Abstract
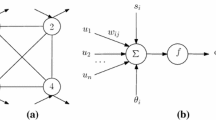
In this paper we consider two kinds of neural networks in which the activation function of each neuron is a multiple valued, piecewised-constant function. The main advantages of the proposed models are that they can store patterns with different grey levels, and that they can store binary patterns with much fewer neurons than the existing models. We prove theoretically the convergence property of the proposed models. Different synthesis methods are developed to guarantee the storage of desired patterns as asymptotic equilibria. Simulation results confirm the effectiveness of the new models.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wong JW. Recognition of general patterns using neural networks. Bio Cybern 1988; 58(6): 361–372
Michel A, Farrel J. Associative memories via artificial neural networks. IEEE Control Syst Mag April 1990; 6–17
Atiya A, Abu-Mostafa YS. An analog feedback associative memory. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 1993; 4: 117–126
Si J, Michel AN. Analysis and synthesis of discrete-time neural networks with multilevel threshold functions. Proc IEEE Int Symposium Circuits and Systems. Singapore, June 1991; 1461–1464
Kohring GA. On the Q-state neuron problem in attractor neural networks. Neural Networks 1993; 6: 573–381
Mertens S, Kohler HM, Bos S. Learning grey-toned patterns in neural networks. J Physics A 1991; 24: 4941–4952
Bijjani R, Das P. An M-ary neural network model. Neural Computation 1990; 2: 536–551
Rieger H. Storing an extensive number of grey-toned patterns in a neural network using multistate neurons. J Physics A 1990; 23: L1273-L1279
Chiueh TD, Goodman RM. Recurrent correlation associative memories. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 1991; 2: 275–284
Chiueh T-D, Tsai H-K. Multivalued associative memories based on recurrent networks. IEEE Trans Neural Networks. March 1993; 4(2): 364–366
Xu Zb, Leung Y, He X-w. Asymmetric bidirectional associative memories. IEEE Trans SMC. October 1994; 24(10): 1558–1564
He XW, Kwong CP, Xu ZB. The competitive associative memory for non-orthogonal patterns. IEEE Trans Neural Networks (to appear)
Chiueh T-D, Tsai H-K. Multivalued associative memories based on recurrent networks. IEEE Trans Neural Networks. March 1993; 4(2): 364–366
Hopfield JJ. Neural networks and physical systems with convergent collective computational properties. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 1982; 79: 2554–2558
Chiueh TD, Goodman RM. Recurrent correlation associative memories. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 1991; 2: 275–284
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z.Y., Kwong, C.P. & Xu, Z.B. Multiple-valued feedback and recurrent correlation neural networks. Neural Comput & Applic 3, 242–250 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01414649
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01414649