Abstract
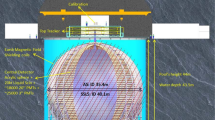
We have repeated the so-called cold fusion experiment by electrolyzing heavy water, with 0.1M LiOD, with palladium rod as the cathode and platinum wire as the anode. The purpose of our experiment is to dectect the neutrons that are produced from the fusion process of deuterium if fusion does occur. We use one3He detector and one BF3 detector to detect the thermal neutrons coming out of the water bath that surrounds the heavy water cell. Possible neutron bursts are detected by the3He detector during a period of about 7 h after electrolyzing for 11 days.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Fleischmann and S. Pons,J. Electroanal. Chem,261, 301 (1989).
S. E. Jones, E. P. Palmer, J. B. Czirr, D. L. Decker, G. L. Jensen, J. M. Thorne, S. F. Taylor, and J. Rafelski,Nature,338, 737 (1989).
R. L. Garwin,Nature,338, 616 (1989).
Elecmat, 11 Edison Drive, Summit, N.J. 07901.
H. Furth, S. Bernabei, S. Cowley, and R. Kulsrud, Baltimore APS Meeting, May 1, 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, T.L., Liu, C.C. Cold fusion experiment at Department of Nuclear Engineering, National Tsing-Hua University. J Fusion Energ 9, 487–490 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01588285
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01588285