Abstract
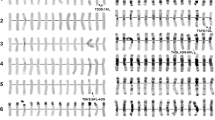
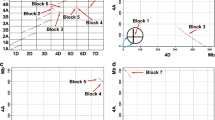
Triticum timopheevii ssp.timopheevii andT. timopheevii ssp.araraticum were analysed by sequential N-banding and genomicin situ hybridization. Three chromosomes, 6At, 1G and 4G, were involved in At-G intergenomic translocations in all six lines analysed. These chromosomes may be derived from a cyclic translocation that is species-specific toT. timopheevii. In contrast,Triticum turgidum has a species-specific cyclic translocation involving chromosomes 4A, 5A and 7B. The discovery of different species-specific chromosome translocations supports the diphyletic hypothesis of the evolution of tetraploid wheats. The results from genomic blocking analysis also revealed that the chromosomes ofAegilops speltoides are closer to the G genome than the B genome chromosomes. The possible role of speciesspecific translocations in the evolution of wheat is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anamthawat-Jónsson K, Schwarzacher T, Leith AR, Bennett MD, Heslop-Harrison JS (1990) Discrimination between closely related Triticeae species using genomic DNA as a probe.Theoret. Appl Genet 79: 721–728.
Badaeva ED, Budashkina EB, Badaev NS, Kalimina NP, Shkutina FM (1991) General features of chromosome substitutions inTriticum aestivum × T. timipheevii hybrids.Theoret Appl Genet 82: 227–232.
Badaeva ED, Badaev NS, Gill BS, Filatenko AA (1993) Intraspecific karyotype divergence and speciation inTriticum araraticum. Plant Syst Evol (submitted).
Bedbrook JR, Jones J, O'Dell M, Thompson RJ, Flavell RB (1980) A molecular description of telomeric heterochromatin inSecale species.Cell 19: 545–560.
Chen PD, Gill BS (1983) The origin of chromosome 4A, and genomes B and G of tetraploid wheat.Proc 6th Internatl Wheat Genet Symp pp. 39–48.
Dvořák J, di Terlizzi P, Zhang, H-B, Resta P (1993) The evolution of polyploid wheat: identification of the A genome donor species.Genome 36: 21–31.
Feldman M (1966) Identification of unpaired chromosomes in F1 hybrids involvingTriticum aestivum andT. timopheevi.Can J Genet Cytol 8: 144–151.
Gill BS (1991) Nucleo-cytoplasmic interaction (NCI) hypothesis of genome evolution and speciation in polyploid plants. In:Proc Dr. H. Kihara Memorial Intern Cytoplasmic Engin in Wheat pp. 48–53.
Gill BS, Chen PD (1987) Role of cytoplasm-specific introgression in the evolution of the polyploid wheats.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 6800–6804.
Hutchinson J, Miller TE (1982) Comparison of the chromosomes ofTriticum timopheevi with related wheat using the techniques of C-banding andin situ hybridization.Theoret Appl Genet 64: 31–40.
Jaaska V (1978) NADP-dependent aromatic alcohol dehydrogenase in polyploid wheats and their diploid relatives. On the origin and phylogeny of polyploid wheat.Theoret Appl Genet 53: 209–217.
Jaaska V (1980) Electrophoretic survey of seedling esterases in wheats in relation to their phylogeny.Theoret Appl Genet 56: 273–284.
Jiang J, Gill BS (1993) Sequential chromosome banding andin situ hybridization analysis.Genome 36: 792–795.
Johnson GD, Nogueira C de, Aranjo JGM (1981) A simple method for reducing the fading of immunofluorescence during microscopy.J Immunol Methods 43: 349–350.
Kenton A, Parokonny AS, Gleba YY, Bennett MD (1993) Characterization of theNicotiana tabacum L. genome by molecular cytogenetics.Mol Gen Genet 240: 159–169.
Liu CJ, Atkinson MD, Chinoy CN, Devos KM, Gale MD (1992) Nonhomoeologous translocations between group 4, 5 and 7 chromosomes within wheat and rye.Theoret Appl Genet 83: 305–312.
Mukai Y, Nakahara Y, Yamamoto M (1993) Simultaneous discrimination of the three genomes in hexaploid wheat by multicolor fluorescencein situ hybridization using total genomic and highly repeated DNA probes.Genome 36: 489–494.
Naranjo T (1990) Chromosome structure of durum wheat.Theoret Appl Genet 79: 397–400.
Naranjo T, Roca A, Goicoecha PG, Giraldz R (1987) Arm homoeology of wheat and rye chromosomes.Genome 29: 873–882.
Ogihara Y, Tsunewaki K (1988) Diversity and evolution of chloroplast DNA inTriticum andAegilops as revealed by restriction fragment analysis.Theoret Appl Genet 76: 321–332.
Rayburn AL, Gill BS (1985) Molecular evidence for the origin and evolution of chromosome 4A in polyploid wheat.Can J Genet Cytol 27: 246–250.
Sarkar P, Stebbins GL (1956) Morphological evidence concerning the origin of the B genome in wheat.Am J Bot 43: 297–304.
Takumi S, Nasuda S, Liu YG, Tsunewaki K (1993) Wheat phylogeny determined by RFLP analysis of nuclear DNA. 1. Einkorn wheat.Japan J Genet 68: 73–79.
Tanaka M, Kawahara T, Sano J (1978) The evolution of wild tetraploid wheat.Proc 5th Internat Wheat Genet Symp pp. 73–80.
Tsunewaki K, Ogihara Y (1983) The molecular basis of genetic diversity among cytoplasms ofTriticum andAegilops species. II. On the origin of polyploid wheat cytoplasms as suggested by chloroplast DNA restriction fragment patterns.Genetics 104: 155–171.
Wagenaar EB (1961) Studies on the genome constitution ofTriticum timopheevi Zhuk. I. Evidence for genetic control of meiotic irregularities in tetraploid hybrids.Can J Genet Cytol 3: 47–60.
Wienberg J, Jauch A, Stanyon R, Cremer T (1990) Molecular cytotaxonomy of primates by chromosomalin situ suppression hybridization.Genomics 8: 347–350.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, J., Gill, B.S. Different species-specific chromosome translocations inTriticum timopheevii andT. turgidum support the diphyletic origin of polyploid wheats. Chromosome Res 2, 59–64 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01539455
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01539455