Summary
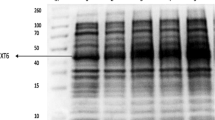
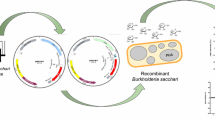
TheEscherichia coli xylose isomerase (EC 5.3.1.5) has been expressed under the control of a thermal inverting promotor system (att-nutL-p-att-N block) and its performance in a hollow fiber bioreactor measured. The conversion of xylose to xylulose was inversely proportional to the flow rate and the system operated up to 60°C. The maximum conversion efficiency observed was 19.05% at 55°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antrim, R.L. and A.L. Auterinen. 1986. A new regenerable immobilized glucose isomerase. Starch/Starke 38: 132–137.
Batt, C.A., S. Carvallo, D.D. Easson, M. Akedo and A.J. Sinskey. 1985. Evidence for a xylose metabolic pathway inSaccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 28: 549–553.
Batt, C.A., M.C. Claps, M.S. Bodis, S. Jamas and A.J. Sinskey. 1985. Analysis of xylose operon regulation by Mud-lac fusion: trans effect of plasmid coded xylose operon. Can. J. Microbiol. 31: 930–933.
Batt, C.A., S.R. Novak, E.O. O'Neill, J. Ko and A.J. Sinskey. 1986. Hyperexpression ofEscherichia coli xylose isomerase. Biotechnol. Prog. 2: 140–144.
Blanch, H.W., T.B. VickRoy and C. Wilkes. 1984. Growth of procaryotic cells in hollo-fiber reactors. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 434: 373–381.
Bruinenberg, P., P. deBot, J. vanDijken and W. Scheffers. 1983. NADH-linked aldose reductase: the key to anaerobic alcoholic fermentation of xylose by yeasts. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 19: 256–260.
Chen, W.P. 1980. Glucose isomerase. A review. Proc. Biochem. 15: 30–41.
Chiang, L., M. Flickinger, L. Chen and G. Tsao. 1982. Ethanol production from pentoses by immobilized microorganisms. Enzyme Microbial Technol. 4: 93–95.
Chiang, L., H. Hsiao, P. Ueng and G. Tsao. 1981. Enzymatic and microbial preparation of d-xylulose from d-xylose. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 42: 66–69.
Chung, B.H., H.N. Chang and Y.H. Kho. 1987. Dual hollow fiber membrane bioreactor for whole cell enzyme immobilization ofStreptomyces griseus with glucose isomerase activity. J. Ferment. Technol. 65: 575–581.
Gong, C., L. Chen, M. Flickinger, L. Chiang and G. Tsao. 1981. Production of ethanol fromd-xylose by usingd-xylose isomerase and yeast. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 41: 430–436.
Hahn-Hagerdal, B., S. Berner and K. Skoog. 1986. Improved ethanol production from xylose with glucose isomerase andSaccharomyces cerevisiae using the respiratory inhibitor azide. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24: 287–293.
Lastick, S., M. Tucker, V. Mackedonski and K. Grohmann. 1986. Overproduction ofEscherichia coli xylose isomerase. Biotechnol. Lett. 8: 1–6.
Maniatis, T., E.F. Fritsch and J. Sambrook. 1982. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Olivier, S. and P. Toit. 1986. Sugar cane bagasse as a possible source of fermentable carbohydrates. II. Optimization of xylose isomerase as well as sugar cane bagasse hydrolyzate to xylulose in laboratory scale units. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 28: 684–699.
Podhajska, A.J., N. Hasan and W. Szybalski. 1985. Control of cloned gene expression by promoter inversion in vivo: construction of the heat-pulse-activated att-nutL-p-att-N module. Gene 40: 163–168.
Sarthy, A., B. McConaughy, Z. Lobo, J. Sundstrom, C. Furlong and B. Hall. 1987. Expression of theEscherichia coli xylose isomerase gene inSaccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53: 1996–2000.
Silhavy, T.J., M.L. Berman and L.W. Enquist. 1984. Experiments in Gene Fusions. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Stevis, P. and N. Ho. 1985. Overproduction ofd-xylose isomerase inEscherichia coli by cloning thed-xylose isomerase gene. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 7: 592–596.
Wovcha, M., D. Steuerwald and K. Brooks. 1983. Amplification ofd-xylose andd-glucose isomerase activities inEscherichia coli by gene cloning. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 45: 1402–1404.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wong, D.W.S., Yee, L.N.H. & Batt, C.A. Thermal inducible expression of xylose isomerase and its performance in a hollow fiber bioreactor. Journal of Industrial Microbiology 4, 1–5 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569686
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569686