Summary
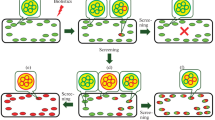
Polyethylene glycol can be used to induce DNA uptake into plant protoplasts. Procedures for isolation, culture and transformation ofN. tabacum protoplasts are described and can be adapted for other dicot and monocot species. Criteria for proof of transformation are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah, R.; Cocking, E. C.; Thompson, J. A. Efficient plant regeneration from rice protoplasts through somatic embryogenesis. Bio/Technology 4:1087–1090; 1986.
Balazs, E.; Bonneville, J. M. Chloramphenicol acetyl transferase inBrassica spp. Plant Sci. 50:65–68; 1987.
Carswell, G. K.; Johnson, C. M.; Shillito, R. D., et al. Acetylsalicylic acid promotes colony formation from protoplasts of elite inbred maize (Zea mays L.). Plant Cell Rep. 8:282–284; 1989.
Chen, D. F.; Tassie, A.; Dale, P. J., et al. Protoplast culture and DNA uptake inEchinocloa. In: Puite, K. J., et al., eds. Progress in plant protoplast research. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academy Press; 1988:369–370.
Chupeau, M.; Bellini, C.; Guerche, P., et al. Transgenic plants of lettuce (Lactuca sativa) obtained through electroporation of protoplasts. Bio/Technology 7:503–507; 1989.
Czernilofsky, A. P.; Hain, R.; Herrera-Estrella, L., et al. Fate of selectable marker DNA integrated into the genome ofNicotiana tabacum. DNA 5:101–113; 1986.
Constabel, F. Isolation and culture of plant protoplasts. In: Gamborg, O. L.; Wetter, L. R., eds. Plant tissue culture methods. Saskatoon: National Research Council of Canada; 1975:11–22.
Dalton, S. J. Plant regeneration from cell suspension protoplasts ofFestuca Arundinacea Shreb;Lolium Perenne L. andL. Multiflorum Lam. In: Puite, K. J., et al., eds. Progress in plant protoplast research. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academy Press; 1988:49–52.
Dellaporta, S. L.; Wood, J.; Hicks, J. B. A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant. Mol. Biol. 1:19–21; 1983.
Fromm, M.; Taylor L. P.; Walbot V. Expression of genes transferred into monocot and dicot plant cells by electroporation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:5824–5828; 1985.
Hain, R.; Stabel, P.; Czernilofsky, A. P., et al. Uptake, integration, expression and genetic transmission of a selectable chimeric gene by plant protoplasts. Mol. Gen. Genet. 199:161–168; 1985.
Hauptmann, R. M.; Vasil, V.; Ozias-Akins, P., et al. Evaluation of selectable markers for obtaining stable transformants in the Gramineae. Plant Physiol. 86:602–606; 1988.
Hille, J.; Verheggen, F.; Roelvink, P., et al. Bleomycin resistance: a new dominant selectable marker for plant cell transformation. Plant. Mol. Biol. 7:171–176; 1986.
Horn, M. E.; Shillito, R. D.; Conger, B. V., et al. Transgenic plants of orchardgrass (Dactylis glomerata L.) from protoplasts. Plant Cell Rep. 7:469–472; 1988.
Jefferson, R. A.; Kavanagh, T. A.; Bevan, M. W. GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907; 1987.
Junker, B.; Zimny, J.; Luhrs, R., et al. Transient expression of chimeric genes in dividing and non-dividing cereal protoplasts after PEG-induced DNA uptake. Plant Cell Rep. 6:329–332; 1987.
Kao, K. N.; Michayluk, M. R. Nutrient requirements for growth ofVicia hajastana cells and protoplasts at very low population density in liquid media. Planta 126:105–110; 1975.
Krens, F. A.; Molendijk, L.; Wullems, G. J., et al. In vitro transformation of plant protoplasts with Ti-plasmid DNA. Nature 296:72–74; 1982.
Linsmaier, E. M.; Skoog, F. Organic growth factor requirements of tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 18:100–127; 1965.
Lorz, H.; Baker, B.; Schell, J. Gene transfer to cereal cells mediated by protoplast transformation. Mol. Gen. Genet. 199:178–182; 1985.
Ludwig, S. R.; Somers, D. A.; Petersen, W. L., et al. High frequency callus formation from maize protoplasts. Theor. Appl. Genet. 71:344–350; 1985.
Maas, C.; Werr, W. Mechanism and optimized conditions for PEG mediated DNA transfection into plant protoplasts. Plant Cell Rep. 8:148–151; 1989.
Maniatis, T.; Fritsch, E. F.; Sambrook, J. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 1982.
Nagy, J. I.; Maliga P. Callus induction and plant regeneration from mesophyll protoplasts ofN. sylvestris. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 78:453–455; 1976.
Negrutiu, I.; Shillito, R. D.; Potrykus, I., et al. Hybrid genes in the analysis of transformation conditions. Plant. Mol. Biol. 8:363–373; 1987.
Ozias-Akins, P.; Lörz, H. Progress and limitations in the culture of cereal protoplasts. Trends Biotech. 2:119–123; 1984.
Paszkowski, J.; Shillito, R. D.; Saul, M., et al. Direct gene transfer to plants. EMBO J 3:2717–2722; 1984.
Perani, L.; Radke, S.; Wilke-Douglas, M., et al. Gene transfer methods for crop improvement: introduction of foreign DNA into plants. Physiol. Plant. 68:566–570; 1986.
Pieterse, C.; Koornneef, M. Optimization of direct gene transfer in tomato. In: Puite, K. J., et al., eds. Progress in plant protoplast research. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academy Press; 1988:357–358.
Potrykus, I.; Paszkowski, J.; Saul, M. W., et al. Molecular and general genetics of a hybrid foreign gene introduced into tobacco by direct gene transfer. Mol. Gen. Genet. 199:169–171; 1985.
Potrykus, I.; Saul, M. W.; Petruska, J., et al. Direct gene transfer to cells of a graminaceous monocot. Mol. Gen. Genet. 199:183–188; 1985.
Power, J. B.; Chapman, J. V. Isolation, culture and genetic manipulation of plant protoplasts. In: Dixon, R. A., ed. Plant cell culture. Washington, DC: IRL Press; 1985:37–67.
Prioli, L. M.; Sondahl, M. R. Plant regeneration and recovery of fertile plants from protoplasts of maize (Zea mays L.) Bio/Technology 7:589–595; 1989.
Smith, J. A.; Green, C. E.; Gengenbach, B. G. Feeder layer support of low density populations ofZea mays L. suspension cells. Plant Sci. Lett. 36:167–172; 1984.
Reiss, B.; Sprengel, R.; Will, H., et al. A new sensitive method of qualitative and quantitive assay of neomycin phosphotransferase in crude cell extracts. Gene 30:211–218; 1984.
Rhodes, C. A., Pierce, D. A.; Mettler, I. J., et al. Genetically transformed maize plants through protoplasts. Science 240:204–207; 1988.
Saiki, R. K.; Gelfand, D. H.; Stoffel, S., et al. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 239:487–492; 1988.
Schocher, R. J.; Shillito, R. D.; Saul, M. W., et al. Co-transformation of unlinked foreign genes into plants by direct gene transfer. Bio/Technology 4:1093–1096; 1986.
Schreier, P. H.; Seftor, E. A.; Schell, J., et al. The use of nuclear-encoded sequences to direct the light-regulated synthesis and transport of a foreign protein into plant chloroplasts. EMBO J 4:25–32; 1985.
Shillito, R. D.; Paszkowski, J.; Potrykus, I. Agarose plating and a bead-type culture technique enable and stimulate development of protoplast-derived colonies in a number of plant species. Plant Cell Rep. 2:244–247; 1983.
Shillito, R. D.; Saul, M. W.; Paszkowski, J., et al. High efficiency direct gene transfer to plants. Bio/Technology 3:1099–1103; 1985.
Shillito, R. D.; Saul, M. W. Protoplast isolation and transformation. In: Shaw, C. H., ed. Plant molecular biology. Oxford, England: IRL Press; 1988:161–186.
Shillito, R. D.; Carswell, G. K.; Johnson, C. M., et al. Regeneration of fertile plants from protoplasts of elite inbred maize. Bio/Technology 7:581–587; 1989.
Shillito, R. D. The fate of DNA introduced into plants. In: Weir, R. S., et al. Proceedings of the 2nd international symposium of quantitative genetics. Raleigh, NC: Sinauer Assoc., Sunderland, MA; 1987.
Uchimaya, H.; Hirochika, H.; Hasimoto, H., et al. Co-expression and inheritance of foreign genes in transformants obtained by direct DNA transformation of tobacco protoplasts. Mol. Gen. Genet. 205:1–8; 1986.
Uchimiya, H.; Fushimi, T.; Hashimoto, H., et al. Expression of a foreign gene in callus derived from DNA-treated protoplasts of rice (Oryza sativa L.) Mol. Gen. Genet. 204:204–207; 1986.
Wang, G. Y.; Hsia, C. A. Mature plant regeneration from cultivated protoplasts of rice (Oryza sativa). In: Puite, K. J., et al., eds. Progress in plant protoplast research. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academy Press; 1988:55–56.
Werr, W.; Lörz, H. Transient gene expression in a Gramineae cell line. Mol. Gen. Genet. 202:471–475; 1986.
Wilson, S. M.; Thorpe, T. A.; Moloney, M. M. PEG-mediated expression of GUS and CAT genes in protoplasts from embryogenic suspension cultures ofPicea glauca. Plant Cell Rep. 7:704–707; 1989.
Zhang, W.; Wu, R. Efficient regeneration of transgenic plants from rice protoplasts and correctly regulated expression of the foreign gene in the plants. Theor. Appl. Genet. 76:835–840; 1988.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnson, C.M., Carswell, G.K. & Shillito, R.D. Direct gene transfer via polyethylene glycol. Journal of Tissue Culture Methods 12, 127–133 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01404438
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01404438