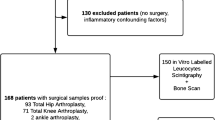
Summary
70 patients with confirmed (23 patients) or suspected (47 patients) bacterial infection in the skeleton following diseases, injuries or operations in orthopedic surgery were investigated using Tc-99m-HMPAO leucocyte scintigraphy in order to evaluate the accuracy of this procedure. Infections could be detected correctly in 37 of 70 patients (right positives) while 28 patients had negative scans corresponding to the clinical course (right negatives). One false negative fording was observed. Five patients with clincially suspected infection had a focal uptake in the WBC-scan and were not operated subsequently. They range as false positive results, although they belong to a special group (Infection: Yes-Operation: No [IYON]-group). In the assessment of the Tc-99m-HMPAO-WBC-scan there was a sensitivity of 97.1%, specificity of 82.9% and an overall accuracy of 90%. The method is suitable for detection of early and late infection as well as chronic or hematogenous osteomyelitis in the locomotor system. This means an important contribution in diagnosis of infection determining further operative or conservative treatment.
Zusammenfassung
70 Patienten mit klinisch gesicherten (23 Patienten) bzw. fraglichen (47 Patienten) bakteriellen Infektionen am Skeletsystem bei unfallchirurgisch/orthopädischen Erkrankungen, Verletzungen oder Operationen wurden mit der Eigenleukocytenszintigrafe untersucht. Hierbei macht man sich das Prinzip der Leukocytenmigration zum Infektionsherd zunutze. Als Markierungssubstanz wurde gegenüber bisher geübten Verfahren das sehr vorteilhafte Tc-99m-HMPAO angewandt. Bei den 23 Patienten mit klinisch gesicherten Infektionen ergaben die szintigrafischen Untersuchungen positive Befunde. Von den 47 Patienten mit klinisch fraglichem Infekt ergab sich bei 14 ein szintigrafsch positiver Befund, was sich operativ als richtig bestätigen ließ. 28 Patienten zeigten einen durch klinischen Verlauf und Operation gesicherten richtig-negativen Szintigrafebefund. 5 Patienten mit klinisch fraglichen Infektzeichen und positiven Leukocyten-Szintigrammen wurden nach Rückgang der Infektsymptomatik nach der LS nicht operativ revidiert und einer Sondergruppe zugeordnet (Infection: Yes-Operation: No [IYON]-Gruppe). Bei der Gesamtbeurteilung des Verfahrens ergab sich eine Sensitivität von 97,1%, Spezifität von 82,9% und eine Gesamt-Genauigkeit von 90%. Die Tc-99m-HMPAO-Leukocytenszintigrafe erweist sich als geeignetes Verfahren zur Bestätigung/Ausschluß von bakteriellen Früh-, Spät- und akuten Schüben von chronischen sowie hämatogenen Infekten am Skeletsystem.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Allgöwer M (1971) Weichteilprobleme und Infektionsrisiko der Osteosynthese. Langenbecks Arch Chir 329:1127
Becker W (1988) Leukozytenszintigraphie — zur Diagnostik entzündlicher Erkrankungen. NUC Compact Schriftenreihe. GIT, Darmstadt
Burri C (1984) Die chronische Osteitis am Unterschenkel. Orthopäde 13:316–323
Crokaert F, Schoutens A, Wagner J, Ansay J (1982) Gallium-67 citrate as an aid to the diagnosis of infection in hip surgery. Int Orthop 6:163–169
Esterhai JL Jr, Alavi A, Mandell GA, Brown J (1985) Sequential 99m-techneticum-67-gallium scintigraphic evaluation of subclinical osteomyelitis complicating fracture nonunion. J Orthop Res 3:219–225
Froelich JW (1985) Nuclear medicine in inflammatory diseases. In: Freeman LM, Weissmann HS (eds) Nuclear medicine annual 1985. Raven Press, New York, pp 23–71
Hotze A, Bockisch A, Rilther M, Biersack HJ (1988) Vergleich von99mTc-HMPAO-markierten Leukozyten und99mTc-Nanokolloid bei Osteomyelitiden. Nucl Med 27:63–65
Iles SE, Ehrlich LE, Saliken JC, Martin RH (1987) Indium-111 chloride scintigraphy in adult osteomyelitis. J Nucl Med 28:1540–1545
Joseph K, Damann V, Energoff G, Gruner KR (1986) Markierung von Leukozyten mit 99m-Technetium-HM-PAO: Erste klinische Ergebnisse. Nucl Compact 17:277–283
Kaps HP, Georgi P, Becker W (1985) Die 111-In-Leukozyten-Szintigraphie bei entzündlichen Erkrankungen des Haltungs- und Bewegungsapparates - erste Ergebnisse. Z Orthop 123:880–888
McAfee JG, Subramanian G, Gagne G, Schneider RF, Zapf-Longo C (1987) 99m-Tc-HM-PAO for leukocyte labeling — experimental comparison with 111-In oxine in dogs. Eur J Nucl Med 13:353–357
Merkel KD, Brown ML, Dewanjaee MK, Fitzgerald RH (1985) Comparison of indium-labeled-leukocyte imaging with sequential technetium-gallium scanning in the diagno sis of low grade musculosceletal sepsis. J Bone Joint Surg 67:465–476
Peters AM, Danpure HJ, Osman S (1986) Clinical experience with99m-Tc hexamethylpropylene-amineoxime for labelling leukocytes and imaging inflammation. Lancet II:946–949
Sayle BA, Fawcett HD, Wilkey DJ (1985) Indium-111 chloride imaging in the detection of infected prostheses. J Nucl Med 26:718–721
Schauwecker DS, Park HM, Mock BH (1984) Evaluation of complicating osteomyelitis with tc-99m, In-111 granulocytes and Ga-67 citrate. J Nucl Med 25:849–853
Schilmichen C, Schölmerich J (1986) Tc-99m, HM-PAO labelling of leukocytes for detection of inflammatory bowel disease. Nucl Compact 17:274–276
Starker M, Brandhorst I, Heippertz W (1988) Die szintigrafische Diagnostik mit99m-Techneticum-HMPAO markierten autologen Leukozyten bei infizierten Kunstgelenken. Vortrag 7. Steglitzer Unfalltagung, 10. 6. 88, Berlin
Thakur ML, Coleman E, Mayhall CG, Welch MJ (1976) Preparation and evaluation of 111-In-labeled leukocytes as an abscess imaging agent in dogs. Radiology 119:731–732
Thakur ML (1977) Indium-111: A new radioactive tracer for leukocytes. Exp Hematol 5:145–150
Willenegger H, Müller J, Roth B (1977) Zur Behandlung der postoperativen Wundinfektion nach Osteosynthese. Zielsetzung und Bewährtes. Orthopäde 6:208–218
Winker KH, Reuland P, Müller J, Weller S, Feine U (1988) Die99mTc-HMPAO-Leukozytenszintigraphie in der Entzündungsdiagnostik am Skelettsystem. Nucl Med 27:121–126
Winker KH, Reuland P, Feine U (1989)99mTc-HMPAO-Leukocytenszintigrafie: Zwingen alle positiven Befunde zur chirurgischen Intervention? 5 Fallbeispiele aus der Unfallchirurgie. Nucl Compact (im Druck)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Winker, K.H., Reuland, P., Weller, S. et al. Infektionsdiagnostik in der Chirurgie des Bewegungsapparates mit der Tc-99m-HMPAO-Leukocytenszintigrafie. Langenbecks Arch Chiv 374, 200–207 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01359554
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01359554