Abstract
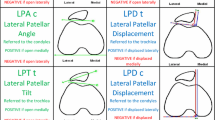
Thirty-eight knees of 26 patients with anterior knee pain (12 bilateral) were included in the study. There were 22 women and 4 men, and their average age was 29 years. Axial computed tomography (CT) examination of both knees were done at 0°, 10°, 20°, 30°, 40° and 60° of flexion with and without muscle contraction. Images were always taken at the mid-patellar level. Patellar tilt angle (PTA), congruence angle (CA) and sulcus angle (SA) were measured at each knee position. Normal values were also obtained from 14 healthy volunteers (28 knees). Thus, the types of patello-femoral incongruence were determined at each knee position: 1, tilt+lateralisation (TL: 12 knees); 2, lateralisation (L: 4 knees); 3, medialisation (M: 5 knees); 4, lateral to medial instability (LM: 1 knee); 5, tilt (T: 1 knee). Fifteen knees were classified as normal. When the groups were analysed separately, in the TL group the T or L component would have been missed in nine cases if the images were taken only at 30° or only in the first 30° of flexion. In the L group two patellae were reduced at 30°. In three knees in the M group, medialisation began at 10°, 20° and 30°. One patella was reduced at 40°. In the LM case, the patella was lateralised at 0°, 10°, 20° and medialised at 30° and 40°. In the T case, the patella was tilted only at 20°, 40° and 60°. This study showed that axial images taken only at 30° will miss important information. Imaging in the first 30° of flexion will not reveal the correct type of instability, either. Serial imaging over a wider range of flexion is necessary for the correct diagnosis. Determination of the type of incongruence at different knee positions is a new concept. With this methodology, the presence of medial and lateral to medial instabilities is verified. Hence, the classification systems including only lateral instability should be questioned.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aglietti P, Insall JN, Cerulli G (1983) Patellar pain and incongruence. Clin Orthop 176: 217–224
Carson WG, James SL, Larson RL, Singer KM, Winternitz WW (1984) Patellofemoral disorders: physical and radiographic evaluation. 2. Radiographic examination. Clin Orthop 185: 178–186
Delgado-Martins H (1979) A study of the position of the patella using computerized tomography. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 61: 443–447
Ficat RP, Hungerford DS (1977) Disorders of the patellofemoral joint. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Fulkerson JP (1982) Awareness of the retinaculum in evaluating patellofemoral pain. Am J Sports Med 10: 147
Fulkerson JP (1992) Radiologic and arthroscopic assessment of the patellofemoral pain patient. American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons. 59th Annual Meeting, Instructional Course Lectures
Hughston JC (1968) Subluxation of the patella. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 50: 1003
Hughston JC, Deese M (1988) Medial subluxation of the patella as a complication of lateral release. Am J Sports Med 16: 383–388
Inoue M, Shino K, Hirose H, Horibe S, Ono K (1988) Subluxation of the patella. Computed tomography analysis of patellofemoral congruence. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 70: 1331–1337
Kujala UM, Österman K, Kvist M, Aalto T, Friberg O (1986) Factors predisposing to patellar chondropathy and patellar apicitis in athletes. Int Orthop 10: 195–200
Kujala UM, Österman K, Karmano M, Komu M, Schlenzka D (1989) Patellar motion analyzed by magnetic resonance imaging. Acta Orthop Scand 60: 13–16
Larson RL (1979) Subluxation-dislocation of the patella. In: Kennedy JC (ed) The injured adolescent knee. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 161–204
Laurin CA, Dussault R, Levesque HP (1979) The tangential X-ray investigation of the patellofemoral joint: X-ray technique, diagnostic criteria and their interpretation. Clin Orthop 144: 16–29
MacNab L (1952) Recurrent dislocation of the patella. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 34: 957–976
Malghem J, Maldague B (1989) 30 degree axial radiographs with lateral rotation of the leg. Radiology 170: 566–567
Martinez S, Korobkin M, Hedlung LW, Goldner JL (1983) Computed tomography of the normal patellofemoral joint. Invest Radiol 18: 249–253
Merchant AC, Mercer RL, Jacobsen RH, Cool CR (1974) Roentgenographic analysis of patellofemoral congruence. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 56: 1391–1396
Mollar BN, Krebs B, Jurik AG (1986) Patellofemoral incongruence in chondromalacia and instability of the patella. Acta Orthop Scand 57: 232–234
Newberg AH, Seligson D (1980) The patellofemoral joint: 30, 60, and 90 degree views. Radiology 137: 57–61
Schutzer SF, Ramsby GR, Fulkerson JP (1986) Computed tomographic classification of patellofemoral pain patients. Orthop Clin North Am 17: 235–248
Schutzer SF, Ramsby GR, Fulkerson JP (1986) The evaluation of patellofemoral pain using computerized tomography. A preliminary study. Clin Orthop 204: 286–293
Shellock FG, Mink IH, Fox JM (1988) Patellofemoral joint: kinematic MR imaging to assess tracking abnormalities. Radiology 168: 551–553
Shellock FG, Mink JH, Deutsch AL, Fox JM (1989) Patellar tracking abnormalities: clinical experience with kinematic MR imaging in 130 patients. Radiology 172: 799–804
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pinar, H., Akseki, D., Karaoğlan, O. et al. Kinematic and dynamic axial computed tomography of the patello-femoral joint in patients with anterior knee pain. Knee Surg, Sports traumatol, Arthroscopy 2, 170–173 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01467920
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01467920



