Summary
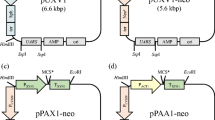
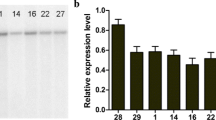
The xyclose isomerase gene inEscherichia coli was cloned complementarily into a Leu2-negativeSchizosaccharomyces pombe mutant (ATCC 38399). The subsequent integration of the plasmid into the chromosomal DNA of the host yeast was verified by using the dot blot and southern blot techniques. The expressed xylose isomerase showed activity on a nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel. The expression of xylose isomerase gene was influenced by the concentration of nutrients in the fermentation broth. The yeast possessed a xylose isomerase activity of 20 nmol/min/mg by growing in an enriched medium containing yeast extract-malt extract-peptone (YMP) andd-xylose. The conversion ofd-xylose tod-xylulose catalyzed by xylose isomerase in the transformed yeast cells makes it possible to fermentd-xylose with ethanol as a major product. When the fermentation broth contained YMP and 5% (w/v)d-xylose, the maximal ethanol yield and productivity reached 0.42 g/g and 0.19 g/l/h, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beach D. and P. Nurse, 1981. High-frequency transformation of the fission yeastSchizosaccharomyces pombe. Nature, 290: 140–142.
Batt, C.A., S. Carva, D.D. Easspm. Jr., M. Aledo and A.J. Sinskey. 1985. Direct evidence for a xylose metabolic pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol. Bioeng 28: 549–553.
Briggs K.A., W.E. Lancashire and B.S. Hartley. 1984. Molecular cloning, DNA structure and expression of theEscherichia coli d-xylose isomerase. EMBO, 3: 611–616.
Chan E.C., P.P. Ueng and L.F. Chen. 1986.d-xylose fermentation to ethanol bySchizosaccharomyces pombe cloned with xylose isomerase gene. Biotechnol. Lett. 8: 231–234.
Chiang C. and S.G. Knight. 1960. Metabolism ofd-xylose by molds. Nature (Lond) 188: 79–81.
Chiang L.C., H.Y. Hsiao, P.P. Ueng, L.F. Chen and G.T. Tsao, 1981. Ethanol production from xylose by enzymic isomerization and yeast fermentation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. Symp. 11: 263–274.
Cryer D.R., R. Eccleshall and J. Marmur. 1975. Isolation of yeast DNS. Meth. Cell Biol. 12: 39–44.
Davis B.J. 1964. Disc Electrophoresis II. Method and application to human serum proteins. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 121: 404–427.
Dishe Z. and E. Borenfreund. 1951. A new spectrophotometric method for the detection and determination of keto sugars and trioses. J. Biol. Chem. 192: 583–587.
Gong C.S., T.A. Claypool, L.D. McCracken, C.M. Mauw, P.P. Ueng and G.T. Twao. 1983. Conversion of pentoses by yeasts. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 15: 85–102.
Gong C.S., L.D. McCracken and G.T. Tsao. 1983. Conversion pentoses by yeasts. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 25: 85–102.
Hinnen A., J.B. James and G.R. Fink, 1978. Transformation of years. Proc. Natl. Sci. U.S.A. 75: 1929–1933.
Ho N.Y., P. Stevis, S. Rosenfeld, J.J. Huang and G.T. Tsao. 1983. Experession of theE. coli isomerase gene by a yeast promoter. Biotech. Bioeng. Symp. 13: 245–250.
Jeffries T.W. 1983. Utilization of xylose by bacteria, yeasts, and fungi. Adv. Biochem. Eng. 27: 1–32.
Lowry O.H., N. Rosebrough, A.L. Farr and R.J. Randall, 1951. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193: 265–275.
Maniatis T., E.F. Futsch and J. Sambrock, 1982. In: Molecular Cloning, pp. 383–389, Cold Springer Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Ornstein L. 1964. Disc Electrophoresis I. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 121: 321–349.
Sarthy A.V., B.L. McConaughy, Z. Lobo, J.A. Sundstrom, C.E. Furlong and B.D. Hall, 1987. Expression of theEscherichia coli xylose isomerase gene inSaccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53: 1996–2000.
Schneider H., P.Y. Wang, Y.K. Chan and R. Maleszka. 1981. Conversion ofd-xylose into ethanol by the yeastPachysolen tannophilus. Biotechnol. Lett. 3: 89–91.
Scopes R.K. 1967. Methods for starch-gel electrophoresis of sarcoplasmic proteins. Biochem. J. 107: 139–150.
Shamanna D.K. and K.E. Sanderson. 1979. Genetics and regulation ofd-xylose utilization inSalmonella typhimurium LT2. J. Bacteriol. 139: 64–70.
Ueng P.P., K.J. Volpp, J.V. Tucker, C. Gong and L.F. Chen. 1985. Molecular cloning of theEscherichia coli gene encoding xylose isomerase. Biotechnol. Lett. 7: 153–158.
Veiga L.A., M. Bacial and B.L. Horecker. 1960. Pentose metabolism in Candida albicans. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2: 48–53.
Yuan R. and Y. Lin. 1978. Chromosomal DNA fromE. coli. In: The purification of restriction enzymes and DNA substrates pp. 130–131.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, EC., Ueng, P.P., Eder, K.L. et al. Integration and expression of theEscherichia coli xylose isomerase gene inSchizosaccharomyces pombe . Journal of Industrial Microbiology 4, 409–417 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569636
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569636