Abstract
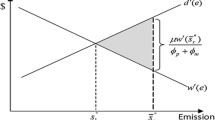
A formal mathematical model is developed to ascertain the effectiveness of a reporting system for improving the enforcement of environmental laws and regulations when reports are costly. To model realistic enforcement problems arising over environmental issues such as compliance to water and air quality standards, a formal enforcement model is constructed using concepts from probability and statistics, non-cooperative game theory, and economics. In order to demonstrate clearly the benefits gained when an environmental agency takes advantage of a reporting system, a formal enforcement model with a costly reporting system is rigorously compared to one with no reporting system. The calculation and comparison of Nash equilibria for a range of values of model parameters indicates under what conditions a reporting system can be truly effective. Overall, it is found that a reporting system, such as whistle-blowing, can be helpful for reducing violations of environmental standards, thereby maintaining better environmental quality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avenhaus, R. 1986: Safeguards systems analysis. Plenum Press, New York
Avenhaus, R. 1990a: Decision procedures for safeguards systems. Information and Decision Technologies 16, 229–247
Avenhaus, R. 1990b: Monitoring the emission of pollutants by means of the inspector leadership method. Information and Decision Technologies 16, 229–247
Box, G.E.P.; Tiao, G.C. 1975: Intervention analysis with applications to economic and environmental problems. J. American Statistical Association 70(349), 70–79
Brams, S.J.; Kilgour, D.M. 1988: Game theory and national security. Basil Blackwell, New York
Brillinger, D.R. 1989: Consistent detection of a monotonic trend superposed on a stationary time series. Biometrika 76(1), 23–30
Cleveland, W.S. 1979: Robust locally weighted regression and smoothing scatter-plots. J. American Statistical Association 74(368), 829–836
Downing, P.B.; Watson, Jr., W.D. 1974: The economics of enforcing air pollution controls. J. Environmental Economics and Management 1, 219–236
Downing, P.B.; Kimball, J.N. 1982: Enforcing pollution control laws in the U.S. Policy Studies Journal 11(1), 55–65
Dresher, M. 1962: A sampling inspection problem in arms control agreement: A game theoretic analysis. Memorandum RM-2972-ARPA. The Rand Corporation, Santa Barbara, CA
El-Shaarawi, A.H. 1993: Environmental monitoring, assessment and prediction of change. Environmentrics 4(4), 381–398
Epple, D.; Visscher, M. 1984: Environmental pollution: Modeling occurrence, detection, and deterrence. Journal of Law and Economics 27, 29–60
Esterby, S.R. 1993: Trend analysis methods for environmental data. Environmentrics 4(4), 459–481
Fang, L.; Hipel, K.W.; Kilgour, D.M. 1993: Interactive decision making: The graph model for conflict resolution. New York: Wiley
Fang, L.; Hipel, K.W.; Kilgour, D.M. 1994: Enforcement of environmental laws and regulations: A literature review, in Hipel, K.W. and Fang, L. (Editors), Effective Environmental Management for Sustainable Development. Kluwer, Dordrecht, the Netherlands, 3–15
Fukuyama, K.; Kilgour, D.M.; Hipel, K.W. 1994: Systematic policy development to ensure compliance to environmental regulations. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics 24(9), 1289–1305
Government of Canada. 1990: Canada's Green Plan. Ministry of Supply and Services, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada
Haimes, Y. Y. 1992: Sustainable development: A holistic approach to natural resource management. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. SMC-22 No.3, 413–417
Harrington, W. 1988: Enforcement leverage when penalties are restricted. Journal of Public Economics 37, 29–53
Hipel, K.W.; Fang, L.; Kilgour, D.M. 1993: Environmental conflict resolution using the graph model. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Le Touquet, France (October 17–20, 1993), Vol. 1, 153–158
Hipel, K.W.; Fang, L. (Editors) 1994: Effective environmental management for sustainable development, Proceedings of the International Conference on Stochastic and Statistical Methods in Hydrology and Environmental Engineering, Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands
Hipel, K.W.; Kilgour, D.M.; Yin, X. 1994: Whistle blowing in enforcement of environmental regulations. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, San Antonio, Texas. United States (October 2–5, 1994), Vol. 1,896–901
Hipel, K.W.; Mcleod, A. I. 1994: Time series modeling of water resources and environmental systems. Elsevier, Amsterdam, the Netherlands
Hirsch, R.M.; Slack, J. R. 1984: A nonparametric trend test for seasonal data with serial dependence. Water Resour. Res. 20(6), 727–732
Kendall, M.G. 1975: Rank correlation methods. Charles Griffin, London, fourth edition
Kilgour, D.M.; Fang, L.; Hipel, K.W. 1992: Game-theoretic analyses of enforcement of environment laws and regulations. Water Resour. Bull. 28(1), 141–153
Kilgour, D.M.; Fang, L.; Hipel, K.W. 1994: The decision support system GMCR and the management of strategy in uncertainty. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Information Processing and the Management of Uncertainty, Paris, France (July 4–8, 1994), Vol. 2, 638–613
Kuhn, H.W. 1963: Recursive inspection games, applications of statistical methodology to arms control and disarmament. A U.S. ACDA Report under Contract ACDA/ST-3, 169–182
Mann, H.B. 1945: Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 13, 245–259
Ministry of Environment and Energy. 1993: Bill 26, an act respecting environmental rights in Ontario
Nash, J.F. 1950: Equilibrium points in n-person games. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of the U.S.A. 36, 48–49
Nash, J.F. 1951: Noncooperative games. Annals of Mathematics 54(2), 286–295
Rapoport, A. 1966: Two-person game theory: The essential ideas. University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor, MI
Sage, A.P. 1991: Decision support systems engineering. New York: Wiley
United States Environmental Protection Agency. 1990: The public's role in environmental enforcement. Office of Enforcement, Washington, D.C.
Von Neumann, J.; Morgenstern, O. 1953: Theory of games and economic behavior. 3rd Edition. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey
Woltemade, C.J. 1991: Environmental impact mitigation under the Clean Water Act and the National Environmental Policy Act: The case of two forks dam. Water Resour. Bull. 27(2), 293–302
Yin, X.; Hipel, K.W.; Kilgour, D.M. 1994: An analysis of a reporting system in environmental enforcement. Technical report No. 200, SM-031194. Department of Systems Design Engineering, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario, Canada
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hipel, K., Yin, X. & Kilgour, D.M. Can a costly reporting system make environmental enforcement more efficient?. Stochastic Hydrol Hydraul 9, 151–170 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01585604
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01585604