Abstract
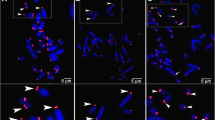
The arrangement of loops and chromomeres at the ends of lampbrush chromosomes in four species of bird is described with reference to chromomeres, loops and transcription units. Unlike the situation described in lampbrush chromosomes of amphibians, the lampbrush chromosomes of birds end in a terminal chromomere with conspicuous loops emerging from it. The fine-scale morphology of the ribonuclear protein matrix of these terminal loops is different from that of the majority of loops elsewhere on the chromosomes. In many cases the loops associated with the terminal chromomere are open ended, emerging from the chromomere but not returning to it at the other end. The distal ends of terminal openended loops therefore represent the true ends of the chromatids that make up a lampbrush half-bivalent. The pattern of binding of three telomeric DNA sequence probes to the terminal regions of bird lampbrush chromosomes, under conditions of DNA/DNA and DNA/RNA transcriptin situ hybridization has been investigated by fluorescencein situ hybridization. All three probes gave the same results. With DNA/DNA and DNA/RNA transcript hybridization, three classes of structure were labelled: the terminal chromomere, a small number of interstitial chromomeres and the terminal transcription unit on telomere loops. Labelling of telomere loops, but not of terminal or interstitial chromomeres, was eliminated by ribonuclease treatment beforein situ hybridization. The labelled regions of telomere loops were spaced away from the labelled terminal chromomere by an unlabelled sub telomeric transcription unit. After DNA/DNAin situ hybridization, no labelled loops were seen. DNA/RNA transcriptin situ hybridization with single-stranded hexamers of each strand of telomeric DNA showed that the terminal transcription unit on telomere loops represents transcription exclusively from the C-rich strand of the repeat outwards towards the end of the chromosome. It is concluded that transcription specifically of the C-rich strand of strictly terminal clusters of telomere repeats is an obligatory event on the lampbrush chromosomes of birds and is unlikely to represent indiscriminate readthrough from proximally located gene elements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adegoke JA, Arnason U, Widegren B (1993) Sequence organization and evolution, in all extant whalebone whales, of a DNA satellite with terminal chromosome localization.Chromosoma (Berl),102: 382–388.
Allshire RC, Dempster M, Hastie ND (1989) Human telomeres contain at least three types of G-rich repeat distributed non-randomly.Nucleic Acids Res 17: 4611–4627.
Blackburn EH (1992) Telomerases.Annu Rev Biochem 61 113–129.
Brown WRA, MacKinnon PJ, Villasante Aet al. (1990) Structure and polymorphism of human telomere-associated DNA.Cell 63: 119–132.
Buckle VJ, Kearney L (1993) Untwirling dirvish.Nature Genet 5: 4–5.
Callan HG (1963) The nature of lampbrush chromosomes.Int Rev Cytol 15: 1–34.
Callan HG (1986)Lampbrush Chromosomes. Berlin: Springer Verlag.
Callan HG, Lloyd L (1960) Lampbrush chromosomes of crested newtsTriturus cristatus (Laurenti).Phil Trans R Soc Lond B243: 135–219.
Chelysheva LA, Solovei IV, Rodionov AV, Yakovlev AF, Gaginskaya ER (1990) The lampbrush chromosomes of the chicken: the cytological maps of macrobivalents (in Russian).Cytology 32: 303–316.
Cross S, Lindsey J, Fantes J, McKay S, McGill N, Cooke H (1990) The structure of a subterminal repeated sequence present on many human chromosomes.Nucleic Acids Res 18: 6649–6657.
de Jonge J 1991) Telomere repeats from chicken erythrocyte chromosomes. EMBL accession number NX63499.
de Lange T, Shiue L, Myers RMet al. (1990) Structure and variability of human chromosome ends.Mol Cell Biol 10: 518–527.
Gall JG (1954) Lampbrush chromosomes from oocyte nuclei of the newt.J Morphol 94: 283–352.
Gall JG, Diaz MO, Stephenson EC, Mahon KA (1983) The transcription unit of lampbrush chromosomes.Soc Dev Biol Symp 41: 137–146.
Grieder CW, Blackburn EH (1989) A telomeric sequence in the RNA ofTetrahymena telomerase required for telomere repeat synthesis.Nature 337: 331–337.
Hastie ND, Allshire RC (1989) Human telomeres: fusion and interstital.Trends Genet 5: 326–331.
Hastie ND, Dempster M, Dunlop MGet al (1990) Telomere reduction in human colorectal carcinoma and with ageing.Nature 346: 866–871.
Hutchison NJ (1987) Lampbrush chromosomes of the chickenGallus domesticus.J Cell Biol 105: 1493–1500.
Kipling D, Cooke HJ (1990) Hypervariable ultra-long telomeres in mice.Nature 347: 400–402.
Lustig AJ, Kurtz S, Shore D (1990) Involvement of the silencer UAS binding protein RAPI in regulation of telomere length.Science 250: 549–553.
Macgregor HC, Varley JM (1988)Working with Animal Chromosomes, 2nd edn. Chichester: John Wiley.
Meyne J, Baker RJ, Hobart HHet al. (1990) Distribution of non-telomeric sites of the (TTAGGG) telomeric sequence in vertebrate chromosomes.Chromosoma (Berl)99: 3–10.
Moyzis RK, Buckingham JM, Cram LSet al. (1988) A highly conserved repetitive DNA sequence, (TTAGGG) is present at the telomeres of human chromosomes.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 6622–6626.
Nanda I, Schmid M. (1994) Localization of the telomeric (TTAGGG)n sequence in chicken (Gallus domesticus) chromosomes.Cytogenet Cell Genet 65: 190–193.
Royle NJ, Hill MC, Jeffreys AJ (1992) Isolation of telomere junction fragments by anchored polymerase chain reaction.Proc R Soc Lond B247: 57–61.
Rudenko G, van der Ploeg LHT (1989) Transcription of telomere repeats in Protozoa.EMBO J 8: 2633–2638.
Solovei I, Gaginskaya E, Hutchison N, Macgregor H (1993) Avian sex chromosomes in the lampbrush form: the ZW lampbrush bivalent from six species of bird.Chromosome Res 1: 153–166.
Varley JM, Macgregor HC, Nardi I, Andrews C, Erba HP (1980) Cytological evidence of transcription of highly repeated DNA sequences during the lampbrush stage inTriturus cristatus carnifex.Chromosoma (Berl) 80: 289–307.
Watson JD, Crick FHC (1953) A structure of deoxyribose nucleic acid.Nature 171: 737–738.
Weber B, Collins C, Robbins Cet al. (1990) Characterization and organization of DNA sequences adjacent to the human telomere associated repeat (TTAGGG)n.Nucleic Acids Res 18: 3353–3361.
Weber B, Allen L, Magenis RE, Hayden MR (1991) A low copy repeat located in subtelomeric regions of 14 different human chromosomal termini.Cytogenet Cell Genet 57: 179–183.
Wells RA, Germino GG, Krishna Set al. (1990) Telomererelated sequences at interstitial sites in the human genome.Genomics 8: 699–704.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to the memory of the late Professor H. G. Callan FRS, who inspired our interest in lampbrush chromosomes and taught us many successful ways of working with them.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solovei, I., Gaginskaya, E.R. & Macgregor, H.C. The arrangement and transcription of telomere DNA sequences at the ends of lampbrush chromosomes of birds. Chromosome Res 2, 460–470 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01552869
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01552869