Abstract
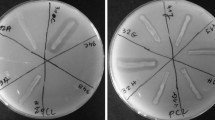
To assess the capacity of the natural environment for degrading plastics, the populations of poly(β-hydroxybutyrate)(PHB)-and poly(ε-caprolactone)(PCL)-degrading aerobic microorganisms and their ratios to the total number of microorganisms in soil samples were estimated by the plate count method with agar medium containing emulsified PHB or PCL. The numbers of the degrading microorganisms were determined by counting colonies that formed clear zones on the plate. It was found that PHB- and PCL-degrading (depolymerizing) microorganisms are distributed over many kinds of material, including landfill leachate, compost, sewage sludge, forest soil, farm soil, paddy soil, weed field soil, roadside sand, and pond sediment. Of total colony counts, the percentages of PHB and PCL degrading microorganisms were 0.2–11.4 and 0.8–11.0%, respectively. The results suggest that many kinds of degrading microorganisms are present in each environment and that specific consortia differing in biodegradation capacity are constructed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. A. Chowdhury,Arch. Mikrobiol. 47 167–200 (1963).
F. P. Delafield, M. Doudoroff, N. J. Palleroni, C. J. Lusty, and R. Contopoulos,J. Bacteriol. 90(5), 1455–1466 (1965).
C. J. Lusty and M. Doudoroff,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 56 960–965 (1966).
T. Tanio, T. Fukui, Y. Shirakura, T. Saito, K. Tomita, T. Kaiho, and S. Masamune,Eur. J. Biochem. 124 71–77 (1982).
P. H. Janssen and C. G. Harfoot,Arch. Microbiol. 154 253–259 (1990).
H. Tanaka, K. Tonomura, and A. Kamibayashi,Nippon Nougeikagaku Kaishi 50(9), 431–436 (1976).
M. Doudoroff and N. J. Palleroni, inBergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, 8th ed., R. E. Buchanan and N. E. Gibbons, eds. (Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, 1974), pp. 227–229.
Y. Tokiwa, T. Ando, and T. Suzuki,J. Ferment. Technol. 54(8), 603–608 (1976).
P. Dave, M. Parikh, M. Reeve, R. A. Gross, and S. P. McCarthy,Polym. Preprints Am. Chem. Soc. Div. Polym. Mater. 63 726 (1990).
K. Mukai, Y. Doi, and K. Yamada,Polym. Preprints Jap. 41(6), 2180–2182 (1992).
D. Jendrossek, I. Knoke, R. B. Habibian, A. Steinbuchel, and H. G. Schlegel,J. Environ. Polym. Degrad. 1(1), 53–63 (1993).
S. Ishikuri and T. Hattori,Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 33(3), 355–362 (1987).
M. I. Timonin,Can. J. Res. C. 13, 32–46 (1935).
M. Alexander,Introduction to Soil Microbiology (John Wiley, New York, 1961), p. 28.
S. C. Vandecaveye and H. Katznelson,Soil. Sci. 46 57–74 (1938).
S. Ishizawa and K. Toyoda,Bull. Natl. Inst. Agr. Sci. Ser. B 14, 203–284 (1964).
K. Morikawa and M. Otsuka,Bull. Jap. Soc. Microbial Ecol. 6(2), 87–94 (1991).
T. Nakamura and T. Yoshikura,Bull. Jap. Soc. Microbial Ecol. 5(1), 13–20 (1989).
M. Nasu, N. Yamaguchi, K. Makino, Y. Takubo, and M. Kondo,Bull. Jap. Soc. Microbial Ecol. 7(1), 1–7 (1991).
D. F. Gilmore, R. C. Fuller, and R. Lenz, inDegradable Materials, S. A. Barenberg, J. L. Brash, R. Narayan, and A. E. Redpath (eds.) (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1990), pp. 481–514.
S. Akita, Y. Einaga, Y. Miyake, and H. Fujita,Macromolecules 9(5), 774–780 (1976).
J. Shishiyama, F. Araki, and S. Akai,Plant Cell Physiol. 11 323–334 (1970).
P. J. Holloway,Chem. Phys. Lipids 9 158–170 (1972).
P. J. Holloway,Chem. Phys. Lipids 9 171–179 (1972).
P. J. Holloway and A. H. B. Deas,Phytochemistry 12 1721–1735 (1973).
P. J. Holloway,Phytochemistry 12 2913–2920 (1973).
P. E. Kolattukudy,Science 208 990–1000 (1980).
A. Brown and P. E. Kolattukudy,J. Agr. Food Chem. 26(5), 1263–1266 (1978).
A. Brown and P. E. Kolattukudy,Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 190(1), 17–26 (1978).
J. Shishiyama, F. Araki, and S. Akai,Plant Cell Physiol. 11 937–945 (1970).
R. E. Purdy and P. E. Kolattukudy,Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 159 61–69 (1973).
R. E. Purdy and P. E. Kolattukudy,Biochemistry 14(13), 2824–2831 (1975).
R. E. Purdy and P. E. Kolattukudy,Biochemistry 14(13), 2832–2840 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishida, H., Tokiwa, Y. Distribution of poly(β-hydroxybutyrate) and poly(ε-caprolactone)aerobic degrading microorganisms in different environments. J Environ Polym Degr 1, 227–233 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01458031
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01458031