Abstract
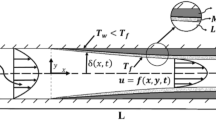
A simple analytical approximative solution was given for calculating the time dependent development of the ice-layers at the cooled walls inside a parallel plate channel. By ignoring the effect of acceleration, resulting from converging ice-layers in the axial direction, an analytical solution for the variation of the ice-layer thickness with time and axial position could be obtained. The approximative solution was checked by numerical calculations and good agreement was found.
Zusammenfassung
Es wurde ein analytisches Näherungsverfahren entwickelt, das es ermöglicht, die zeitliche Entwicklung der Erstarrungsfronten im gekühlten, ebenen Kanal zu bestimmen. Die Methode liefert unter Vernachlässigung der Beschleunigungsterme durch die konvergenten Eisschichten eine exakte Lösung der Phasengrenzbeziehung. Das Näherungsverfahren wurde mittels numerischer Berechnungen überprüft und stimmt bis zu Wandunterkühlungsverhältnissen vonB=10 sehr gut mit der numerischen Lösung überein.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
thermal diffusivity
- B :
-
dimensionless freezing parameter
- D :
-
hydraulic diameter:D=4 h
- f :
-
function according to Eq. (27)
- F o :
-
Fourier number
- h :
-
distance from centerline to the wall
- k :
-
thermal conductivity
- P :
-
pressure
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- r s :
-
heat of fusion
- Re h :
-
Reynolds number based onh
- Re D :
-
Reynolds number based on the hydraulic diameter
- T :
-
temperature
- T F :
-
freezing temperature of the liquid
- T o :
-
constant inlet temperature of the liquid
- t :
-
time
- u, v :
-
fluid velocity components
- ū :
-
mean axial velocity
- ū o :
-
mean axial velocity at the entrance
- x, y :
-
coordinates
- δ :
-
distance from centerline to the liquid-solid interface
- δ s :
-
steady state distance from centerline to the liquid-solid interface
- ϱ :
-
density
- τ :
-
dimensionless time
- ν :
-
kinematic viscosity
- ξ :
-
integral coordinate
- s :
-
solid
- L :
-
liquid
- w :
-
at the wall
- 0:
-
at the entrance
- ∼:
-
dimensionless quantity
References
Zerkle, R. D.; Sunderland, J. E.: The effect of liquid solidification in a tube upon laminar-flow heat transfer and pressure drop. J. Heat Transfer 90 (1968) 183–190
Özisik, M. N.; Mulligan, J. C.: Transient freezing of liquids in forced flow inside circular tubes. J. Heat Transfer 91 (1969) 385–390
Bilenas, J. A.; Jiji, L. M.: Numerical solution of a nonlinear free boundary problem of axisymmetric fluid flow in tubes with surface solidification. Proc. 4th Int. Heat Transfer Conference 1 Paris. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1970 Cu 2.1, 1–11
Chida, K.: Heat Transfer in steady laminar pipe flow with liquid solidification. Heat Transfer: Jap. Res. 81 (1983) 81–94
Hwang, G. J.; Sheu, J. P.: Liquid solidification in combined hydrodynamic and thermal entrance region of a circular tube. Canadian J. Chem. Eng. 54 (1976) 66–71
Lee, D. G.; Zerkle, R. D.: The effect of liquid solidification in a parallel plate channel upon laminar-flow heat transfer and pressure drop. J. Heat Transfer 91 (1969) 583–585
Cheng, K. C.; Wong, L. S.: Liquid solidification in a convectively cooled parallel-plate channel. Canadian J. Chem. Eng. 55 (1977) 149–155
Kikuchi, Y.; Shigemasa, Y., Ogata, T.: Steady-state freezing of liquids in laminar flow between two parallel plates. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 23 (1986) 43–55
Weigand, B.; Beer, H.: Liquid solidification in a parallel plate channel upon laminar-flow heat transfer: stationary case. Wärme-Stoffübertrag. 26 (1991) 233–240
Bennon, W. D.; Incropera, F. P.: Developing laminar mixed convection with solidification in a vertical channel. J. Heat Transfer 110 (1988) 410–415
Cebeci, T.; Chang, K. C.: A general method for calculating momentum and heat transfer in laminar and turbulent duct flows. Numerical Heat Transfer 1 (1977) 39–68
Cebeci, T.; Bradshaw, P.: Physical and computational aspects of convective heat transfer. New York: Springer 1984
Shah, R. K.; London, A. L.: Laminar flow forced convection in ducts. Advances in Heat Transfer. New York: Academic Press 1978
Sampson, P.; Gibson, R. D.: A mathematical model of nozzle blockage by freezing. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer (1981) 231–241
Cebeci, T.; Bradshaw, P.: Momentum transfer in boundary layers. New York: McGraw-Hill 1977
Batchelor, G. K.: An introduction to fluid dynamics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1985
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weigand, B., Beer, H. Transient freezing of liquids in forced laminar flow inside a parallel plate channel. Wärme- und Stoffübertragung 27, 77–84 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01590122
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01590122