Abstract
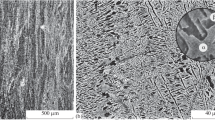
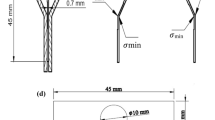
Electrochemical machining (ECM), depending upon the conditions of operation, may bring about a variety of surface finishes. This is particularly true for electrochemically machined titanium and its alloys, and as it is known that surface defects act as stress-raisers, a study of fatigue life was made. A number of different surface finishes was obtained in a study of the dissolution of titanium alloys, and these will be discussed in terms of the metallography of the alloy and of the machining conditions. For example, differential dissolution and hence a poor, uneven finish was frequently obtained in the case of the two-phase alloys under conditions where the single phase alloys showed a bright finish. Using a vibration generator producing a constant bending moment at mains frequency, the effect of electrochemically machined surface on fatigue life was found to be only small although samples with surfaces damaged by intergranular oxidation or by sparking showed reduced lives.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. A. Pope, Ed., ‘Metal fatigue’, Chapman and Hall (1959).
P. J. E. Forsyth, ‘The physical basis of metal fatigue’, Blackie (1969).
N. Thompson, N. J. Wadsworth and N. Louat,Phil. Mag. 1 (1956) 113.
U. F. Franck, Proc. 1st Intl. Congr. Metallic Corros., Butterworth (1962).
T. P. Hoar,Corrosion Sci. 7 (1967) 341.
T. P. Hoar, D. C. Mears and G. P. Rothwell,ibid,5 (1965) 279.
P. J. Boden and J. M. Evans,Electrochim. Acta 16 (1971) 1071.
P. J. Boden, and M. F. Abd Rabboh. Private communication.
P. J. Boden, J. M. Evans and A. A. Baker, Proc. 12th Intl. Machine Tool Design and Research Conf., Macmillan (1972).
F. B. Fuller,Metals Prog. 56 (1949) 348.
J. W. Spretnak, M. G. Fontana and A. E. Brooks,Trans. Am. Soc. Metals,43 (1951) 547.
H. H. Hanink,Prod. Engineering,22 (1951) 164.
C. J. Beevers, ‘The Science, Technology and Application of Titanium’, Pergamon (1970) p. 535.
D. Hull,J. Inst. Met. 86 (1957) 425.
R. A. Jukes, ‘The Science, Technology and Application of Titanium’, Pergamon (1970) p.923.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bannard, J. Effect of surface finish obtained by electrochemical machining on the fatigue life of some titanium alloys. J Appl Electrochem 4, 229–234 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01637232
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01637232