Summary
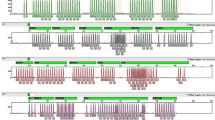
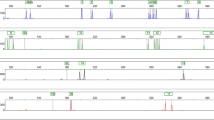
Selected stain cases are presented which highlight various problems associated with DNA investigations on stain materials, especially risks of artefacts. These cases involve stain materials (blood, semen) which were exposed to different external conditions so that the DNA was partially degraded and of variable quantity. One multi locus probe (MLP) and 4-6 single locus probes (SLP's) were used for individualisation but artefacts such as extra bands, band deficiencies or shifts only occurred with the MLP. In one case where only a few spermatozoa were present in the vaginal swab, DNA extraction was carried out without preferential lysis to avoid loss of sperm DNA. The resulting mixed band pattern could be clearly attributed to the bands from the corresponding blood samples after SLP hybridisation.
Zusammenfassung
Anhand ausgesuchter Spurenfälle wurden verschiedene Problembereiche, insbesondere Artefaktrisiken, bei DNA-Untersuchungen an Spurenmaterial behandelt. In den vorgestellten Fällen lagen Spurenmaterialien (Blut, Sperma) in deutlich verschiedener Quantität vor, die unterschiedlichen exogenen Bedingungen ausgesetzt und dementsprechend tw. degradiert waren. Die Individualisierungsnachweise erfolgten mit 4–6 Singlelocus-Sonden (SLS's) und mit einer Multilocus-Sonde (MLS). Artefakte, wie Zusatzbanden, Defizienzen oder „shifts” ergaben sich nur mit der MLS, so daß die SLS's, auch aufgrund ihrer erhöhten Sensitivität, der MLS vorzuziehen waren. Als methodische Alternative wurde in einem Fall mit nur wenig Spermien im Vaginalsekret bei der DNA-Extraktion auf eine preferentielle Lyse verzichtet, um DNA-Verluste zu vermeiden. Das Mischbandenmuster konnte mit SLS-Hybridisierung anhand der Vergleichsblutproben von Tatverdächtigem und Opfer zweifelsfrei zugeordnet werden. In allen vorgestellten Fällen führte die SLS-Anwendung zu eindeutig auswertbaren Ergebnissen, die MLS-Anwendung teilweise zu Interpretationsschwierigkeiten.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brinkmann B, Rand S, Wiegand P (1991) Population and family data of RFLP's using selected single- and multi-locus systems. Int J Leg Med 104: 81–86
Budowle B, Waye JS, Shutler GG, Baechtel FS (1990) Hae III — a suitable restriction endonuclease for restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of biological evidence samples. J Forensic Sci 35: 530–536
Budowle B, Chakraborty R, Giusti AM, Eisenberg AJ, Allen RC (1991) Analysis of the variable number of tandem repeats locus D1S80 by the polymerase chain reaction followed by high resolution polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Am J Genet 48: 137–144
Gill P, Jeffreys AJ, Werrett DJ (1985) Forensic applications of DNA “fingerprints”. Nature 318: 577–579
Grossman LI (1989) Gel electrophoresis of DNA. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium on the Forensic Aspects of DNA Analysis. FBI Academy Quantico, June 19–23,1989. US Department of Justice, pp 37–46
Howard BH (1989) Restriction enzymes: basic properties and use in RFLP analysis. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium on the Forensic Aspects of DNA Analysis. FBI Academy Quantico, June 19–23, 1989. US Department of Justice, pp 29–35
Kasai K, Nakamura Y, White R (1990) Amplification of a variable number of tandem repeats (VNTR) locus (pMCT 118) by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and its application to forensic science. J Forensic Sci 35 (5): 1196–1200
McNally L, Baird M, McElfresh K, Eisenberg A, Balazs I (1990) Increased migration rate observed in DNA from evidentiary material precludes the use of sample mixing to resolve forensic cases of identity. Appl Theor Electrophor 1: 267–272
Rand S, Schiirenkamp M, Schütte U, Brinkmann B (1990) Evaluation of unusual band patterns in stains of biological interest. In: Polesky HIT, Mayr WR (eds) Advances of forensic haemogenetics 3. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 352–354
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning. A new laboratory manual, Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbour, New York
Washio K, Ueda S, Misawa S (1990) Effects of cytosine methylation at restriction sites on Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) typing. J Forensic Sci 35: 1277–1283
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rand, S., Wiegand, P. & Brinkmann, B. Problems associated with the DNA analysis of stains. Int J Leg Med 104, 293–297 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01369589
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01369589