, R. A. A cooperative controlled study of the use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in chronic urinary infections. J. Infect. Dis. 128 Suppl. (1973) 647–651.
Harding, G. K. M., Ronald, A. R. Efficacy of trimethoprim-sulfametoxazole in bacteriuria. J. Infect. Dis. 128 Suppl. (1973) 641–646.
O'Grady, F., Fry, I. K., McSherry, A., Cattell, W. R. Long-term treatment of persistent or recurrent urinary tract infection with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. J. Infect. Dis. 128 Suppl. (1973) 652–656.
Frisch, J. M. Clinical experience with adverse reactions to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. J. Infect. Dis. 128 Suppl. (1973) 607–611.
Otten, H., Plempel, M., Siegenthaler, W. Antibiotika-Fibel. Georg Thieme, Stuttgart 1975, pp. 143–145.
Kucers, A., Bennett, N. M. The use of antibiotics. William Heinemann, London 1975, pp. 466–475.
Madsen, S. T. Trimethoprim + sulfametoxazol (co-trimoxazol). T. norske Lægeforen. 93 (1973) 2323–2324.
Sokal, R. R., Rohlf, F. J.: Biometry. W. H. Freeman and Company, San Francisco 1969.
Bünger, P. Praktische Erfahrungen mit der Anwendung neuer Langzeitsulfonamide. Regensburger Jahrbuch für ärztliche Fortbildung 10 (1962) 34–48.
Holloman, J. L., Fullolove, R. E., Yergan, C. M., Barouk, E. Clinical experience with a new sulfonamide sulphamethoxazole. Appl. Therapeut. 3 (1961) 775–779.
Brumfitt, W., Pursell, R. Double-blind trial to compare ampicillin, cephalexin, co-trimoxazole, and trimethoprim in treatment of urinary infection. Br. Med. J. II (1972) 673–676.
Koch, U. J., Schumann, K. P., Küchler, R., Kewitz, H. Efficacy of trimethoprim, sulfamethoxazole and the combination of both in acute urinary tract infection. Chemother. 19 (1973) 314–321.
Havas, L., Fernex, M., Lenox-Smith, I. The clinical efficacy and tolerance of co-trimoxazole (Bactrim; Septrim). An analysis of 37,340 cases. Clin. Trials J. 10 (1973) 81–86.
Bergan, T. Sulfonamider. T. norske Lægefor. 93 (1973) 2252–2255.
Örsten, P. A., Bucht, H., Holmgård, Å., Josephson Long-term treatment of pyelonephritis and other urinary tract infections with a new combination of sulfonamides. J. Urol. 87 (1962) 220–229.
Scherer, J., Plattner, H. C. L'importance des concentrations urinaires et plasmatiques d'un agent chimiothérapique dans le traitement des infections urinaires. Etude comparative de trois sulfamidés. Schw. Med. Wschr. 97 (1967) 1429–1434.
Weinstein, L. The sulfonamides. In:Goodman, L. S., Gilman, A. (eds.): The pharmacological basis of therapeutics. The Macmillan Company, New York 1970. pp. 1177–1203.
Carrol, O. M., Bryan, P. A., Robinson, R. J.: Stevens-Johnson syndrome associated with long-acting sulfonamides. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 195 (1966) 691–693.
Böttiger, L. E., Westerholm, B. Adverse drug reactions during treatment of urinary tract infections. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 11 (1977) 439–442.
Lemieux, G. Trimetoprim-sulfamethoxazole compared with sulfamethoxazole in urinary tract infection. Canad. Med. Ass. J. 20 (1974) 910–912.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergan, T., Skjerven, O. Comparison of sulfamethoxazole alone and combined with trimethoprim in urinary tract infections. Infection 7, 14–16 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01640549
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01640549