Abstract
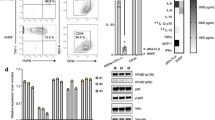
In rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial fibroblasts are activated by growth factors and cytokines to proliferate and to express matrix-degrading proteases and pro-inflammatory cytokines. This contributes to cartilage degradation and joint destruction. To analyse the parameters that lead to activation of synovial fibroblasts, we established a stable human synoviocyte line (K4IM) from a healthy donor by immortalization with SV40 T antigen (TAg). Characterizing the phenotype of the immortalized K41M cells, we found that they maintained CD44, CD54 (intercellular adhesion molecule; ICAM-1) and CD95 (Fas) expression, but lost the expression of CD106 (vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; VCAM-1) and the receptors for interleukin 1 (IL-1) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF). We also monitored normal expression kinetics of transcription factor Egr-1 upon activation with tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) or synovial fluid from RA patients. In addition, we showed that HLA-DR expression could still be upregulated by recombinant interferon gamma (HNF-Y). The immortalized K41M cell line therefore represents a valuable and unique tool to study mechanisms that induce or maintain synoviocyte activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burmester GR, Menche D, Merryman P, Klein M, Winchester R (1983) Application of monoclonal antibodies to the characterization of cell eluted from human articular cartilage. Expression of la antigens in certain diseases and identification of an 85-kD cell surface molecule accumulated in the pericellular matrix. Arthritis Rheum 26:1187–1195
Trabandt A, Aicher WK, Gay RE, Sukhatme VP, Fassbender HG, Gay S (1992) Spontaneous expression of immediately-early response genes c-fos and Egr-1 in collagenase-producing rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Rheumatol Int 12:53–59
Aicher WK, Heer AH, Trabandt A, Bridges SL Jr, Schroeder HW Jr, Stransky G, Gay RE, Eibel H, Peter HH, Siebenlist U, et al (1994) Overexpression of zinc-finger transcription factor Z-225/Egr-1 in synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients J Immunol 152:5940–5948
Sukhatme VP, Cao X, Chang LC, Tsai-Morris C-H, Stamenkovich D, Ferreira PC, Cohen D, Edwards SA, Shows TB, Curran T, LeBeau MM, Adamson ED (1988) A zink finger-encoding gene coregulated with c-fos during growth and differentiation, and after cellular depolarization. Cell 53:37–43
Cao XM, Guy GR, Sukhatme VP, Tan YH (1992) Regulation of the Egr-1 gene by tumor necrosis factor and interferons in primary human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 267:1345–1349
Sukhatme VP, Kartha S, Toback G, Taub R, Hoover RG, Tsai-Morris C-H (1987) A novel early growth response gene rapidly induced by fibroblast, epithelial cell and lymphocyte mitogens. Oncogene Research 1:343–355
Sukhatme VP (1992) The Egr-1 transcription factor family: from signal transduction to kidney differentiation. Kidney Int 41:550–553
Pelletier JP, Faure MP, DiBattista JA, Wilhelm S, Visco D, Martel Pelletier J (1993) Coordinate synthesis of stromelysin interleukin-1, and oncogene proteins in experimental osteoarthritis. An immunohistochemical study. Am J Pathol 142:95–105
Bucala R, Ritchlin C, Winchester R, Cerami A (1991) Constitutive production of inflammatory and mitogenic cytokines by rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. J Exp Med 173:569–574
Keyszer GM, Heer AH, Kriegsmann J, Geiler T, Trabandt A, Keysser M, Gay RE, Gay S (1995) Comparative analysis of cathepsin L, cathepsin D, and collagenase messenger RNA expression in synovial tissues of patient with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, by in situ hybridization. Arthritis Rheum 38:976–984
Trabandt A, Aicher WK, Gay RE, Sukhatme VP, Nilson-Hamilton M, Hamilton RT, McGhee JR, Fassbender HG, Gay S (1990) Expression of the collagenolytic and Ras-induced cysteine proteinas cathepsin L and proliferation-associated oncogenes in synovial cells of MRL/I mice and patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Matrix 10:349–361
Trabandt A, Gay RE, Fassbender HG, Gay S (1991) Cathepsin B in synovial cells at the site of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 34:1444–1451
Tanaka A, O'Sullivan FX, Koopman WJ, Gay S (1988) Etiopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis-like disease in MRL/I mice. 2. Ultrastructural basis of joint destruction. J Rheumatol 15:10–16
Sack U, Kuhn H, Ermann J, Kinne RW, Vogt S, Jungmichel D, Emmrich F (1994) Synovial tissue implants from patients with rheumatoid arthritis cause cartilage destruction in knee joints of SCID.bg mice. J Rheumatol 21:10–16
Geiler T, Kriegsmann J, Keyszer GM, Gay RE, Gay S (1994) A new model for rheumatoid arthritis generated by engraftment of rheumatoid synovial tissue and normal human cartilage into SCID mice. Arthritis Rheum 37:1664–1671
Zvaifler NJ, Firestein GS (1994) Pannus and pannocytes. Alternative models of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 37:783–789
Rubelj I, Pereira-Smith OM (1994) SV40-transformed human cells in crisis exhibit changes that occur in normal cellular senescence. Exp Cell Res 211:82–89
Neufeld DS, Ripley S, Henderson A, Ozer HL (1987) Immortalization of human fibroblasts transformed by origin-defective simian virus 40. Mol Cell Biol 7:2794–2802
Wright WE, Pereira-Smith OM, Shay JW (1989) Reversible cellular senescence: implications for immortalization of normal human diploid fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol 9:3088–3092
Gotoh S, Gelb L, Schlessinger D (1979) SV40-transformed human diploid cells that remain transformed throughout their limited lifespan. J Gen Virol 42:409–414
Pereira-Smith OM, Smith JR (1983) Evidence for the recessive nature of cellular immortality. Science 221:964–966
Shay JW, Wright WE (1989) Quantitation of the frequency of immortalization of normal human diploid fibroblasts by SV40 large T-antigen. Exp Cell Res 184:109–118
Lemaire R, Flipo RM, Monte D, Dupressoir T, Duquesnoy B, Cesbron JY, Janin A, Capron A, Lafyatis R (1994) Synovial fibroblast-like cell transfection with the SV40 large T antigen in duces a transformed phenotype and permits transient tumor formation in immunodeficient mice. J Rheumatol 21:14091419
Shimozato O, Watanabe N, Goto M, Kobayashi Y (1996) Cytokine production by SV40-transformed adherent synovial cells from rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine 8:99–105
Goto M, Okamoto M, Sasano M, Nishizawa K, Aotsuka S, Yamaguchi N, Obinata M, Ikeda K (1991) Functional characterization of SV40-transformed adherent synovial cells from rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol 86:387–392
Brombacher F, Köhler G, Eibel H (1991) B cell tolerance in mice transgenic for anti-CD8 immunoglobulin mu chain. J Exp Med 174:1335–1345
Chu CQ, Field M, Allard S, Abney E, Feldmann M, Maini RN (1992) Detection of cytokines at the cartilage/panmus junction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: implications for the role of cytokines in cartilage destruction and repair. Br J Rheumatol 31:653–661
Trabandt A, Gay RE, Sukhtame VP, Gay S (1992) Expression of collagenase and potential transcriptional factors c-fos and egr-1 in periodontal gingival fibroblasts. J Oral Pathol Med 21:232–240
Herschmann HR (1991) Primary response genes induced by growth factors and tumor promoters. Annu Rev Biochem 60:281–319
Hayflick L (1968) Human cells and aging. Sci Am 218:32–37
Stein GH (1985) SV40-trans formed human fibroblasts: evidence for cellular aging in pre-crisis cells. J Cell Physiol 125:36–44
Goldstein S (1990) Replicative senescence: the human fibroblast comes of age. Science 249:1129–1133
Zeng G, Millis AJ (1996) Differential regulation of collagenase and stromelysin mRNA in late passage cultures of human fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res 222:150–156
Bizot-Foulon V, Bouchard B, Hornebeck W, Dubertret L, Bertaux B (1995) Uncoordinate expressions of type I and III collagens, collagenase and tissue inhibitor of matrix metall oproteinase 1 along in vitro proliferative life spanof human skin fibroblasts. Regulation by all-trans retinoic acid. Cell Biol Int 19:129–135
Millis AJ, Hoyle M, McCue HM, Martini H (1992) Differential expression of metalloprotemase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase genes in aged human fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res 201:373–379
Zeng G, Millis AJ (1994) Expression of 72-kDa gelatinise and TIMP-2 in early and late passage human fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res 213:148–155
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haas, C., Aicher, W.K., Dinkel, A. et al. Characterization of SV40 T antigen immortalized human synovial fibroblasts: maintained expression patterns of EGR-i, HLA-DR and some surface receptors. Rheumatol Int 16, 241–247 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01375656
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01375656