Abstract
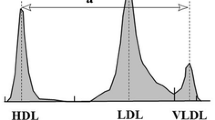
Plasma lipids, apoprotein A-I and B in serum and in lipoprotein fractions (VLDL + LDL, HDL2, and HDL3) obtained by preparative ultracentrifugation, as well as postheparin lipoprotein lipase activity (H-TGL and LPL) were evaluated in 17 subjects with primary biliary cirrhosis (stage II and III) subdivided into two groups according to the presence or absence of lipoprotein X (Lp-X). A reduction in total lipoprotein lipase activity was observed in both patient groups, compared to controls (P<0.01); the hepatic lipoprotein lipase was significantly reduced (P<0.01) only in the Lp-X-positive group. The lipid (477.8+154.3 vs 239.6±51.1; P<0.01) and protein (147.4±37.1 vs 83.3±19.7; P< 0.01) masses in the VLDL + LDL fraction of the Lp-X-positive group were increased compared to controls. In the same group, the HDL2 fraction also showed an increase in lipid (186.6±80.0 vs 77.9±21.6; P<0.01) and protein (133.9±60.0 vs 67.9±16.5; P <0.01) masses; in addition, the HDL2 percent lipid composition was different in the two patient groups, showing a decrease in esterified cholesterol (20.4±3.6 vs 25.7±2.2; P <0.01) and an increase in phospholipids (59.2±2.9 vs 54.8±2.6; p<0.01) in the Lp-X-positive group. Apo B was also increased in Lp-X-positive patients both in the serum (134.0±27.6 vs 90.9±7.3; P<0.01) and in the VLDL + LDL fraction (134.0±22.2 vs 72.5±16.5; P<0.01). The differences seen in lipoprotein concentration and composition in the two patient groups seem related, in part, to the presence of Lp-X or, better, to the stage of the disease. The reduction in hepatic lipase may play an important role in determining the increase and altered composition of the HDL2 subfraction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
James SP (moderator): Primary biliary cirrhosis: A model autoimmune disease. Ann Intern Med 99:500–512, 1983
Seidel D, Alaupovic P, Furman RH, McConathy WJ: A lipoprotein characterizing obstructive jaundice. II Isolation and partial characterization of the protein moieties of low density lipoproteins. J Clin Invest 59:2396–2407, 1970
Manzato E, Fellin R, Baggio G, Walch S, Neubeck W, Seidel D: Formation of lipoprotein-X; its relationship to bile compounds. J Clin Invest 57(5): 1248–1260, 1976
Sabesin SM: Cholestatic lipoproteins. Their pathogenesis and significance. Gastroenterology 83(3):704–708, 1982
Ahrens EH Jr, Kunkel HG: The relationship between serum lipids and skin xanthomata in eighteen patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. J Clin Invest 28:1565–1574, 1949
Baruch Y, Brook JR, Eidelman S, Aviram M: Increased concentration of high density lipoprotein in plasma and decreased platelet aggregation in primary biliary cirrhosis. Atherosclerosis 53:151–162, 1984
Aly A, Carlson K, Johansson C, Kirstein P, Rössner S, Wallentin L: Lipoprotein abnormalities in patients with early primary biliary cirrhosis. Eur J Clin Invest 14:156–162, 1984
Jahn CE, Schaefer EJ, Taam LA, Hoofnagle JH, Lindgren FT, Albers JJ, Jones EA, Brewer HB Jr: Lipoprotein abnormalities in primary biliary cirrhosis. Association with hepatic lipase inhibition as well as altered cholesterol esterification. Gastroenterology 89:1266–1278, 1985
Koga S, Miyata Y, Ibayashi H: Plasma lipoproteins and apoproteins in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 5(2):286–292, 1985
Blomhoff JP: High density lipoproteins in cholestasis. Scand J Gastroenterol 9:591–596, 1974
Mc Intyre N, Harry DS, Pearson AJG: The hypercholesterolaemia of obstructive jaundice. Gut 16:379–391, 1975
Agorastos J, Fox C, Harry DS, Mc Intyre N: Lecithin-cholesterol acyl-transferase and lipoprotein abnormalities of obstructive jaundice. Clin Sci Mol Med 54:369–379, 1978
Blomhoff JP, Skrede S, Ritland S: Lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase and plasma proteins in liver disease. Clin Chim Acta 53:197–207, 1974
Danielsson B, Ekman R, Petersson BG: An abnormal high density lipoprotein in cholestatic plasma isolated by zonal ultracentrifugation. FEBS Lett 50(2): 180–184, 1975
Etienne J, Beucler I, Ayrault M, Cloarec M, Polonovski J, Debray J: Abnormal lipoproteins in a case of primary biliary cirrhosis. Biomedicine 29:33–37, 1978
Scheuer PJ: Primary Biliary cirrhosis. Proc R Soc Med 60:1257–1260, 1967
Burstein M, Scholnick HR, Morfin R: Rapid method for the isolation of lipoproteins from human serum by precipitation with polyanions. J Lipid Res 11:583–595, 1970
Wieland H, Seidel D: Eine neue und vereinfachte Methode zum Nachweis des Lp-X, eines cholestase-spezifischen Lipoproteins. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 98:1474–1475, 1973
Neubeck W, Seidel D: Direct method for measuring lipoprotein-X in serum. Clin Chem 21(7):853–856, 1975
Gidez LI, Miller GJ, Burstein M, Slagle S, Eder HA: Separation and quantitation of subclasses of human plasma high density lipoproteins by a simple precipitation procedure. J Lipid Res 23:1206–1223, 1982
Mancini G, Carbonara AO, Heremans JF: Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry 2:235–254, 1965
Allain CC, Poon LS, Chan CSG, Richmond W, Fu PC: Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin Chem 20(4):470–475, 1974
Wahlefeld AW: Triglycerides determination after enzymatic hydrolisis.In Methods of Enzymatic Analysis. HU Bergmeyer (ed). New York, Academic Press, 1976, pp 1831–1835
Zilversmit DB, Davis AK: Microdetermination of plasma phospholipids by trichloracetic acid precipitation. J Lab Clin Med 35:155–160, 1950
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275, 1951
Catapano AL, Jackson RL, Gilliam EB, Gotto AM, Smith LC: Quantification of apo C-II and apo C-III of human very low density lipoproteins by analytical isoelectric focusing. J Lipid Res 19:1047–1052, 1978
Huttunen JK, Ehnholm C, Kekki M, NikkilÄ EA: Postheparin plasma lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase in normal subjects and in patients with hypertriglyceridaemia: Correlations to sex, age and various parameters of triglyceride metabolism. Clin Sci Mol Med 50:249–260, 1976
Guenther WC: Analysis of Variance. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, Prentice-Hall Inc, 1964, p 57
Ritland S, Blomhoff JP, Gjone E: Lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase and lipoprotein-X in liver disease. Clin Chim Acta 49:251–259, 1973
Patsch W, Patsch JR, Kunz F, Sailer S, Braunsteiner H: Studies on the degradation of lipoprotein-X. Eur J Clin Invest 7:523–530, 1977
Ritland S, Stokke KT, Gjone E: Changes in the concentration of lipoprotein-X during incubation of postheparin plasma from patients with familial lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) deficiency. Clin Chim Acta 67:63–69, 1976
Rubiés-Prat J, Ras MR, Frisón JC, Miquel C, Masdeu S, Bacardi R: Effect of heparin on lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase and lipids in cholestasis. Digestion 14:250–255, 1976
Sauar J, Holme R, Blomhoff JP: Triglyceride lipase activity in post heparin plasma lipoproteins in liver disease. Clin Chim Acta 87:327–340, 1978
Jansen H, Hulsmann WC: Heparin-releasable (liver) lipase(s) may play a role in the uptake of cholesterol by steroid-secreting tissues. Trends Biochem Sci 5:265–268, 1980
Jansen H: Inhibition of liver lipasein vivo leads to induction ofde novo cholesterol synthesis in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 131(2):574–578, 1985
Kuusi T, Saarinen P, NikkilÄ EA: Evidence for the role of hepatic endothelial lipase in the metabolism of plasma high density lipoprotein 2 in man. Atherosclerosis 36:589–593, 1980
Jansen H, Van Tol A, Hülsmann WC: On metabolic function of heparin releasable liver lipase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 92(1):53–59, 1980
Van Tol A, Van Gent T, Jansen H: Degradation of high density lipoprotein by heparin-releasable liver lipase. Biochem Biophys Res Com 94(1): 101–108, 1980
Grosser J, Schrecker O, Greten H: Function of hepatic triglyceride lipase in lipoprotein metabolism. J Lipid Res 22:437–442, 1981
Kubo M, Matsuzawa Y, Tajima S, Ishikawa K, Yamamoto A, Tarui S: Apo A-I and apo A-II inhibit hepatic triglyceride lipase from human post-heparin plasma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 100(1):261–266, 1981
Jahn CE, Osborne JC, Schaefer EJ, Brewer HB Jr: Activation of the enzymic activity of hepatic lipase by apolipoprotein A-II. Characterization of a major component of high density lipoprotein as activating componentin vitro. Eur J Biochem 131:25–29, 1983
Patton JS, Carey MC: Inhibition of human pancreatic lipasecolipase activity by mixed bile salt-phospholipid micelles. Am J Physiol 4(4)G328-G336, 1981
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baldo-Enzi, G., Baiocchi, M.R., Grotto, M. et al. Lipoprotein pattern and plasma lipoprotein lipase activities in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. Digest Dis Sci 33, 1201–1207 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01536666
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01536666