Summary
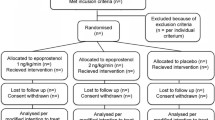
A prospective randomized double blind study was conducted in 70 patients suffering from subarachnoid haemorrhage, due to aneurysm rupture, to determine if the use of nimodipine reduces the severity of ischaemic deficits secondary to vasospasm.
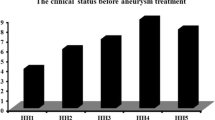
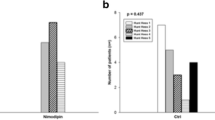
At the end of the study, two patients had severe deficit or died in the treated group, while 10 had a bad outcome in the placebo group. Angiographic vasospasm was not significantly different in its frequency or its severity between the two groups. However, the association of extensive and diffuse vasospasm was less frequent in the nimodipine group.
This study confims the effectiveness of Nimodipine in reducing the occurrence of neurological deficit due to vasospasm, even if this action is not observed in all cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen GS, Gross CJ, Henderson LM, Chou SN (1976) Cerebral arterial spasm, 4. In vitro effects of temperature serotonin analogues, large non-physiological concentration of serotonin and extra cellular calcium and magnesium on serotonin-induced contractions of the canine basilar artery. J Neurosurg 44: 585–593
Allen GS, Bahr AL (1979) Cerebral arterial spasm, 10. Reverse of acute and chronic spasm in dogs with orally administered nifedipine. Neurosurgery 4: 43–47
Allen GS, Ahn H, Preziosi T et al (1983) Cerebral arterial spasm. A controlled trial of nimodipine in patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage. New England Med 308: 619–624
Auer LM (1982) Pial arterial and venous reaction to intravenous infusion of nimodipine in cats. J Neurol Sci 26: 213–218
Auer LM, Ito H, Suzuki H, Ohta (1982) Prevention of symptomatic vasospasm by topically applied nimodipine. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 63: 297–302
Auer LM, Oberbauer RN, Schalk HU (1983) Human pial vascular reactions to intravenous nimodipine infusion during EC-IC bypass surgery. Stroke 14: 210–213
Auer LM (1984) Acute operation and preventive nimodipine improve outcome in patients with ruptured cerebral aneurysms. Neurosurgery 15: 57–66
Espinosa F, Weir B, Overton T, Castor W, Grace M, Boisvert P (1984) A randomized placebo controlled trial of nimodipine after subarachnoid haemorrhage in monkeys. Part I: clinical and radiological findings. J Neurosurg 60: 1167–1175
Fischer CM, Kistler JP, Davis JM (1983) Relation of cerebral vasospasm to subarachnoid haemorrhage visualized by computerized tomographic scanning Neurosurgery 6: 1–8
Kazda S, Hoffmeister F, Garthoff B, Towart R (1979) Prevention or the post ischaemic impaired reperfusion of the brain by nimodipine. Acta Neurol Scand [Suppl] 72: 358–359
Kazda S, Towart R (1982) Nimodipine: a new calcium antagonist drug with a preferential cerebro-vascular action. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 63: 259–265
Ljunggren B, Brand T, Sundbarg G (1982) Early management of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Neurosurgery 11: 412–418
Ljunggren B, Brant L, Saveland H (1984) Outcome in 60 consecutive patients treated with early aneurysm operation and intravenous nimodipine. J Neurosurg 61: 864–873
Nosko M, Weir B, Krueger C (1985) Nimodipine and chronic vasospasm in monkeys: Part I: clinical and radiological findings. Neurosurgery 16: 129–136
Steen PA, Newberg LA, Milde JH (1983) Nimodipine improves cerebral blood flow and neurologic recovery after complete cerebral ischaemia in the dog. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 3: 38–43
Vermeulen M, Lindsay W, Murray D (1984) Antifibrinolytic treatment in subarachnoid haemorrhage. New England J Med 311: 432–437
Voldby B, Buhl OF, Petersen S (1981) Modification of cerebral vasospasm by intraventricular administration of a calcium antagonist in the dog. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 59: 287
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Philippon, J., Grob, R., Dagreou, F. et al. Prevention of vasospasm in subarachnoid haemorrhage. A controlled study with nimodipine. Acta neurochir 82, 110–114 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01456369
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01456369