Summary
Bacterial abscesses involving the spinal canal are associated with a high morbidity and mortality. Most frequently, these lesions are found in the epidural, rarely in the subdural space. In this report, our clinical material consists of a series of 16 patients treated during the last seven years.
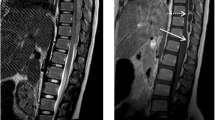
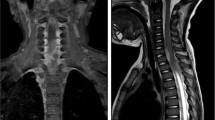
The clinical presentation included local neurological signs (back pain, para-/tetraparesis, bladder dysfunction), disturbances of consciousness (ranging from drowsiness to deep coma) and general inflammatory signs (meningism, fever). All patients presented with risk factors (septic foci, chronic diseases, and iatrogenic causes). Laboratory investigations revealed typically pathological blood sedimentation rate, leucocytosis and CSF-pleocytosis. Radiologically, the diagnosis was confirmed by myelography, CT and preferably MRI. The abscesses were located epidurally in 14 and subdurally in 2 cases. The surgical treatment included laminectomy, or multiple flavectomies in extensive lesions. Drainage systems (either simple silicon outflow drains or suction-/irrigation systems) were installed in all cases, as well as antibiotic treatment.
Results of treatment: Following an observation period of 0,5–6 years, we found complete recovery in six (38%) cases, six (38%) others were mildly disabled and four (25%) patients died.
Focussing on the results of the two different drainage systems, we found a statistically significant superiority of the inflow-/outflow system.
Complications included mandatory re-exploration, post-inflammatory hydrocephalus, syringomyelia, spinal instability, surgical treatment of peripheral septic foci and therapy resistant septicaemia.
In conclusion, we propose that spinal epi-or subdural abscesses require surgical evacuation, using a suction-/irrigation drainage system, as well as antibiotic and intensive care treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramovitz JN, Batson RA, Yablon JS (1986) Vertebral osteomyelitis, the surgical management of neurologic complications. Spine 11: 418–420
Aitken RJ, Wright JP, Bok A, Elliot M (1986) Crohn's disease precipitating a spinal extradural abscess and paraplegia. Br J Surg 73: 1004–1005
Albers (1833) Die Entzündung der harten Haut des Rückenmarkes, Perimeningitis spinalis. Journal für Chirurgie und Augenheilkunde 19: 347
Angtuaco EJC, McConnell JR, Chadduck WM Flanigan St (1987) MR-Imaging of spinal epidural sepsis. AJNR 8: 879–883
Babu R, Jafar JJ, Huang PP, Budzilovich GN, Ransohoff J (1992) Intramedullary abscess associated with a spinal cord ependymoma: case report. Neurosurgery 30 (1): 121–124
Baker AS, Ojemann RG, Morton MD, Schwartz N, Richardson EP (1975) Spinal epidural abscess. N Engl J Med 293 (10): 463–468
Bartels RH, Rob de Jong T, Grotenhuis JA (1992) Spinal subdural abscess. J Neurosurg 76: 307–311
Bergamashi G (1820) Sulla mielitide stenica e sul tetano loro identia. Thesis, Pavia.
DelCurling O. Jr., Gower DJ, McWhorter JM (1990) Changing concepts in spinal epidural abscess: a report of 29 cases. Neurosurgery 27: 185–192
Caplan LR, Norohna AB, Amico LL (1990) Syringomyelia and arachnoiditis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 53: 106–113
Dandy W (1926) Abscesses and inflammatory tumors in the spinal epidural space (so-called pachymeningitis externa). Arch Surg 13: 477–494
Dei-Anang K, Hase U, Schürmann K (1990) Epidural spinal abscesses. Neurosurg Rev 13: 285–288
Delorme (1892) (cited by Schmalz)
Dillon WP, Norman D, Newton TH, Bolla K, Mark A (1989) Intradural spinal cord lesions: Gd-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 170: 229–237
Dús V (1960) Spinal peripachymeningitis (epidural abscess). Report of 8 cases. J Neurosurg 17: 972–983
Eriksen KD, Gjerris F (1992) Spinal epidural abscess after epidural catheter. Abstract-book. The 44th Annual Meeting of the Scandinavian Neurosurgical Society, Tampere, Finland, June 1992, p 50
Firsching R, Richard KE, Thun F (1988) Acute hydrocephalus in infectious spinal disorder. Neurosurg Rev 11: 103–105
Frank B, Dörr BF, Penkert G, Vogel E, Tidow G (1991) Epiduraler spinaler Abszeß mit Kaudasymptomatik als Komplikation eines Morbus Crohn. Dtsch Med Wochen 116: 1313–1316
Garrido E, Rosenwasser B (1983) Experience with the suction-irritgation technique in the management of the spinal epidural infection. Neurosurgery 12: 678–679
Hakin RN, Burt AA, Cook JB (1979–80) Acute spinal epidural abscess. Paraplegia 17: 330–336
Hancock DO (1973) A study of 49 patients with acute spinal extradural abscess. Paraplegia 10: 285–288
Hanigan WC, Nesher PhD, Asner G, Elwood PW (1990) Magnetic resonance imaging and the nonoperative treatment of spinal epidural abscess. Surg Neurol 34: 408–413
Hershkowitz S, Link R, Ravden M, Lipow K (1990) Spinal empyema in Crohn's disease. J Clin Gastroenterol 12: 67–69
Heusner AP (1948) Nontuberculous spinal epidural infections. N Engl J Med 239: 845–854
Hlavin ML, Kaminski HJ, Ross JS, Ganz E (1990) Spinal epidural abscess: a ten-year perspective. Neurosurgery 27: 177–184
Hulme A (1954) Spinal epidural abscess. BMJ 9: 64–68
Jacoby W (1952) Der akute spinale Epiduralabszeß bei bakterieller Allgemeininfektion. Zbl Neurochir 5: 265–285
Kaminski R (1917) Eine metastatische Peripachymeningitis und Periostitis spinalis nach Furunkulose. Inaugural-Dissertation, Greifswald
Keeling P, Clery AP, (1984) Retrorectal abscess: a complication of terminal ileal Crohn's disease. Br J Surg 71: 831
Klinger M, Druschky KF, Mokrusch Th (1987) Spinaler epiduraler Abszeß als Ursache eines progredienten Querschnittssyndroms. In: Brock WJ, Schirmer M (eds) Differentialdiagnosen in der Neurochirurgie. Urban-Schwarzenberg, München, pp 170–172
Knudsen Ll, Voldby B, Stagaard M (1987) Computed tomographic myelography in spinal subdural empyema. Neuroradiology 29: 99
Leys D, Lesoin F, Viaud C, Pasquier F, Rousseaux M, Jomin M, Petit H (1985) Decreased morbidity from acute bacterial spinal epidural abscesses using computed tomography and non-surgical treatment in selected patients. Ann Neurol 17: 350–355
Lownie SP, Ferguson GG (1989) Spinal subdural empyema complicating cervical discography. Spine 14: 1415–1417
Mampalam TJ, Rosegay H, Andrews BT, Rosenblum ML, Pitts LH (1989) Nonoperative treatment of spinal epidural infections. J Neurosurg 71: 208–210
Menezes AH, Graf CJ, Perret GE (1977) Spinal cord abscess: a review. Surg Neurol 8: 461–467
Menezes AH, VanGilder JC (1985) Spinal cord abscess. In: Wilkins RH, Rengachary SS (eds) Neurosurgery. Mc Graw Hill, New York, pp 1969–1972
Mooney RP, Hockberger RS (1987) Spinal epidural abscess: a rapidly progressive disease. Ann Emerg Med 16: 1168–1170
Morgagni GB (1796) De sedibus et causis morborum per anatomen indagatis. Epist X, art 13, p 46
Patronas NJ, Marx WJ, Duda EE (1979) Radiographic presentation of spinal abscess in the subdural space. AJR 132: 138–139
Ravicovitch MA, Spallone A (1982) Spinal epidural abscesses. Surgical and parasurgical management. Eur Neurol 21: 347–457
Rockney R, Ryan R, Knuckey N (1989) Spinal epidural abscess. An infectious emergency. Clin Pediatr 28: 332–334
Sacher M, Göpfrich H, Hochberger O (1989) Crohn's disease penetrating into the spinal canal. Acta Paediatr Scand 78: 647–649
Sachs L (1974) Angewandte Statistik: Planung und Auswertung, Methoden und Modelle. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Sandhu FS, Dillon WP (1991) Spinal epidural abscess: evaluation with contrast-enhanced MR imaging. AJNR 12: 1087–1093
Schmalz A (1925) Über akute Pachymeningitis spinalis externa. Virch Arch 257: 521–562
Schon F, Bowler JV (1990) Syringomyelia and syringobulbia following tuberculous meningitis. J Neurol 237: 122–123
Strohecker J, Grobovschek M (1986) Der spinale Epiduralabszeß: Eine interdisziplinäre Notfallsituation. Zentralbl Neurochir 47: 120–124
Theodotou B, Woosley RE, Whaley RA (1984) Spinal subdural empyema: diagnosis by spinal computed tomography. Surg Neurol 21: 610–612
Verner EF, Musher DM (1985) Spinal epidural abscess. Med Clin North Am 69: 375–384
Watts JW, Mixter WJ (1931) Spinal epidural granuloma. N Engl J Med 204: 1335–1344
Weber W (1955) Über spinale epidurale Eiterungen und ihre Komplikationen (Rückenmarksabszeß). Zentralbl Neurochir 15: 226–231
West D, Russell TR, Brotman M (1983) Rectalepidural fistula complicating Crohn's enterocolitis. Dis Colon Rectum 26: 622–624
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lange, M., Tiecks, F., Schielke, E. et al. Diagnosis and results of different treatment regimes in patients with spinal abscesses. Acta neurochir 125, 105–114 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01401836
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01401836