Summary
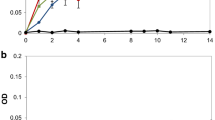
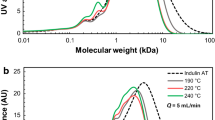
The ability of the lignino-cellulolytic actinomyceteStreptomyces viridosporus T7A to attack purified fractions of kraft lignin was examined. In the presence of 0.3% yeast extract, high-molecular weight kraft lignin (MW>3000, ether-insoluble fraction) does not affect growth of this microorganism significantly, whereas low-molecular weight kraft lignin (MW<3000, ether-soluble fraction) inhibits its development. Accordingly, average molecular weight of the ether-insoluble fraction after bacterial growth remained unaltered, as measured by Sephadex G-50 gel permeation chromatography. Slight modifications were detected by high performance liquid chromatography in the ether-soluble fraction after incubation with the microorganism.S. viridosporus T7A partially decolorized Remazol Brilliant Blue R during growth on wheat lignocellulose. However, decolorization of either fraction of kraft lignin was not observed. These results suggest that the filamentous bacteriumS. viridosporus T7A is not suitable for pulp mill effluent treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antai, A.P. and D.L. Crawford. 1981. Degradation of softwood, hardwood, and grass lignocelluloses by twoStreptomyces strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 42: 378–380.
Crawford, D.L. and R.L. Crawford. 1976. Microbial degradation of lignocellulose: the lignin component. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 3: 714–717.
Crawford, D.L., S. Floyd and A.L. Pometto III. 1977. Degradation of natural and kraft lignins by the microflora of soil and water. Can. J. Microbiol. 23: 434–440.
Crawford, D.L. 1978. Lignocellulose decomposition by selectedStreptomyces strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 35: 1041–1045.
Crawford, D.L., A.L. Pometto and R.L. Crawford 1983. Lignin degradation byStreptomyces viridosporus: isolation and characterization of a new polymeric lignin degradation intermediate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 45: 898–904.
Crawford, R.L. 1981. In: Lignin Biodegradation and Transformation. pp. 15–19, John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Deobald, L.A., D.L. Crawford. 1987. Activities of cellulase and other extracellular enzymes during lignin solubilization byStreptomyces viridosporus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 26: 158–163.
Deschamps, A.M., G. Mahoudeau and J.M. Lebeault 1980. Fast degradation of kraft lignin by bacteria. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 9: 45–51.
Eaton, D., H-m. Chang and T.K. Kirk. 1980. Fungal decolorization of kraft bleach plant effluents. Tappi 63: 103–109.
Eaton, D.C., H-m. Chang, T.W. Joyce, T.W. Jeffries and T.K. Kirk. 1982. Method obtains fungal reduction of extraction-stage kraft bleach effluents. Tappi 65: 89–92.
Fukuzumi, T. 1980. Microbial decolorization and defoaming of pulping waste liquors. In: Lignin Biodegradation: Microbiology, Chemistry, and Potential Applications. (T.K. Kirk, T. Higuchi and H-m. Chang, eds.), pp. 161–177, CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, Florida.
Glenn, J.K. and M.H. Gold. 1983. Decolorization of several polymeric dyes by the lignin-degrading basidiomycetePhanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 45: 1741–1747.
González, B., A. Merino, M. Almeida and R. Vicuña. 1986. Comparative growth of natural bacterial isolates on various lignin-related compounds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 52: 1428–1432.
Goycoolea, M., D. Seelenfreund, C. Rüttimann B. González and R. Vicuña. 1986. Monitoring bacterial consumption of low molecular weight lignin derivatives by high performance liquid chromatography. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 8: 213–216.
Janshekar, H., C. Brown, Th. Haltmeier, M. Leisola and A. Fiechter. 1982. Bioalteration of kraft pine lignin byPhanerochaete chrysosporium. Arch. Microbiol. 132: 14–21.
Janshekar, H., and A. Fiechter. 1983. In: Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology (Fiechter, A., Jeffries, T.W., eds.), pp. 119–178, Springer Verlag, Berlin.
Kawakami, H. and T. Ohyama. 1980. Bacterial degradation of lignin II. Degradation of kraft lignin by pseudomonads isolated from natural waters. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 26: 564–570.
Livernoche, D., L. Jurasek, M. Desrochers and I.A. Veliky. 1981. Decolorization of a kraft mill effluent with fungal mycelium immobilized in calcium alginate gel. Biotechnol. Lett. 3: 701–705.
Lundquist, K. and T.K. Kirk. 1980. Fractionation-purification of an industrial kraft lignin. Tappi 63: 80–82.
McCarthy, A.J., A. Paterson and P. Broda. 1986. Lignin solubilization byThermomonospora mesophila. Appl. Microb. Biotechnol. 24: 347–352.
McCarthy, A.J. 1987. Lignin-degrading actinomycetes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 46: 145–163.
Ramachandra, M., D.L. Crawford and A.L. Pometto III. 1987. Extracellular enzyme activities during lignocellulose degradation byStreptomyces spp.: a comparative study of wild-type and genetically manipulated strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53: 2754–2760.
Rüttimann, C., D. Seelenfreund and R. Vicuña. 1987. Metabolism of low molecular weight lignin-related compounds byStreptomyces viridosporus T7A. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 9: 526–530.
Sjöstrom, E. 1981. In: Wood Chemistry. Fundamentals and applications, pp. 124–145, Academic Press, New York.
Sutherland, J.B., D.L. Crawford and A.L. Pometto III. 1981. Catabolism of substituted benzoic acids byStreptomyces species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 41: 442–448.
Whalen, D.M.. 1975. A simple method for precipitating easily filterable acid lignin from kraft black liquor. Tappi 58: 110–112.
Zeikus, J-G., A.L. Wettstein and T.K. Kirk. 1982. Molecular basis for the degradative recalcitrance of lignin in anaerobic environments. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 15: 193–197.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seelenfreund, D., Vicuña, R. Effect ofStreptomyces viridosporus T7A on kraft lignin. Journal of Industrial Microbiology 5, 17–23 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569602
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569602