Summary
The light curve of Cl−-uptake (uptake vs. light intensity) byElodea densa in pure N2 shows that saturation is reached at a very low light intensity. In N2+3% CO2, on the other hand, there is considerably less Cl- uptake. Under these conditions, the saturation attained at low light intensity is only temporary, and the Cl--uptake increases steadily with a further rise in light intensity. It is suggested that the reason for the low intensity of light saturation may be the necessity for an intracellular transport of ATP from the site of its formation to the site of Cl--uptake.
CO2 exerts a strong inhibitory influence on the Cl--uptake, especially at low light intensities. At higher intensities the inhibition diminishes and it is nearly absent at high intensities of white light.
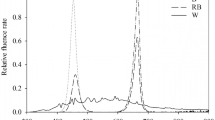
The inhibition by CO2 is also a function of the wavelength of the light; it is greatest in the region below 683 nm, where photosynthesis occurs with high efficiency, but it is still present at wavelengths beyond 700 nm.
CO2 also inhibits the Cl--uptake at high light intensities of white light when small concentration of DCMU (5×10-7 M) is present at the same time.
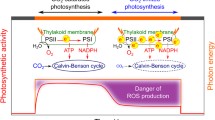
The inhibitory action of CO2 is partly interpreted as a consequence of a competition for ATP between CO2-assimilation (espectially below 683 nm) and the light-dependent Cl--uptake. In addition, however, it is suggested that at low light intensities the presence of CO2 effects a regulation between noncyclic and cyclic electron transports and photophosphorylation which is supposed to be a consequence of a change in the redox potential of ferredoxin or another cofactor acting in noncyclic and cyclic electron transports. Especially the inhibition of the Cl--uptake by CO2 in far-red light (λ>700 nm) and in the presence of DCMU is taken to be an indication of this intracellular regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DCMU:
-
3-(3,4-Dichlorphenyl)-1,1-dimethylharnstoff
- DCPIP:
-
2,6-Dichlorphenolindophenol
- Fd:
-
Ferredoxin
- PMS:
-
Phenazinmethosulfat
- I:
-
Lichtintensität
Literatur
Arnon, D. I.: Cell-free photosynthesis and the energy conversion process. In: Light and life (Hrsg. W. D. McElroy and B. Glass) Baltimore John Hopkins Press 1961.
—: The chloroplast as a functional unit in photosynthesis. Handb. Pflanzenphysiologie, Bd. V, p. 773–829 (Hrsg. W. Ruhland). Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1960.
—,H. Y. Tsujimoto, andB. D. McSwain: Ferredoxin and photosynthetic phosphorylation. Nature (Lond.)214, 562–566, 1967.
Avron, M.: Mechanism of photoinduced electron transport in isolated chloroplasts. Current topics in bioenergetics, vol. II, p. 1–22 (Hrsg. D. R. Sanadi). New York: Academic Press 1967.
—, —: Photophosphorylation in chloroplasts. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol.19, 137–65 (1968).
Batra, P. T., andA. T. Jagendorf: Bicarbonate effects of the Hill reaction and photophosphorylation. Plant Physiol.40, 1074–1079 (1965).
Baltscheffsky, H., andD. Y. de Kieweit: Existence and localization of two phosphorylation sites in photophosphorylation of isolated spinach chloroplasts. Acta chem. scand.18, 2406–2408 (1964).
Bianchetti, R.: Azione della luce sull'assorbimento salino da parte di tessuti chlorofilliani in ambiente privo di CO2. G. bot. ital.70, 321–328 (1963).
Calvin, M.: Der Weg des Kohlenstoffs in der Photosynthese. Angew. Chemie74, 165–188 (1962).
Emerson, R., andC. M. Lewis: The dependence of the quantum yield ofChlorella photosynthesis on wave length of light. Amer. J. Bot.30, 165–178 (1943)
Essl, A.: Diss. Würzburg, 1969.
Forti, A., andB. Parisi: Evidence for the occurrence of cyclic photophosphorylation in vivo. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)71, 1–6 (1963).
Gimmler, H.: Untersuchungen über den Einfluß von Kohlendioxid auf Phosphorylierungsprozesse bei der einzelligen GrünalgeAnkistrodesmus braunii unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Photosynthesephosphorylierung. Diss. Würzburg, 1967.
Grohmet-Elhanan, Z.: The relationship of cyclic and non-cyclic electron flow pattern with reduced indophenols to photophosphorylation. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)131, 526–537 (1967)
Grant, G. R., andF. R. Whatley: Some factors affecting the onset of cyclic photophosphorylation. Biochemistry of chloroplasts, vol. 2, p. 505 (Hrsg. T. W. Goodwin). London and New York: Acad. Press, 1967.
Jeschke, W. D.: Die cyclische und die nichtcyclische Photophosphosphorylierung als Energiequellen der lichtabhängigen Chloridionenaufnahme beiElodea. Planta (Berl.)73, 161–174 (1967).
—, u.W. Simonis: Über die Aufnahme von Phosphat-und Sulfationen durch Blätter vonElodea densa und ihre Beeinflussung durch Licht, Temperatur und Außenkonzentration. Planta (Berl.)67, 6–32 (1965).
—, u. —: Effect of CO2 on photophosphorylation in vivo, as revealed by the light-dependent Cl--uptake inElodea densa. Z. Naturforsch.22b, 873–876 (1967).
—, u. —: Effects of carbon dioxide and light quality upon the light-dependent Cl--uptake inElodea densa. European Photobiology Symposion, Book of Abstracts, p. 101–104. Zagred: Yugoslav Academy of Sciences (1967b).
Kandler, O.: Über die Beziehungen zwischen Phosphathaushalt und Photosynthese II, Gesteigerter Glucoseeinbau im Licht als Indikator einer lichtabhängigen Phosphorylierung. Z. Naturforsch.9b, 625–644 (1954).
—, u.W. Tanner: Die Photoassimilation von Glucose als Indikator für die Licht-phosphorylierungin vivo. Ber. dtsch. bot. Ges.79, 48–57 (1966).
Keister, D. L.: Indophenols as electron donors and catalysts of photophosphorylation in chloroplasts reactions. J. biol. Chem.240, 2673–77, 1965.
Kylin, A.: The influence of photosynthetic factors and metabolic inhibitors on the uptake of phosphate in P-deficientScenedesmus. Physiol. Plant. (Copenh.)19, 644–649 (1966).
—: The uptake and metabolism of sulphate inScenedesmus as influenced by citrate, carbon dioxide, and metabolic inhibitors. Physiol. Plant. (Copenh.)20, 139–148 (1967).
Lookeren Campagne, R. N. van: Light-dependent chloride absorption inVallisneria leaves. Acta bot. neerl.6, 543–582 (1957).
MacRobble, E. A. C.: The nature of the coupling between light energy and active ion transport inNitella translucens. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)94, 64–73 (1965).
Mohr, H., u.G. Schoser: Eine Interferenzfiltermonochromatoranlage für photobiologische Zwecke. Planta (Berl.)53, 1–17 (1959).
Nielsen, P. T.: Light-promoted uptake of chloride inChlorella. Plant Physiol., Suppl.38, IV (1963).
Pringsheim, E. G., andW. Wiesner: Photoassimilation of acetate by green organisms. Nature (Lond.)188, 919–21 (1960).
Raven, J. A.: Photosynthesis and light-stimulated ion transport inHydrodictyon africanum. Abh. dtsch. Akad. Wiss. Berl. 1968,4a, 145–151 (1968).
Simonis, W.: Zyklische und nichtzyklische Photophosphorylierung in vivo. Ber. dtsch. bot. Ges.80, 395–402 (1967).
—, u.K. H. Grube: Untersuchungen über den Zusammenhang von Phosphathaushalt und Photosynthese. Z. Naturforsch.7b, 194–196 (1956).
—, u.H. Kating: Untersuchungen zur lichtabhängigen Photophosphorylierung. III. Die CO2-Abhängigkeit der32P-Einlagerung inAnkistrodesmus. Z. Naturforsch.11b, 704–708 (1956).
Steemann-Nielsen, E.: Uptake of CO2 by the plant. In: Handbuch der Pflanzenphysiologie, Bd. V/1, S. 70–84 (Hrsg. W. Ruhland) Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1960.
Tagawa, K., H. Y. Tsujimoto, andD. I. Arnon: Analysis of photosynthetic reactions by the use of monochromatic light. Nature (Lond.)199, 1247–1252 (1963).
Tanner, W., L. Dächsel, andO. Kandler: Effects of DCMU and antimycin A on photoassimilation of glucose inChlorella. Plant. Physiol.40, 1151–1156 (1965).
Ullrich, W.: In Vorbereitung.
Urbach, W., andW. Simonis: Inhibitor studies on the photophosphorylation in vivo by unicellular algae (Ankistrodesmus) with antimycin A, HOQNO, salicylaldoxime, and DCMU. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.17, 39–45 (1964).
Wassink, E. C., J. F. G. M. Wintermanns, andJ. E. Tjia: Phosphate exchanges inChlorella in relation to conditions for photosynthesis. Proc. kon. ned. Acad. Wet.54, 3–14, 1951.
Weigl, J.: Über den Zusammenhang von Photophosphorylierung und aktiver Ionenaufnahme. Z. Naturforsch.19b, 845–851 (1964).
Wintermanns, J. F. G. M.: Polyphosphate formation inChlorella in relation to photosynthesis. Med. Landbouwhog. Wagen. (Ned.)55, 69–126 (1955).
Witt, H. T.: Über die Analyse der Photosynthese mit Blitzlicht. Angew. Chemie77, 821–842 (1965).
Zalenski, O. V., andT. A. Glagolewa: Relative intensity of photophosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation in the intact cells ofChlorella pyrenoidosa Chick. European Photobiology Symposion, Book of Abstracts, p. 123–126 (1967).
Sweig, G., andM. Avron: Dependence of photophosphorylation by isolated chloroplasts on the oxidation-reduction state of methyl sulphate N-methylphenazinium (phenazin methosulphate). Nature (Lond.)208, 190 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeschke, W.D., Simonis, W. Über die Wirkung von CO2 auf die lichtabhängige Cl--Aufnahme beiElodea densa: Regulation zwischen nichtcyclischer und cyclischer Photophosphorylierung. Planta 88, 157–171 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01391122
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01391122