Summary
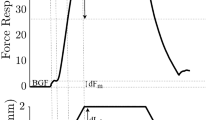
The mechanisms of the clasp-knife reflex were studied in the soleus muscle of an animal model, the decerebrate cat with a dorsal hemisection of the lower thoracic cord. The reflex is shown to be autogenetic, and to depend on muscle length in keeping with previous suggestions. However, the magnitude of the inhibition increases with increasing initial force, and the inhibition is mimicked by gentle manipulation of the muscle and tendon surface. Concurrent muscle afferent recordings showed that the electromyogram (emg) reduction was not a result of a decline in Ia afferent input and was not well related to secondary or tendon organ afferent discharge.
It is now known that many group III and some group IV muscle afferents are also activated by muscle stretch and contraction, and we here report limited stretch sensitivity in four non-spindle group II afferents. Since these fiber groups each include afferents that produce inhibition of extensor motoneurons, it is proposed that the clasp-knife reflex may result from the activation of these slowly conducting afferent fibers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreassen, S.: Interval pattern of single motor units. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Neurophysiology, University of Copenhagen (1977)
Ballif, L., Fulton, J.F., Liddell, E.G.T.: Observations on spinal and decerebrate knee-jerks with special reference to their inhibition by single break-shocks. Proc. Roy. Soc. B.98, 589–607 (1925)
Barker, D., Ip, M.C., Adal, M.N.: A correlation between the receptor population of the cat's soleus muscle and the afferent fibre diameter spectrum of the nerve supplying it. In: Symposium on muscle receptors (ed. Barker, D.), pp. 257–261. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press 1962
Bessou, P., Laporte, Y.: Etude des recepteurs musculaires innervés par les fibres afferentes du groupe III (Fibres myelinisées fines) chez le chat. Arch. Ital. Biol.99, 203–321 (1961)
Brock, L.G., Eccles, J.C., Ryall, W.: Experimental investigations on the afferent fibres in muscle nerves. Proc. R. Soc. B.138, 453–475 (1951)
Brown, M.C., Engberg, I., Matthews, P.B.C.: The relative sensitivity to vibration of muscle receptors in the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)192, 773–800 (1968)
Burke, D., Andrews, C., Ashby, P.: Autogenic effects of static muscle stretch in spastic man. Arch. Neurol.25, 367–372 (1971)
Burke, D., Gillies, J.D., Lance, J.W.: The quadriceps stretch reflex in human spasticity. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat.33, 216–223 (1970)
Burke, D., Knowles, L., Andrews, C., Ashby, P.: Spasticity, decerebrate rigidity and the clasp-knife phenomenon: An experimental study in the cat. Brain95, 31–48 (1972)
Cangiano, A., Lutzemberger, L.: The action of selectively activated group II muscle afferent fibers on extensor motoneurons. Brain Res.41, 475–478 (1972)
Eccles, R.M., Lundberg, A.: Synaptic actions in motoneurones by afferents which may evoke the flexion reflex. Arch. Ital. Biol.97, 199–221 (1959)
Eldred, E., Granit, R., Merton, P.A.: Supraspinal control of the muscle spindles and its significance. J. Physiol. (Lond.),122, 498–523 (1953)
Ellaway, P.H., Trott, J.: Autogenic reflex actions on to gamma motoneurones by stretch of triceps surae in the decerebrated cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)276, 49–66 (1978)
Engberg, I., Lundberg, A., Ryall, R.W.: Reticulospinal inhibition of transmission in reflex pathways. J. Physiol. (Lond.)194, 201–223 (1968)
Franz, M., Mense, S.: Muscle receptors with group IV afferent fibres responding to application of Bradykinin. Brain Res.92, 369–383 (1975)
Fromm, C., Haase, J., Noth, J.: Length-dependent autogenetic inhibition of extensor motoneurones in the decerebrate cat. Pflügers Arch. Ges. Physiol.346, 251–262 (1974)
Fulton, J.F., Pi-Suner, J.: A note concerning the probable function of various afferent end-organs in skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol.83, 554–562 (1928)
Grillner, S.: Is the tonic stretch reflex dependent upon group II excitation? Acta Physiol. Scand.78, 431–432 (1970)
Grillner, S., Udo, M.: Motor unit activity and stiffness of the contracting muscle fibres in the tonic stretch reflex. Acta Physiol. Scand.81, 422–424 (1971)
Herman, R.: Myotatic reflex: clinico-physiological aspects of spasticity and contracture. Brain93, 273–312 (1970)
Holmqvist, B., Lundberg, A.: Differential supraspinal control of synaptic actions evoked by volleys in the flexion reflex afferents in alpha moto-neurons. Acta Physiol. Scand.54, Suppl. 186, 51 (1961)
Houk, J.C., Crago, P.E., Rymer, W.Z.: Functional properties of Golgi tendon organs. In: Segmental motor control in man (ed. Desmedt, J.E.) Progress in Clinical Neurophysiol. Basel: Karger (in press)
Houk, J.C., Henneman, E.: Responses of Golgi tendon organs to active contractions of the soleus muscle of the cat. J. Neurophysiol.30, 466–481 (1967)
Houk, J.C., Singer, J., Hennemann, E.: Adequate stimulus for tendon organs with observations on mechanics of ankle joint. J. Neurophysiol.34, 1051–1065 (1971)
Hunt, C.C.: Relation of function to diameter in afferent fibers of muscle nerves. J. Gen. Physiol.38, 117–131 (1954)
Hunt, C.C., Kuffler, S.W.: Stretch receptor discharges during muscle contractions. J. Physiol. (London)113, 298–315 (1951)
Jansen, J.K.S., Rudjord, T.: On the silent period and Golgi tendon organs of the soleus muscle of the cat. Acta Physiol. Scand.62, 364–379 (1964)
Joyce, G.C., Rack, P.M.H., Westbury, D.R.: The mechanical properties of cat soleus muscle during controlled lengthening and shortening movements. J. Physiol. (Lond.)204, 461–474 (1969)
Kanda, K., Rymer, W.Z.: An estimate of the secondary spindle receptor afferent contribution to the stretch reflex in extensor muscles of the decerebrate cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)264, 63–87 (1977)
Kirkwood, P.A., Sears, T.A.: Monosynaptic excitation of motoneurons from secondary endings of muscle spindles. Nature (Lond.)252, 243–244 (1974)
Kniffki, K.D., Mense, S., Schmidt, R.F.: Mechanisms of muscle pain: a comparison with cutaneous nociception. In: Sensory functions of the skin. Wenner-Gren Symposium, (ed. Zotterman, Y.), Vol. 27, pp. 463–473. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1976
Kuno, M., Perl, E.R.: Alteration of spinal reflexes by interaction with suprasegmental and dorsal root activity. J. Physiol. (Lond.)151, 103–122 (1960)
Laporte, Y., Bessou, P.: Modifications d'excitabilité de motoneurones homonymes provoquées par l'activation physiologique de fibres afferentes d'origine musculaire du Group II. J. Physiol. (Paris)51, 897–908 (1959)
Lloyd, D.P.C.: Reflex action in relation to pattern and peripheral source of afferent stimulation. J. Neurophysiol.6, 111–210 (1943)
Lundberg, A., Malmgren, K., Schomberg, E.D.: Comments on reflex actions evoked by electrical stimulation of group II afferents. Brain Res.122, 551–555 (1977)
Mark, R.F., Coquery, J.M., Paillard, J.: Autogenic reflex effects of slow or steady stretch of the calf muscles in man. Exp. Brain Res.6, 130–145 (1968)
Matthews, B.H.C.: Nerve endings in mammalian muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)78, 1–53 (1933)
Matthews, P.B.C.: The dependence of tension upon extension in the stretch reflex of the soleus muscle of the decerebrate cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)147, 521–546 (1959)
Matthews, P.B.C.: Evidence that the secondary as well as the primary endings of the muscle spindles may be responsible for the tonic stretch reflex of the decerebrate cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)204, 365–393 (1969)
Matthews, P.B.C.: Mammalian muscle receptors and their central actions. London: Arnold 1972
McCouch, G.P., Deering, I.D., Stewart, W.B.: Inhibition of knee jerk from tendon spindles of crureus. J. Neurophysiol.13, 343–350 (1950)
McGrath, G.J., Matthews, P.B.C.: Evidence from the use of vibration during procaine nerve block that the spindle group II fibres contribute excitation to the tonic stretch reflex of the decerebrate cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)235, 371–408 (1973)
Paintal, A.S.: Functional analysis of group III afferent fibres of mammalian muscles. J. Physiol. (Lond.)152, 250–270 (1960)
Paintal, A.S.: Responses and reflex effects of pressure-pain receptors of mammalian muscles. In: Symposium on muscle receptors (ed. Barker, D.), pp. 133–142. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press 1962
Patton, H.D.: Reflex regulation of movement and posture. In: Ruch, T., Patton, H., Woodbury, J., Towe, A.: Neurophysiology. Philadelphia: Saunders 1965
Stacey, M.: Free nerve endings in skeletal muscle of the cat. J. Anat.105, 231–254 (1969)
Stauffer, E.K., Watt, D.G.D., Taylor, A., Reinking, R.M., Stuart, D.G.: Analysis of muscle receptor connections by spike-triggered averaging. 2. Spindle group II afferents. J. Neurophysiol.39, 1393–1402 (1976)
Westbury, D.R.: A study of stretch and vibration reflexes of the cat by intracellular recording from motoneurones. J. Physiol. (Lond.)226, 37–56 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rymer, W.Z., Houk, J.C. & Crago, P.E. Mechanisms of the clasp-knife reflex studied in an animal model. Exp Brain Res 37, 93–113 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01474257
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01474257