Summary
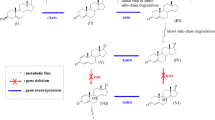
A large number of valuable starting materials for steroids synthesis (e.g. 4-androstene-3,17-dione, 1,4-androstadiene-3,17-dione, 9α-hydroxy-4-androsten-17-one) have been produced by microbial transformation methods. This review helps to evaluate the microbial physiological interest of the widely used sterol sidechain degradation processes. Four inducible groups of the catabolic enzymes are involved in the sterol sidechain degradation pathway; the fatty acid β-oxidation system, the ω-oxidase reaction, a methyl-crotonyl-CoA carboxylation system and the propionyl-CoA carboylase system.
Altogether nine catabolic enzymes are involved in the β-sitosterol sidechain degradation pathway. They work in 14 consecutive enzymatic steps. Summing up: three molecules of FADH2, three molecules of propionyl-SCoA, three of NADH and one molecule of acetic acid are formed, while the sidechain of one mole of sitosterol is removed selectively. The metabolism of the propionates and the acetate yield 18 molecules of NADH and 7 molecules of FADH2. Taking into consideration the whole process more than 80 molecules of ATP could be formed during the sitosterol sidechain degradation process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrus, G., K. Albrecht, I. Barta, M. Fábian and K. Köncöl. 1986. Hung. Pat. 190665 01 Oct. 1980. Bioconversion of 3β-carbamoyloxy-5-cholestene to 3β-carbamoyloxy-5-androsten-17-one. Chem. Abs. 105: 113608.
Arima, H., T. Beppu and W. Nakamatsu. 1979. Japan Kokai Tokkyo Kobo. 78130643. 17 Apr. 1977. 3a-αH-4α-acetyl-5-hydroxy-7a, β-methyl-hexahydro-1-indanone. Chem. Abs. 90: 150312.
Arima, K., H. Nagasawa, H. Bae and G. Tamura. 1969. Microbial transformation of sterols. I. Decomposition of cholesterol by microorganisms. Agr. Biol. Chem. 33: 1636–1643.
Büki, K., G. Ambrus and Gy. Horváth. 1975. Metabolic fate of cholesteryl methyl ether in Mycobacterium phlei. Acta Microbiol. Acad. Sci. Hung. 22: 447–451.
Büki, K., G. Ambrus, M. Halmos, and J. Szabó. 1976. Hungarian Pat. 11189 16 Aug. 1974. 3β-alkoxycholest-5-ene is transformed to dehydroepiandrosterone. Chem. Abs. 85: 157962.
Dodson, R.H. and R.D. Muir. 1958. Microbial transformation II. The microbial aromatization of steroids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80: 5004.
Eder, U., G. Sauer, G. Haffer, G. Neef, R. Wiechert, A. Weber and A. Popper. 1977. Ger. Offen 25349111. 01 Aug. 1975. Formation of androst-5-en-17-one. Chem. Abs. 86: 187659.
Fujimoto, Y., C.S. Chen, A.S. Gopalan and C.J. Sih. 1982. Microbial degradation of the phytosterol side-chain. II. Incorporation of NaH14CO3 onto C-28 position. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 104: 4720–4722.
Fujimoto, Y., C.S. Chem, Z. Szeleczky, D. Di Tullio and C.J. Sih. 1982. Microbial degradation of the phytosterol sidechain. I. Enzymatic conversion of 3-oxo-24-ethylcholest-4-en-26-oic acid into 3-oxochol-4-en-24-oic-acid and androst-4-ene-3,17-dione. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 104: 4718–4720.
Gordon, E. Mallett. 1973. US Pat. 3741870 12 Oct. 1971. Δ9/11/-Estrone is produced from 19-hydroxycholesterol-3-acetate. Chem. Res. 79: 64555.
Hayakawa, S. 1973. Microbiological transformation of bile acids. Adv. Lipid Res. 11: 143.
Hill, F., W. Preuss, J. Schindler, R. Schmid and A. Struve. 1980. Euro. Pat. 04913 17 Apr. 1978. Production of 17-C-steroid-α-propionic acid derivatives by blockmutant microbes. Chem. Abs. 92: 126930.
Hill, F., W. Preuss, J. Schindler, R. Schmid, A. Struve. 1980. Euro. Pat. 15308 07 March 1979. Blockmutants for the production of 17-C-steroid-α-proponic acid derivatives. Chem. Abs. 93: 236940.
Imada, Y., Takahashi, K. and S. Katogy. 1979. Japan Kokai Tokkyo Kobo 7959395 17 Oct. 1977. Microbial production of androstanes. Chem. Abs. 91: 122153.
Imada, Y. and T. Yutaka. 1979. Japan Kokai Tokkyo Kobo 79 73191 24 Nov. 1977. Preparation of androstanes by Arthrobacter mutants. Chem. Abs. 91: 156036.
Imada, Y. and K. Takahashi. 1980. Eur. Pat. 01622 14 Oct. 1977. 20α-hydroxy-methylpregnane derivatives. Chem. Abs. 92: 4699.
Jiu, J. and W.J. Marsheck. 1977. US. Pat. 4032408 30 Apr. 1975. Process of preparing 3-oxo-pregna-4,17/20-diene-20-carboxylic acid and esters with Mycobacterium. Chem. Abs. 87: 132321.
Kieslich, K. 1985. Microbial side-chain degradation of Sterols. J. Basic Microbiol. 25: 461–474.
Knight, J.C. and M.G. Wovcha. 1977. Ger. Offen 2652377. 17 Nov. 1975. 7a, β-methylhexahydro-1/5/-indanedione compounds. Chem. Abs. 87: 100688.
Knight, J.C. and M.G. Wovcha. 1980. Microbial degradation of the phytosterol sidechain to 24-oxo products. Stroids 36: 723–730.
Kraychy, S., W.J. Marsheck and R.D. Muir. 1972. US. Pat. 3684657 11 May 1970, Selective microbiological degradation of steroidal 17-alkyls. Chem. Abs. 77: 124777.
Marsheck, W.J. 1971. Current trends in the microbiological transformation of steroids. Prog. Ind. Microbiol. 10: 49–103.
Marsheck, W.J. and S. Kraychy. 1973. Brit. Pat. 1329387 Dec. 10 1970. Selective microbiological preparation of androst-4-ene-3,17-dione. Chem. Abs. 79: 144867.
Martin C.K.A. 1977. Microbial cleavage of sterol side chains. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 22: 29–58.
Martin, C.K.A. 1984. Sterols. In: Biotechnology, A Comprehensive Treatise in 8 Volumes, Vol. 6a: Biotransformations (Kieslich, K., ed.), p. 79–96, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim.
Noda Institute for Sci. Res. Netherlands. 1966. Pat. 6502883 3 Dec. 1965. (Prior Japanese Pat. 30915 02 June 1964) Androst-4-en-3,17-dione and androsta-1,4-dien-3,17-dione production from sterols. Chem. Abs. 65: 6262g.
Pyke, T.R. and M.P. Salmond. 1979. Ger Offen. 2802524. 14 Feb. 1977. 3a-αH-4α-/3-hydroxypropyl/-7a,β-methylhexahydro-1,5-indandione hemiketal. Chem. Abs. 90: 53151.
Schoemer, U. and C.K.A. Martin. 1980. Microbial transformation of sterols. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 22: 11–25.
Schubert, K., K.H. Böhme and C. Hörhold. 1961. Bildung einer Ketosäure durch mikrobiellen Abbau von Progesteron. Hoppe Seyler's Z. physiol. Chem. 325: 260–262.
Shaw, D.A., L.F. Berkenhagen and P. Talalay. 1963. Enzymatic oxidation of steroids by cell free extracts of Pseudomonas testosteroni. Isolation of cleavage of ring A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 54: 837.
Sih, C.J., S.S. Lee, Y.Y. Tsong, K.C. Wang and F.M. Chang. 1965. An efficient synthesis of estrone and 19-norsteroids from cholesterol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 87: 2765.
Sih, C.J., H.H. Tai, Y.Y. Tsong and R.G. Coombe. 1986. Mechanism of steroid oxidation by microorganisms. XIV. Pathway of cholesterol side-chain degradation. Biochemistry 7: 808–818.
Sih, C.J. and K.C. Wang 1965. A new route to estrone from sterols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 87: 1387.
Sih, C.J. K.C. Wang, D.T. Gibson and H.W. Whitlock. 1965. On the mechanism of ring cleavage in the degradation of 9,10-seco steroids by microorganisms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 87: 1386.
Sih, C.J., K.C. Wang and H.H. Tai 1968. Mechanism of steroid oxidation by microorganisms XIII. C22 acid intermediates in the degradation of the cholesterol side chain. Biochemistry 7: 796–807.
Stadtman, T.C., A. Cherkes and C.N. Anfinsen. 1954. Studies on the microbial degradation of cholesterol. J. Biol. Chem. 206: 511–523.
Upjohn Co. 1979. US Pat. 4293644 09 Oct. 77 and 4345033 08 Sept. 1980. Androst-4-ene-3,17-dione production by selective degradation of 17-alkyl-steroids with M. fortuitum NRRL B-11045 (DSM 1134). Chem. Abs. 89: 40889.
Turfitt, G.E. 1944. Microbiological agencies in the degradation of steroids. I-III. J. Bacteriol. 47: 487, Biochem. J. 40: 79 (1946); Biochem. J. 42: 3376 (1948).
Weber, A. and M. Kennecke. 1978. H. Dahl. Ger. Offen. 2632677. 16 July 1976. Formation of androstan-17-one derivatives from 3β-methoxycholestene. Chem. Abs. 88: 15026.
Weber, A., M. Kennecke and R. Mueller. 1979. Ger. Offen. 2757156 19 Dec. 1977. 21-Hydroxy-20-methylpregnane derivatives production. Chem. Abs. 91: 173386.
Weber, A., R. Mueller, M. Kennecke, U. Eder and R. Wiechert. 1977. Ger. Offen. 2558089. 19 Dec. 1975. 17-β-hydroxyl-1-α-methyl-5-α-androstan-3-one production from 1α-methyl-5α-cholestan-3-one. Chem. Abs. 87: 165995.
van der Waard, W.F. 1968. Netherlands Pat. 6513718 22 Oct. 1965. Process for the microbiological preparation of steroids. Chem. Abs. 68: 114844.
Wovcha, M.G. 1977. Ger. Offen. 2647895 (US Prior. 24 Oct. 1975) Process for the production of 9α-hydroxyandrost-4-ene-3,17-dione. Chem. Abs. 87: 66595.
Wovcha, M.G., F.J. Antosz, J.M. Beaton, A.B. Garcia and L.A. Kominek. 1980. US. Pat. 4175006 21 Oct. 1977. 9α-hydroxy-3-keto-bisnorchol-4-en-22-oic acid methyl ester formation. Chem. Abs. 92: 126929.
Wovcha, M.G. and C.B. Biggs. 1979. Ger. Offen. 2746383 22 oct. 1976. Mycobacterium mutant (DSM 1134) and uses in the production of androst-4-ene-3,17 dione. Chem. Abs. 89: 40889.
Wovcha, M.G., C.B. Biggs and T.R. Pyke. 1979. FR Pat. 2408621 9 Nov. 1977. Mutant microorganisms for selectively degrading sterols to androstane-3,17-dione derivatives. Chem. Abs. 91: 173395.
Wovcha, M.G., J.C. Knight and A.B. Garcia. 1983. Fr. Pat. 2505360 11 May 1981. 9α-hydroxy-3-oxo-4,17/20/-pregnadiene-20-carboxylic acid by mutant. Chem. Abs. 98: 105712.
Wix, G., K. Büki and E. Tömörkény. 1967. Hung. Pat. 153173 05 March 1965 Microbiological preparation of 1,4-androstadien-3,17-dione. Chem. Abs. 66: 114594.
Wix, G., K. Büki, E. Tömörkény and G. Ambrus. 1967. Hung. Pat. 153831 23 Sept. 1965. Microbiological preparation of androsta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione derivatives. Chem. Abs. 67: 107385.
Zajaczkowska, Ewa, L. Sedlaczek, 1988. Microbiological degradation of sterols. I. Selective induction of enzymes of the cholesterol sidechain cleavage in Rhodococcus sp. IM 58. Acta Microbiol. Polon. 37: 27–44.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szentirmai, A. Microbial physiology of sidechain degradation of sterols. Journal of Industrial Microbiology 6, 101–115 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01576429
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01576429