Abstract
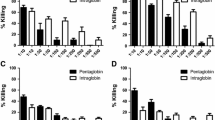
The effect of phagocytic killing on serum bactericidal activity againstStreptococcus pneumoniae was investigated 0, 1.5, 8 and 12 h after a single 875 mg oral dose of amoxicillin in healthy adults. Killing curves were determined with polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN), serum or PMN plus serum. Global killing (i. e. intracellular and extracellular killing) over 3 h of incubation was expressed as the area under the killing curve (AUKC; log cfu × h/ml). Amoxicillin did not affect the activity of PMN alone. For serum alone, the AUKC of post-administration samples (with supra-inhibitory amoxicillin concentrations) was significantly lower than in baseline samples. For serum plus PMN, significant bactericidal activity of serum was still found in samples after antibiotic concentrations had reached sub-inhibitory levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mandell LA, Afnan M: Synergistic killing of gramnegative bacilli by cefotaxime, its desacetylmetabolite and human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1991, 27: 817–828.
McDonald PJ, Wetherall BL, Pruul H: Postantibiotic leukocyte enhancement: increased susceptibility of bacteria pretreated with antibiotics to activity of leukocytes. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1981, 3: 38–44.
Labro MT, Pochetm I, Babin-Chevaye C, Hakim J: Effect of ceftriaxone-induced alterations of bacteria on neutrophil bactericidal activity. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1987, 20: 857–869.
Darvaeau RP, Cunningham MD: Influence of sub-inhibitory concentrations of cephalosporins on the serum sensitivity ofPseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1990, 162: 914–921.
Cuffini AM, Carlone NA, Xerri L, Pizzoglio MF: Synergy of ceftazidime and human macrophages on phagocytosis and killing ofStaphylococcus aureus andPseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1987, 20: 261–271.
Lingaas E, Midtvedt T: The influence of cefoperazone, cefotaxime, ceftazidime, and aztreonam on phagocytosis by human neutrophils in vitro. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1989, 23: 701–710.
Cuffini AM, Tullio V, Paizis G, Carlone NA: Potential effects of amoxycillin/clavulanic acid and ticarcillin/clavulanic acid on human granulocyte activity: a comparative study. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1996, 38: 1013–1022.
Aguilar L, Rosendo J, Balcabao IP, Martín M, Giménez MJ, Frías J, Prieto J: Pharmacodynamic effects of amoxicillin versus cefotaxime against penicillin-susceptible and penicillin-resistant pneumococcal strains: a phase I study. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1997, 41: 1389–1391.
Martín M, Gómez-Lus ML, Aguilar L, Martínez P, Giménez MJ, Prieto J: Effect of clavulanic acid and/or polymorphonuclear neutrophils on amoxicillin bactericidal activity againstStreptococcus pneumoniae. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 1997, 16: 512–516.
Pascual A, Martínez Martínez L, Aragón J, Perea EJ: Effect of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid, alone and in combination, on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte function againstStaphylococcus aureus. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 1989, 8: 277–281.
White R, Friedrich L, Burgess D, Warkentin D, Bosso J: Comparative in vitro pharmacodynamics of imipenem and meropenem againstPseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1996, 40: 904–908.
Tisdale JE, Pasko MT, Mylotte JM: Antipseudomonal activity of simulated infusions of gentamicin alone or with piperacillin assessed by serum bactericidal rate and area under the killing curve. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1989, 33: 1500–1505.
Yancey RJ, Sánchez MS, Ford CW: Activity of antibiotics againstStaphylococcus aureus within polymorphonuclear neutrophils. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 1991, 10: 107–113.
Labro MT, El Benna J: Effects of anti-infectious agents on polymorphonuclear neutrophils. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 1991, 10: 124–131.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gómez-Lus, M.L., Giménez, M.J., Prieto, J. et al. Effect of polymorphonuclear neutrophils on serum bactericidal activity againstStreptococcus pneumoniae after amoxicillin administration. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 17, 40–43 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01584362
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01584362