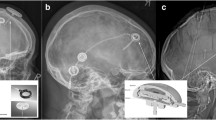
Abstract
Retrospective clinical experience with our first 46 patients monitored with a fiberoptic intracranial pressure device is described. In 43 of 46 patients, the transducer was introduced into brain parenchyma. A ventriculostomy system was used in 3 of 46 patients. The monitoring system was generally characterized by ease of placement and system maintenance and by technical simplicity. Several problems were encountered, including breakage of system components (12%), erroneous readings requiring transducer repositioning (8.6%), epidural hematoma (3.4%), and infection (1.7%). No infections or hematomas occurred in the 3 cases in which the ventriculostomy system was used. Overall, our experience with the Camino intracranial pressure fiberoptic monitoring system confirms previous reports of its favorable features.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marshall LF. The role of aggressive therapy for head injury: does it matter? Clin Neurosurg 1986;34:549–559
Marshall LF, Smith RW, Shapiro HM. The outcome with aggressive treatment in severe head injuries. Part I: the significance of intracranial pressure monitoring. J Neurosurg 1979;50:20–25
Miller JD. Intracranial pressure monitoring. Arch Neurol 1985;42:1191–1193
Miller JD, Becker DP, Ward JD, Sullivan HG, Adams WE, Rosner MJ. Significance of intracranial hypertension in severe head injury. J Neurosurg 1977;47:503–516
Miller JD, Butterworth JF, Gudeman SK, Faulkner JE, Choi SC, Selhorst JB, Harbison JW, Lutz HA, Young HF, Becker DP. Further experience in the management of severe head injury. J Neurosurg 1981;54:289–299
Narayan RK, Kishore PR, Becker DP, Ward JD, Enas GG, Greenberg RP, DaSilva AD, Lipper MH, Choi SC, Mayhall CG, Lutz HA, Young HF. Intracranial pressure: to monitor or not to monitor? J Neurosurg 1982;56:650–659
Saul TG. Is ICP monitoring worthwhile? Clin Neurosurg 1986;34:560–571
Saul TG, Ducker TB. Effect of intracranial pressure monitoring and aggressive treatment on mortality in severe head injury. J Neurosurg 1982;56:498–503
Winn HR, Dacey RG, Jane JA. Intracranial subarachnoid pressure recording: experience with 650 patients. Surg Neurol 1977;8:41–47
Guilluame J, Janny P. Manometric intracranienne cositinue. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1951;84:131–142
Lundberg N. Continuous recording and control of ventricular fluid pressure in neurosurgical practice. Acta Psychiatr Neurol Scand Suppl 1960:149:1–193
Atkinson JR, Shurtleff DB, Foltz EL. Radio telemetry for the measurement of intracranial pressure. J Neurosurg 1967;27:428–432
Brock M, Winkemuller W, Poll W, Markakis E, Dietz H. Measurement of brain-tissue pressure. Lancet 1972;1:595–596
Mollman HD, Rockswold GL, Ford SE. A clinical comparison of subarachnoid catheters to ventriculostomy and subarachnoid bolts: a prospective study. J Neurosurg 1988;68:737–741
Hoppenstein R. A device for measuring intracranial pressure. Lancet 1965;1:90–91
Iwata K, Shibahara H. Continuous recording of brain pressure with semiconductor strain gauge. Presented at the 4th International Congress of Neurological Surgery, 1969
Purin VR. Measuring intracranial pressure of a child without the help of puncture. A new method. Pediatriia 1964;43:82–85
Shellock FG. A fiberoptic transducer-tipped pressure catheter. Med Elec 1985;16:103–106
Narayan RK, Bray RS, Robertson CS, Gokaslan ZL, Grossman RG. Experience with a new fiberoptic device for intracranial pressure monitoring. Presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons, May 3–7, 1987
Ostrup RC, Luerssen TG, Marshall LF, Zornow MH. Continuous monitoring of intracranial pressure with a miniaturized fiberoptic device. J Neurosurg 1987;67:206–209
Crutchfield JS, Narayan RK, Robertson CS, Michael LH. Evaluation of a fiberoptic intracranial pressure monitor. J Neurosurg 1990;72:482–487
Eisenberg HM, Frankowski RF, Contant CF, Marshall LF, Walker MD. High-dose barbiturate control of elevated intracranial pressure in patients with severe head injury. J Neurosurg 1988;69:15–23
Friedman WA, Vries JK. Percutaneous tunnel ventriculostomy. Summary of 100 procedures. J Neurosurg 1980;53:662–665
Hollingsworth-Fridlund P, Vos H, Daily EK. Use of fiber-optic pressure transducer for intracranial pressure measurements: a preliminary report. Heart Lung 17:111–120, 1988
Aucoin PJ, Kotilainen HR, Gantz NM, Davidson R, Kellogg P, Stone B. Intracranial pressure monitors. Epidemiologic study of risk factors and infections. Am J Med 1986;80:369–376
Rosner MJ, Becker DP. ICP monitoring: complications and associated factors. Clin Neurosurg 1976;23:494–519
Mayhall CG, Archer NH, Lamb VA, Spadora AC, Baggett JW, Ward JD, Narayan RK. Ventriculostomy-related infections. A prospective epidemiologic study. N Engl J Med 1984:310:553–559
Kanter RK, Weiner LB, Patti AM, Robson LK. Infectious complications and duration of intracranial pressure monitoring. Crit Care Med 1985;13:837–839
Wyler AR, Kelly WA. Use of antibiotic with external ventriculostomies. J Neurosurg 1972;37:185–187
Chambers IR, Mendelow AD, Sinar EJ, Modha P. A clinical evaluation of the Camino subdural screw and ventricular monitoring kits. Neurosurgery 26:421–423, 1990
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yablon, J.S., Lantner, H.J., McCormack, T.M. et al. Clinical experience with a fiberoptic intracranial pressure monitor. J Clin Monitor Comput 9, 171–175 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01617024
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01617024