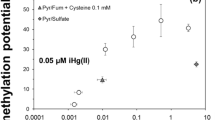
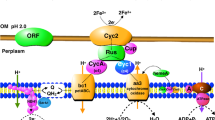
Abstract
Thiobacillus ferrooxidans became significantly more tolerant to mercury stress after culturing in media of increasing mercury(II) concentrations. When mercuric chloride was added to the growth medium, the resistant organisms were found to volatilize elemental mercury (Hg0).T. ferrooxidans may be an important factor in the natural mercury cycle, since the environments whereT. ferrooxidans is found typically contain elevated levels of heavy metals, including mercury.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Arkesteyn, G. J. M. W. 1979. Pyrite oxidation byThiobacillus ferrooxidans with special reference to the sulphur moiety of the mineral. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek45:423–435.
Bailey, E. H., Clark, A. L., Smith, R. M. 1972. Mercury, pp. 401–414. In: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 820. Washington D.C.: U. S. Government Printing Office.
Blair, W. R., Iverson, W. P., Brinckman, F. E. 1974. Application of a gas chromatograph-atomic absorption detection system to a survey of mercury transformations by Chesapeake Bay microorganisms. Chemosphere4:167–174.
Brierley, C. L. 1978. Bacterial leaching. CRC Critical Reviews in Microbiology6:207–262.
Carter, L. J. 1977. Chemical plants leave unexpected legacy for two Virginia rivers. Science198:1015–1020.
Chakrabarty, A. M. 1978. Genetic mechanisms in metal-microbe interactions, pp. 137–149. In: Murr, L. E., Torma, A. E., Brierley, J. A. (eds.), Metallurgical applications of bacterial leaching and related microbiological phenomena. New York: Academic Press.
Clark, D. L., Weiss, A. A., Silver, S. 1977. Mercury and organomercurial resistances determined by plasmids inPseudomonas. Journal of Bacteriology132:186–196.
Guay, R., Silver, M. 1975.Thiobacillus acidophilus sp. nov.; isolation and some physiological characteristics. Canadian Journal of Microbiology21:281–288.
Imai, K., Sugio, T., Tsuchida, T., Tano, T. 1975. Effect of heavy metal ions on the growth and iron-oxidizing activity ofThiobacillus ferrooxidans. Agricultural Biological Chemistry39:1349–1354.
Iverson, W. P., Brinckman, F. E. 1978. Microbial metabolism of heavy metals, pp. 201–232. In: Mitchell, R. (ed.), Water pollution microbiology. New York: Wiley.
Joensuu, O. L. 1971. Fossil fuels as a source of mercury pollution. Science172:1027–1028.
Manning, H. L. 1975. New medium for isolating iron-oxidizing and heterotrophic acidophilic bacteria from acid mine drainage. Applied Microbiology30:1010–1016.
Mao, W. H., Dugan, P. R., Martin, P. A. W., Tuovinen, O. H. 1980. Plasmid DNA in chemoorganotrophicThiobacillus ferrooxidans andT. acidophilus. FEMS Microbiology Letters8:121–125.
Nelson, J. D., Blair, W., Brinckman, F. E., Colwell, R. R., Iverson, W. P. 1973. Biodegradation of phenylmercuric acetate by mercury resistant bacteria. Applied Microbiology26:321–326.
Norris, P. R., Kelly, D. P. 1978. Toxic metals in leaching systems, pp. 83–102. In: Murr, L. E., Torma, A. E., Brierley, J. A. (eds.), Metallurgical applications of bacterial leaching and related microbiological phenomena. New York: Academic Press.
Olson, B. H., Barkay, T., Colwell, R. R. 1979. Role of plasmids in mercury transformation by bacteria isolated from the aquatic environment. Applied and Environmental Microbiology38:478–485.
Parris, G. E., Blair, W. R., Brinckman, F. E. 1977. Chemical and physical considerations in the use of atomic absorption detectors coupled with a gas chromatograph for determination of trace organometallic gases. Analytical Chemistry49:378–386.
Rogers, R. D. 1979. Volatility of mercury from soils amended with various mercury compounds. Soil Science Society of America Journal43:289–291.
Schottel, J., Mandal, A., Clark, D., Silver, S., Hedges, R. W. 1974. Volatilization of mercury and organomercurials determined by inducible R-factor systems in enteric bacteria. Nature251:335–337.
Silverman, M. P., Lundgren, D. G. 1959. Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacteriumFerrobacillus ferrooxidans. I. An improved medium and a harvesting procedure for securing high cell yields. Journal of Bacteriology77:642–647.
Summers, A. O., Silver, S. 1978. Microbial transformation of metals. Annual Review of Microbiology32:637–672.
Tuovinen, O. H., Niemela, S. I., Gyllenberg, H. G. 1971. Tolerance ofThiobacillus ferrooxidans to some metals. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek Journal of Microbiology and Serology37:489–496.
U. S. Environmental Protection Agency. 1974. Mercury in water, pp. 118–126. In: Methods for chemical analysis of water and wastes. Washington, D. C.: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Weiss, A. A., Murphy, S. D., Silver, S. 1977. Mercury and organomercurial resistances determined by plasmids inStaphylococcus aureus. Journal of Bacteriology132:197–208.
Yen, T. F., Chilingar, G. V. 1976. Introduction to oil shales, pp. 1–12. In: Yen, T. F., Chilingar, G. V. (eds.), Oil shale. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olson, G.J., Iverson, W.P. & Brinckman, F.E. Volatilization of mercury byThiobacillus ferrooxidans . Current Microbiology 5, 115–118 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01567431
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01567431