Summary
Investigations were undertaken to evaluate which uraemic solutes decrease drug protein binding. This was done by performing HPLC-fractionation of uraemic biological fluids and studying the effect of addition of a lyophilisate of each fraction to normal plasma containing standard quantities of radiolabelled drugs.
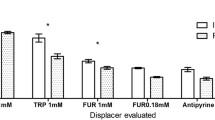
From a first study, based only on fractionation of uraemic ultrafiltrate with an HPLC-gradient mainly aimed at elution of hydrophilic compounds, hippuric acid appeared to be a major protein binding inhibitor for theophylline and phenytoin. The problem with this approach was that it did not include the compounds with the most substantial protein binding. Therefore, studies were planned to fractionate deproteinized uraemic sera, but first it was necessary to define which deproteinisation methods gave the highest yields of protein bound ligand.
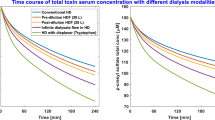
Heat denaturation was found to be one of the most effective deproteinisation methods. When a lyophilisate of uraemic serum, deproteinised by this method, was added to normal plasma, a higher capacity to displace theophylline from protein binding sites was found compared to the effect of an identical volume of an ultrafiltrate of the same samples. Fractionation of the deproteinised sample by HPLC revealed a larger number of fractions able to inhibit drug protein binding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lindup WE, Bishop KA, Collier R (1986) Drug binding defect of uraemic plasma: contribution of endogenous binding inhibitors. In: Tillement JP, Lindenlaub E (eds) Protein binding and drug transport. Schattauer, Stuttgart, pp 397–414
Farrell PC, Grib NL, Fry DL, Popovich RP, Broviac JW, Babb AL (1972) A comparison of in vitro and in vivo solute-protein binding interactions in normal and uremic subjects. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs 18: 268–276
Depner TA, Sanaka T, Stanfel LA (1984) Suppression of paraaminohippurate transport in the isolated perfused kidney by an inhibitor of protein binding in uremia. Am J Kidney Dis 3: 280–286
Bourke E, Frindt G, Preuss H, Rose E, Weksler M, Schreiner GE (1970) Studies with uremic serum on the renal transport of hippurates and tetraethylammonium in the rabbit and the rat: effects of oral neomycin. Clin Sci 38: 41–48
Boumendil-Podevin EF, Podevin RE, Richet G (1975) Uricosuric agents in uremic sera. Identification of indoxyl sulfate and hippuric acid. J Clin Invest 55: 1142–1152
Porter RD, Cathcart-Rake WF, Wan SH, Whittier FC, Grantham JJ (1975) Secretory activity and aryl acid content of serum, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid in normal and uremic man. J Lab Clin Med 85: 723–733
Cathcart-Rake W, Porter R, Whittier F, Stein P, Carey M, Grantham J (1975) Effect of diet on sérum accumulation and renal excretion of aryl acids and secretory activity in normal and uremic man. Am J Clin Nutrition 28: 1110–1115
Gulyassy PF, Bottini AT, Stanfel LA, Jarrard EA, Depner TA (1986) Isolation and chemical identification of inhibitors of plasma ligand binding. Kidney Int 30: 391–398
Mac Namara PJ, Lalka D, Gibaldi M (1981) Endogenous accumulation products and serum protein binding in uremia. J Lab Clin Med 98: 730–740
Hsu CH, Patel SR, Young EW, Vanholder R (1991) Effects of purine derivatives on calcitriol metabolism in rats. Am J Physiol 260: F596-F601
Hsu CH, Vanholder R, Patel S, De Smet R, Sandra P, Ringoir SMG (1991) Subfractions in uremic plasma ultrafiltrate inhibit calcitriol metabolism. Kidney Int 40: 868–873
Vanholder R, Van Landschoot N, De Smet R, Schoots A, Ringoir S (1988) Drug protein binding in chronic renal failure: evaluation of nine drugs. Kidney Int 33: 996–1004
Arendt RM, Greenblatt DJ (1984) Liquid chromatographic retention ofβ-adrenoceptor antagonists: an index of lipid solubility. J Pharm Pharmacol 36: 400–401
Ganansia J, Bianchetti G, Thénot JP (1987) Correlation between reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography and plasma protein binding. J Chromatogr 421: 83–90
Vanholder R, Hoefliger N, De Smet R, Ringoir S. Extraction of protein bound ligands from azotemic sera: comparison of 12 deproteinization methods. Kidney Int (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vanholder, R., De Smet, R. & Ringoir, S. Factors influencing drug protein binding in patients with end stage renal failure. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 44 (Suppl 1), S17–S21 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01428386
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01428386