Summary
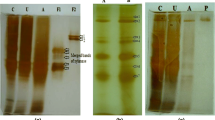
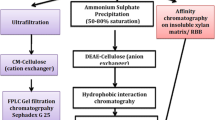
The yeast-like fungusAureobasidium is a promising source of xylanase (EC 3.2.1.8) with an exceptionally high specific activity. For enzyme production in volumes of several liters, xylose was the preferred carbon source and inducer. Xylanase in clarified cultures was concentrated by reversible adsorption to cation-exchange matrix to 5% of the initial volume, and recovered at nearly 2 million IU/1. Selective conditions permitted 97% recovery of xylanase with a 1.8-fold enrichment in specific activity, to 70% of purity. The predominant xylanase species (20 kDa) was subsequently purified to >99% of homogeneity by gel filtration chromatography. Purified enzyme exhibited an isoelectric point of 8.5, and specific activity of 2100 IU/mg under optimal conditions, determined to be pH 4.5 and 45°C. The activity of purified enzyme was specific for polymeric xylan.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allenza, P., D.S. Scherl, R.W. Detroy and T.D. Leathers 1986. Hydrolysis of xylan by an immobilized xylanase fromAureobasidium pullulans. Biotechnol. Bioengin. Symp. 17: 425–433.
Biely, P., Z. Kratky, M. Vrsanska and D. Urmanicova. 1980. Induction and inducers of endo-1,4-B-xylanase in the yeastCryptococcus albidus. Eur. J. Biochem. 108:323–329.
Biely, P., D. Mislovicova and R. Toman. 1985. Soluble chromogenic substrates for the assay of endo-1,4-B-xylanases and endo-1,4-B-glucanases. Anal. Biochem. 144:142–146.
Biely, P., M. Vrsanska and Z. Kratky. 1980. Xylan-degrading enzymes of the yeastCryptococcus albidus. Eur. J. Biochem. 108:313–321.
Dekker, R.F.H. 1979. The hemicellulase group of enzymes, In: Polysaccharides in food. (J.M.V. Blanshard and J.R. Mitchell, eds.), pp. 93–108. Butterworth, London and Boston.
Detroy, R.W. 1981. Bioconversion of agricultural biomass to organic chemicals, In: Organic chemicals from biomass. (I.S. Goldstein, ed.), pp. 19–43, CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, FL.
Frederick, M.M., C. Kiang, J.R. Frederick and P.J. Reilly. 1985. Purification and characterization of endo-xylanases fromAspergillus niger. I. Two isozymes active on xylan backbones near branch points. Biotechnol. Bioengin. 27:525–532.
Laemmli, U.K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature (London) 277:680–685.
Leathers, T.D. 1986. Color variants ofAureobasidium pullulans overproduce xylanase with extremely high specific activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 52:1026–1030.
Leathers, T.D., R.W. Detroy and R.J. Bothast. 1986. Induction and glucose respression of xylanase from a color variant strain ofAureobasidium pullulans. Biotech. Lett. 8:867–872.
Leathers, T.D., C.P. Kurtzman and R.W. Detroy. 1984. Overproduction and regulation of xylanase inAureobasidium pullulans andCryptococcus albidus. Biotech. Bioengin. Sym. 14:225–240.
Lowry, O.H., N.J. Rosebrough, A.L. Farr and R.J. Randall. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–275.
Miller, G.L. 1959. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 31:426–428.
O'Farrell, P.Z., H.M. Goodman and P.H. O'Farrell. 1977. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell 12:1133–1142.
Paice, M.G. and L. Jurasek. 1984. Removing hemicellulose from pulps by specific enzymic hydrolysis. J. Wool Chem. Technol. 4:187–198.
Shapiro, A.L., E. Vinuela and J.V. Maizel. Jr. 1967. Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 28:815–820.
Stuttgen, E. and H. Sahm. 1982. Purification and properties of endo-1,4-B-xylanase fromTrichosporon cutaneum. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 15:93–99.
Tan, L.U.L., E.K.C. Yu, G.W. Louis-Seize, and J.N. Saddler. 1987. Inexpensive, rapid procedure for bulk purification of cellulase-free B-1,4-xylanase of high specific activity. Biotechnol. Bioengin. 30:96–100.
Tangnu, S.K., H.W. Blanch and C.R. Wilke. 1981. Enhanced production of cellulase, hemicellulase, and B-glucosidase byTrichoderma reesei (RUT C-30). Biotechnol. Bioengin. 23: 1837–1849.
Toda, S., H. Suzuki and K. Nisizawa. 1971. Some enzymatic properties and the substrate specificities ofTrichoderma cellulases with special reference to their activity toward xylan. J. Ferment. Technol. 49:499–521.
Wickerham, L.J. and C.P. Kurtzman. 1975. Synergistic color variants ofAureobasidium pullulans. Mycologia 67:342–361.
Woodward, J. 1984. Xylanases: Functions, properties, and applications. In: (A. Wiseman ed.), Top. Enz. Ferment. Biotechnol. 8. pp. 9–30. Ellis Horwood, W. Sussex.
Wray, W., T. Boulikas, V.P. Wray and R. Hancock. 1981. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 118:197–203.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The mention of firm names or trade products does not imply that they are endorsed or recommended by the U.S. Dept. of Agirculture over other firms or similar products not mentioned.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leathers, T.D. Purification and properties of xylanase fromAureobasidium . Journal of Industrial Microbiology 4, 341–347 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569536
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569536