Summary
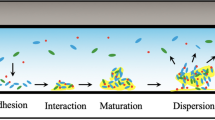
Descriptions of biofilms and their elemental compositions based on scanning electron micrographs and energy dispersive x-ray analysis cannot be related to the original condition of the biofilm on the surface. Solvent replacement of water removes extracellular polymeric material and reduces the concentration of elements bound within the biofilm. In the wet state, bacteria and microalgae are enmeshed in a gelatinous film that is either removed or dried to a thin inconspicuous residue during sample preparation for scanning electron microscopy. The environmental scanning electron microscope provides a fast, accurate image of biofilms, their spatial relationship to the substratum and elemental composition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baier, R.E. 1975. Applied chemistry at protein interfaces. In: Advances in Chemistry, Series 145. American Chemistry Society, Washington, D.C., 399 pp.
Battersby, B.L. 1988. Sulphate-reducing bacteria. In: Methods in Aquatic Bacteriology (Austin, B., ed.), pp. 269–299, John Wiley and Sons, NY.
Beaman, D.R., J.A. Isasi. 1974. Electron Beam Microanalysis. ASTM STP 506, Philadelphia, PA.
Blunn, G. 1986. Biological fouling of copper and copper alloys. In: Biodeterioration VI, pp. 567–575, CAB Int., Slough, Barkshire.
Chandra, D., P. Roy, A.K. Mishra, J.N. Chakrabarti and B. Sengupta. 1979. Microbial removal of organic sulfur from coal. Fuel 58: 549.
Characklis, W., M. Turakhia and N. Zelver. 1990. Transport and interfacial transfer phenomena. Biofilms. (Characklis, W.G. and K.C. Marshall, eds.), pp. 265–340, John Wiley and Sons, New York, NY.
Ciba Foundation Symposium. 1980. Adhesion and Microorganism Pathogenicity. Pitman Medical Press, Bath, Avon.
Cooksey K.E. and B. Cooksey. 1986. Adhesion of fouling diatoms to surfaces: some biochemistry. In: Algal Biofouling (Evans, L.V. and Hoagland, K.D., eds.), pp. 41–53, Elsevier, New York, NY.
Corpe W.A. 1975. Metal-binding properties of surface materials from marine bacteria. Dev. Industr. Microbiol. 16: 249–255.
Costerton, J.W. and G.G. Geesey. 1986. The microbial ecology of surface colonization and of consequent corrosion. In: Biologically Induced Corrosion (Dexter, S.C., ed.), pp. 223–232. NACE, Houston.
Costerton, J.W., G.G. Geesey and K.J. Cheng, 1978. How bacteria stick. Sci. Am. 238: 86–95.
Daniel, G.F., A.H.L. Chamberlain, and E.B.G. Jones. 1980. Ultrastructural observations on the marine fouling diatom Amphora. Helgolander Wiss. Meeresunters, 34: 123–149.
P. Duncumb and S.J.B. Reed. 1968. The calculation of stopping power and backscatter effects in the electron probe microanalysis. In: Quantitative Electron Probe Microanalysis (Heinrich, K.F.J., ed.), NBS Special Publication 298, p. 133.
Ehrlich, H.L. 1981. Geomicrobiology. Marcel Dekker, New York, NY.
Ehrlich, H.L. and C.L. Brierley. 1990. Microbial Mineral Recovery. McGraw-Hill Publishing Co., New York, NY.
Grady, C.P.L. and H.C. Lim. 1980 Biological Wastewater Treatment. Marcel Dekker. New York, NY.
Gudas, J.P. and H.P. Hack. 1979. Sulfide-induced corrosion of copper-nickel alloys. Corrosion 35: 67–73.
Heinrich, K.F.J. 1986. Proc. 11th International Conference, X-Ray Optics and Microanalysis, London, Ontario.
Henke, B.L., P. Lee, T.J. Tanaka, R.L. Shimabukuro and B.K. Fujikawa. 1982. Atomic Data and Nuclear Data Tables 27: 1–144.
Kargi, F. and J.M. Robinson. 1982. Microbial desulfurization of coal by thermophilic microorganismsSulfolobus acidocaldarius. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 24: 2115.
Lawrence, R.W. and A. Bruynesteyn. 1983. Biological preoxidation to enhance gold and silver recovery from refractory pyritic ores and concentrates. CIM Bull. 76: 107.
Little, B., R. Ray, P. Wagner, Z. Lewandowski, W.C. Lee, W.G. Characklis and F. Mansfeld. 1990. Electrochemical behavior of stainless steels in natural seawater. Corrosion/90, paper no. 150, NACE, Houston.
Little, B., P. Wagner and J. Jacobus. 1988. The impact of sulfate-reducing bacteria on welded copper-nickel seawater piping systems. Mat. Perf. 27: 57–61.
Little, B., P. Wagner, J. Jacobus and L. Janus. 1989. Evaluation of microbiologically induced corrosion in an estuary. Estuaries 12: 138–141.
Little, B.J., P. Wagner, J.S. Maki, M. Walch and R. Mitchell. 1986. Factors influencing the adhesion of microorganisms to surfaces. J. Adhesion 20: 187.
Little, B., P. Wagner and F. Mansfeld. 1991. An overview of microbiologically influenced corrosion of metals and alloys. International Materials Review, in press.
Little, B., P. Wagner, R. Ray and J. Jones. 1990. Microbiologically influenced corrosion of copper alloys in saline water containing sulfate-reducing bacteria. Corrosion/91, paper no. 101, NACE, Houston.
Mansfeld, F., A. Postyn, H. Shih, J. Devinny, R. Islander and C.L. Chen. 1990. Corrosion monitoring and control in concrete sewer pipes. In: Proc. Corrosion/90, paper no. 113, NACE, Houston.
Marshall, K.C. 1976. Interfaces in Microbial Ecology. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA.
Marszalek, D.S., M. Gerchakov and L.R. Udey. 1979. Influence of substrate composition on marine microfouling. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 38: 987.
McEldowney, S. and M. Fletcher. 1988. Bacterial desorption from food container and food processing surfaces. Microb. Ecol. 15: 229.
Mitchell, R. and D. Kirchman. 1981. The microbial ecology of marine surfaces. In: Marine Biodeterioration (Costlow, J.D. and R.C. Tipper, eds.), pp. 49–56, Naval Institute Press, Annapolis, MD.
Mittleman, M.W. and G. Geesey. 1987. Fouling of industrial water systems: A problem solving approach, pp. 138–193. Water Micro Associates, San Diego, CA.
Moreton, B.B. and T.G. Glover. 1980. New marine industry applications for corrosion and biofouling resistant, coppernickel alloys. In: Proc. 5th Int. Congr. Marine Corrosion and Fouling, p. 267. Biologia Marina, Barcelona, Spain.
Nickol, G.F. 1979. Vinegar. In: Microbial Tech. (Poppler, H.J. and D. Perlman, eds.), Chapter 6, Academic Press, New York, NY.
Nilsson, I. and S. Ohlson. 1982. Columnar denitrification of water by immobilizedPseudomonas denitrificans cells. Europ. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 14: 86.
Nilsson, I., S. Ohlson, L. Haggstrom, N. Molin, and K. Mosbach. 1980. Denitrification of water using immobilizedPseudomonas denitrificans cells. Europ. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 10: 261.
North, N.A. and I.D. MacLeod. 1987. Corrosion of metals. In: Conservation of Archeological Objects (Pearson, C., ed.), pp. 68–98, Butterworths, London.
Pfennig, N., F. Widdel, and H.G. Truper. 1981. The dissimulatory sulfate-reducing bacteria. In: The Prokaryotes: A Handbook on Habitats (Starr, M.P., Stolp, M., Trüper, H.G., Balows, A. and Schlegel, H.G., eds.), pp. 926–940, Springer-Verlag, New York, NY.
Postgate, J.R. 1979. Cultivation and growth. The Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria (Postgate, J.R., ed.), pp. 24–40, Cambridge University Press, London.
Ribbe, P.H. (ed.). 1976. Sulfide Mineralogy. Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, D.C.
Rowlands, J.C. 1965. Corrosion of tube and pipe alloys due to polluted seawater. J. Appl. Chem. 15: 57–63.
Sieburth, J.M. 1975. A Pictorial Essay on Marine Microorganisms and Their Environments. University Press, Baltimore, MD.
Staffeldt, E.E. and D.A. Kohler. 1973. Assessment of corrosion products removed from “La Fortuna”, Punta del Mar., Venezia. Petrolia e Ambiente, pp. 163–170.
Syrett, B.C. 1980. The mechanism of accelerated corrosion of copper-nickel alloys in sulfide polluted seawater. Corrosion/80, paper no. 33, NACE, Houston.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Little, B., Wagner, P., Ray, R. et al. Biofilms: An ESEM evaluation of artifacts introduced during SEM preparation. Journal of Industrial Microbiology 8, 213–221 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01576058
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01576058