Summary
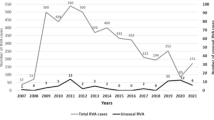
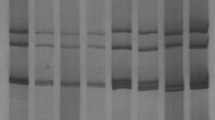
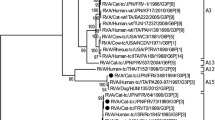
To determine the relative frequency of intergenogroup reassortants of rotavirus in nature, we analyzed the genetic composition of 22 electrophoretically distinct stool isolates which accounted for 95.2% of stool rotaviruses with a short RNA pattern collected during 10 rotavirus seasons. These strains all showed subgroup I and G2 specificities, but two distinct hybridization patterns were observed when the probes prepared from Wa (a member of the Wa genogroup) and KUN (a member of the DS-1 genogroup) were used. Genomic RNAs from 10 strains (accounting for 64% of the field rotaviruses with short RNA pattern) hybridized exclusively to the KUN probe, and thus belonged to the DS-1 genogroup. On the other hand, genomic RNAs of the remaining 12 strains (accounting for 36% of the field rotaviruses with short RNA pattern) formed one hybrid band with the Wa probe and 10 hybrid bands with the KUN probe. Thus, they were single gene substitution intergenogroup reassortants between members of the Wa and DS-1 genogroups. They had a similar genetic constellation in that a gene segment encoding either NS35 or NS34 from a Wa-like strain was introduced into a DS-1-like genome background.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chanock SJ, Wenske EK, Fields BN (1983) Human rotaviruses and genomic RNA. J Infect Dis 148: 49–50
Dunn SJ, Greenberg HB, Ward RL, Nakagomi O, Burns JW, Vo PT, Pax KA, Das M, Gowda K, Rao CD (1993) Serotypic and genotypic characterization of human serotype 10 rotaviruses from asymptomatic neonates. J Clin Microbiol 31: 165–169
Dyall-Smith ML, Holmes IH (1981) Gene-coding assignments of rotavirus doublestranded RNA segments 10 and 11. J Virol 38: 1099–1103
Estes MK, Cohen J (1989) Rotavirus gene structure and function. Microbiol Rev 53: 410–449
Georges-Courbot MC, Beraud AM, Beards GM, Campbell AD, Gonzalez JP, Georges AJ, Flewett TH (1988) Subgroups, serotypes, and electropherotypes of rotavirus isolated from children in Bangui, Central African Republic. J Clin Microbiol 26: 668–671
Gunasena S, Nakagomi O, Isegawa Y, Kaga E, Nakagomi T, Steele AD, Flores J, Ueda S (1993) Relative frequency of VP4 gene alleles among human rotaviruses recovered over a 10 year period (1982–1991) from Japanese children with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol 31: 2195–2197
Kalica AR, Greenberg HB, Espejo RT, Flores J, Wyatt RG, Kapikian AZ, Chanock RM (1981) Distinctive ribonucleic acid patterns of human rotavirus subgroups 1 and 2. Infect Immun 33: 958–961
Kitaoka S, Nakagomi T, Fukuhara N, Hoshino Y, Suzuki H, Nakagomi O, Kapikian AZ, Ebina T, Konno T, Ishida N (1987) Serologic characteristics of a human rotavirus isolate, AU-1, which has a “long” RNA pattern and subgroup I specificity. J Med Virol 23: 351–357
Kutsuzawa T, Konno T, Suzuki H, Ebina T, Ishida N (1982) Two distinct electrophoretic migration patterns of RNA segments of human rotaviruses prevalent in Japan in relation to their serotypes. Microbiol Immunol 26: 271–273
Kutsuzawa T, Konno T, Suzuki H, Kapikian AZ, Ebina T, Ishida N (1982) Isolation of human rotavirus subgroups 1 and 2 in cell culture. J Clin Microbiol 16: 727–730
Mascarenhas JDP, Linhares AC, Gabbay YB, de Freitas RB, Mendez E, Lopez S, Arias CF (1989) Naturally occurring serotype 2/subgroup II rotavirus reassortants in Northern Brazil. Virus Res 14: 235–240
Nakagomi O, Kaga E, Gerna G, Sarasini A, Nakagomi T (1992) Subgroup I serotype 3 human rotavirus strains with long RNA pattern as a result of naturally occurring reassortment between members of the bovine and AU-1 genogroups. Arch Virol 126: 337–342
Nakagomi O, Kaga E, Nakagomi T (1992) Human rotavirus strain with unique VP4 neutralization epitopes as a result of natural reassortment between members of the AU-1 and Wa genogroups. Arch Virol 127: 365–371
Nakagomi O, Nakagomi T (1991) Molecular evidence for naturally occurring single VP7 gene substitution reassortant between human rotaviruses belonging to two different genogroups. Arch Virol 119: 67–81
Nakagomi O, Nakagomi T, Akatani K, Ikegami N (1989) Identification of rotavirus genogroups by RNA-RNA hybridization. Mol Cell Probes 3: 251–261
Nakagomi O, Nakagomi T, Akatani K, Ikegami N, Katsushima N (1990) Relative frequency of rotavirus serotypes in Yamagata, Japan, over four consecutive rotavirus seasons. Res Virol 141: 459–463
Nakagomi O, Nakagomi T, Hoshino Y, Flores J, Kapikian AZ (1987) Genetic analysis of a human rotavirus that belongs to subgroup I but has an RNA pattern typical of subgroup II human rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol 25: 1159–1164
Nakagomi O, Nakagomi T, Oyamada H, Suto T (1985) Relative frequency of human rotavirus subgroups 1 and 2 in Japanese children with acute gastroenteritis. J Med Virol 17: 29–34
Nakagomi O, Oyamada H, Kuroki S, Kobayashi Y, Ohshima A, Nakagomi T (1989) Molecular identification of a novel human rotavirus in relation to subgroup and electropherotype of genomic RNA. J Med Virol 28: 163–168
Nakagomi O, Oyamada H, Nakagomi T (1991) Experience with serotyping rotavirus strains by reverse transcription and two-step polymerase chain reaction with generic and type-specific primers. Mol Cell Probes 5: 285–289
Nakagomi T, Akatani K, Ikegami N, Katsushima N, Nakagomi O (1988) Occurrence of changes in human rotavirus serotypes with concurrent changes in genomic RNA electropherotypes. J Clin Microbiol 26: 2586–2592
Nakagomi T, Katsushima N, Nakagomi O (1988) Relative frequency of human rotavirus subgroups I and II in relation to «short» and «long» electropherotypes of viral RNA. Ann Inst Pasteur/Virol 139: 295–300
Unicomb LE, Bishop RF (1989) Epidemiology of rotavirus strains infecting children throughout Australia during 1986–1987 A study of serotype and RNA electropherotype. Arch Virol 106: 23–34
Ward RL, Nakagomi O, Knowlton DR, McNeal MM, Nakagomi T, Clemens JD, Sack DA, Schiff GM (1990) Evidence for natural reassortants of human rotaviruses belonging to different genogroups. J Virol 64: 3219–3225
Ward RL, Clemens JD, Sack DA, Knowlton DR, McNeal MM, Huda N, Ahmed F, Rao M, Schiff GM (1991) Culture adaptation and characterization of group A rotaviruses causing diarrheal illnesses in Bangladesh from 1985 to 1986. J Clin Microbiol 29: 1915–1923
Ward RL, Knowlton DR (1989) Genotypic selection following coinfection of cultured cells with subgroup 1 and subgroup 2 human rotaviruses. J Gen Virol 70: 1691–1699
Wyatt R, James W, Bohl E, Theil K, Saif L, Kalica A, Greenberg H, Kapikian A, Chanock R (1980) Human rotavirus type 2: cultivation in vitro. Science 207: 189–191
Yamakawa K, Nakagomi O (1990) Improved detection of rotavirus RNA in dot-blot hybridization assay by chromatographic extraction and acid denaturation of double-stranded RNA. Mol Cell Probes 4: 415–418
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaga, E., Nakagomi, O. Recurrent circulation of single nonstructural gene substitution reassortants among human rotaviruses with a short RNA pattern. Archives of Virology 136, 63–71 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01538817
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01538817