Summary
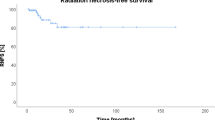
Late radiation necroses constitute a hazard in low dose rate interstitial irradiation for inoperable gliomas. An incidence of 40% (8/20 patients) was found after permanent implantation of Iodine-125 seeds. This finding may even underestimate the real frequency, because follow-up of unaffected patients was shorter than in patients with radiation necrosis. The necrotic reactions caused a transient mass effect, which lead to a significant deterioration of performance scores. Further manifestations of late delayed radiation damage were observed in two patients.
The occurrence of radiation necrosis was correlated with total radiation dose, amount of implanted radioactivity, and with velocity of tumour shrinkage. A mechanism underlying the development of radiation necrosis is proposed: A rapid shrinkage of tumour after interstitial Iodine-125 implantation may cause a significant irradiation of surrounding brain tissue, which was initially lying outside the target volume. Since most patients affected by radiation necrosis were children or adolescents, the risk of radiation damage should be minimized. This could probably be achieved either by reduction of irradiation dose, or by using temporary implants of Iodine-125.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauer B, Schlegel W, Scharfenberg H, Sturm V, Lorenz WJ (1984) Computerized optimization of treatment planning in the brachytherapy of brain tumours. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on the Use of Computers in Radiation Therapy EE, pp 395–398
Bernstein M, Gutin PH (1981) Interstitial irradiation of brain tumors: a review. Neurosurgery 9 (6): 741–750
Fike JR, Sheline GE, Cann CE, Davis RL (1984) Radiation necrosis. Prog Exp Tumor Res 28: 136–151
Findlay PA, Wright DC, Rosenow U, Harrington FS, Miller RW (1985) Iodine-125 interstitial brachytherapy for primary malignant brain tumors: Technical aspects of treatment planning and implantation methods. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 11: 2021–2026
Groothius DR, Wright DC, Ostertag CB (1987) The effect of 125-I interstitial radiotherapy on blood-brain barrier function in normal canine brain. J Neurosurg 67: 895–902 (1987)
Gutin PH, Bernstein M (1984) Stereotactic interstitial brachytherapy for malignant brain tumors. Prog Exp Tumor Res 28: 166–182
Gutin PH, Leibel SA (1985) Stereotaxic interstitial irradiation of malignant brain tumors. Neurol Clin 3 (4): 883–893
Gutin PH, Leibel SA, Wara MW, Choucair A, Levin VA, Philips TL, Silver P, Da Silva V, Edwards MSB, Davis RL, Weaver KA, Lamb S (1987) Recurrent malignant gliomas: survival following interstitial brachytherapy with high-activity iodine-125 sources. J Neurosurg 67: 864–873
Hohwieler ML, Lo TMC, Silverman ML, Freidberg SR (1986) Brain necrosis after radiotherapy for primary intracerebral tumor. Neurosurgery 18 (1): 67–72 (1986)
Kjellberg RN (1979) Isoeffective dose parameters for brain necrosis in relation to proton radiosurgical dosimetry. In: Szikla G (ed) Stereotactic cerebral irradiation. INSERM Symposium No. 12. Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam New York, pp 157–166
Leibel SA, Sheline GE (1987) Radiation therapy for neoplasms of the brain. J Neurosurg 66: 1–22
Marks JE, Wong J (1985) The risk of cerebral radionecrosis in relation to dose, time and fractionation. A follow-up study. Prog Exp Tumor Res 29: 210–218
Ostertag CB (1987) Oral communication
Safdari GhH, Fuentes J-M, Dubois J-B, Alirezai M, Castan P, Vlahovitch B (1985) Radiation necrosis of the brain: Time of onset and incidence related to Neuroradiology 27: 44–47
Schlegel W, Scharfenberg H, Doll J, Pastyr O, Sturm V, Netzeband G, Lorenz WJ (1982) CT-Images as the basis of operation planning in stereotactical neurosurgery. Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Medical Imaging and Image Interpretation ISMIII (1982)
Schmitt HP, Wowra B, Sturm V (1988) Diagnostic value of the Stereotactic approach to focal lesions in the deep brain of children and adolescents. Brain Dev 10: 305–311
Sheline GE (1986) Normal tissue tolerance and radiation therapy of gliomas of the adult brain. In: Bleehen NM (ed) Tumours of the brain. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 141–160
Sturm V, Pastyr O, Schlegel W, Scharfenberg H, Zabel H-J, Netzeband G, Schabbert S, Berberich W (1983) Stereotactic computer tomography with a modified Riechert-Mundinger device as the basis for integrated Stereotactic neuroradiological investigations. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 68: 11–17
Wigg DR, Koschel K, Hodgson GS (1981) Tolerance of the mature human central nervous system to photon irradiation. Br J Radiol 54: 787–798
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study results from a cooperation between the Clinic of Neurosurgery, University of Heidelberg, FRG (Professor Dr. St. Kunze) and the Institute of Nuclear Medicine, German Cancer Research Centre, Heidelberg, FRG (Professor Dr. W. J. Lorenz). The work was supported by the Tumour Centre Heidelberg/Mannheim [Project of Neurooncology (Professor Dr. V. Sturm)].
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wowra, B., Schmitt, H.P. & Sturm, V. Incidence of late radiation necrosis with transient mass effect after interstitial low dose rate radiotherapy for cerebral gliomas. Acta neurochir 99, 104–108 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01402316
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01402316