Summary
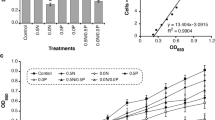
The effects of NH4Cl and KNO3 on biodegradation of light Arabian crude oil by an oil-degrading enrichment culture were studied in respirometers. In poorly buffered sea salts medium, the pH decreased dramatically in cultures that contained NH4Cl, but not in those supplied with KNO3. The ammonia-associated pH decline was severe enough to completely stop oil biodegradation as measured by oxygen uptake. Regular adjustment of the culture pH allowed oil biodegradation to proceed normally. A small amount of nitrate accumulated in all cultures that contained ammonia, but nitrification accounted for less than 5% of the acid that was observed. The nitrification inhibitor, nitrapyrin, had no effect on the production of nitrate or acid in ammonia-containing cultures. When the culture pH was controlled, either by regular adjustment of the culture pH or by supplying adequate buffering capacity in the growth medium, the rate and extent of oil biodegradation were similar in NH4Cl- and KNO3-containing cultures. the lag time was shorter in pH-controlled cultures supplied with ammonia than in nitrate-containing cultures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, M. 1977. Introduction to Soil Microbiology. John Wiley and Sons, NY.
Brock, T.D., D.W. Smith and M.T. Madigan. 1984. Biology of Microorganisms. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Bronchart, R.D., J. Cadron, A. Charlier, A.A.R. Gillot and W. Verstraete. 1985. A new approach in enhanced biodegradation of spilled oil: development of an oil dispersant containing oleophilic nutrients. Proc. 1985 Oil Spill Conf., pp. 453–462, Los Angeles, CA.
Bushnell, L.D. and F.F. Haas. 1941. The utilization of certain hydrocarbons by microorganisms. J. Bacteriol. 41: 653–673.
Cooney, J.J., S.A. Silver and E.A. Beck. 1985. Factors influencing hydrocarbon degradation in three freshwater lakes. Microbial Ecol. 11: 127–137.
Dibble, J.T. and R. Bartha. 1976. Effect of iron on the biodegradation of petroleum in seawater. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 31: 544–550.
Dibble, J.T. and R. Bartha. 1979. Effect of environmental parameters on the biodegradation of oil sludge. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 37: 729–739.
Gottschalk, G. 1986. Bacterial Metabolism. Springer-Verlag, New York.
Haines, J.R., M. Kadkhodayan, D.J. Mocsny, C.A. Jones, M. Islam and A.D. Venosa. 1994. Effect of salinity, oil type, and incubation temperature on oil biodegradation. In: Applied Biotechnology for Site Remediation (Hinchee, R.E., D.B. Anderson, F.B. Metting, Jr and G.D. Sayles, eds), pp. 75–83, Lewis, Boca Raton, FL.
Horowitz, A. and R.M. Atlas. 1977. Continuous open flowthrough system as a model for oil degradation in the Arctic Ocean. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 33: 647–653.
Jobson, A., M. McLaughlin, F.D. Cook and D.W.S. Westlake. 1974. Effect of amendments on the microbial utilization of oil applied to soil. Appl. Microbiol. 27: 166–171.
Lehtomaki, M. and S. Niemela. 1975. Improving microbial degradation of oil in soil. Ambio 4: 126–129.
Macleod, R.A. and E. Onofrey. 1956. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. II. Observation on the relation of seawater to the growth of marine bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 72: 661–667.
Moucawi, J., E. Fustec, P. Jambu, A. Ambles and R. Jacquesy. 1981. Biooxidation of added and natural hydrocarbons in soils: effect of iron. Soil Biol. Biochem. 13: 335–342.
Olivieri, R., P. Bacchin, A. Robertiello, N. Oddo, L. Degen and A. Tonolo. 1976. Microbial degradation of oil spills enhanced by a slow release fertilizer. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 31: 629–634.
Oremland, R.S. and D.G. Capone. 1988. Use of ‘specific’ inhibitors in biogeochemistry and microbial ecology. Advances in Microbial Ecology 10: 285–383.
Raymond, R.L., J.O. Hudson and V.W. Jamison. 1976. Oil degradation in soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 31: 522–535.
Schmidt, E.L., J.A.E. Molina and C. Chiang. 1973. Isolation of chemoautotrophic nitrifiers from Moroccan soils. Bull. Ecol. Res. Comm. 17: 166–167.
Soriano, S. and N. Walker. 1968. Isolation of ammonia-oxidizing autotrophic bacteria. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 31: 493–497.
USEPA. 1979. Methods for Analysis of Water and Wastes. EPA 600/4-79-020 Method 353.1.
Ward, D.M. and T.D. Brock. 1976. Environmental factors influencing the rate of hydrocarbon oxidation in temperate lakes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 31: 764–772.
Zubay, G. 1983. Biochemistry. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wrenn, B.A., Haines, J.R., Venosa, A.D. et al. Effects of nitrogen source on crude oil biodegradation. Journal of Industrial Microbiology 13, 279–286 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569729
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569729