Abstract
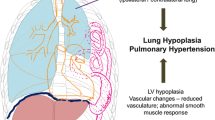
The first description diaphragmatic hernia appeared in 1575. In 1848, Bochdalek described congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) occurring through a posterolateral defect. Successful surgical treatment of CDH in an infant was first performed in 1902, whereas the first neonate operated within 24 hours of life was reported in 1946. However, early surgery did not improve survival rates and the mortality was in the region of 50%. One reason for this was that more neonates underwent surgery who previously would have died without the repair of the CDH. Pulmonary hypoplasia and pulmonary hypertension were early recognised as important reasons for the high mortality rate. In recent years, an enormous effort has been made by research groups all over the world to describe the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of CDH, and apply these findings to clinical practice. Attempts have been made to define prognostic factors. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) has produced encouraging results. Fetal surgical therapy remains an option in selected cases despite huge technical and ethical problems. Recently, several new therapeutic methods have been suggested, such as high frequency oscillatory ventilation, partial liquid ventilation, nitric oxide inhalation, surfactant therapy, and fetal tracheal ligation. However, more experience is required before the value of these approaches is clear. Despite these efforts, the mortality remains unacceptably high. The challenge for the future is to continue development of therapeutic approaches in order to improve survival of neonates with CDH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adzick NS, Harrison MR (1994) Fetal surgical therapy. Lancet 343: 897–902
Alshafei M, Okazaki T, Gischler SJ, Albert A, Ijsselstijn H, Lachmann B, Tibboel D (1996) Partial liquid ventilation in experimental congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) significantly improves lung function. Presented at the XLIII Annual International Congress of the British Association of Paediatric Surgeons, Jersey, Channel Islands, 16–19 July 1996
Areechon W, Reid L (1963) Hypoplasia of the lung with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. BMJ 1: 230–233
Aue O (1920) Über angeborene Zwerchfellhernien. Dtsch Z Chir 160: 14–35
Azarow K, Pearl R, Messineo A, Filler R, Bohn D (1996) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia - a tale of two cities: the Toronto experience. Presented at the XLIII Annual International Congress of the British Association of Paediatric Surgeons, Jersey, Channel Islands, 16–19 July 1996
Barlett RH, Gazzaniga AB, Jefferies MR, Huxtable RF, Haiduc NJ, Fong SW (1976) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in infancy. Trans Am Soc Artif Internal Organs 22: 80–93
Bax NMA, Collins DL (1984) The advantages of reconstruction of the dome of the diaphragm in congenital posterolateral diaphragmatic defects. J Pediatr Surg 19: 484–487
Bell MJ, Ternberg JL (1977) Antenatal diagnosis of diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatrics 60: 738–740
Benacerraf BR, Adzick NS (1987) Fetal diaphragmatic hernia: ultrasound diagnosis and clinical outcome in 19 cases. Am J Obstet Gynecol 156: 573–576
Bettman DB, Hass JH (1929) Incarcerated diaphragmatic hernia in an infant. JAMA 92: 2014–2016
Bianchi A, Doig C, Cohen SJ (1983) The reverse latissimus dorsi flap for congenital diaphragmatic hernia repair. J Pediatr Surg 18: 560–563
Bochdalek VA (1848) Einige Betrachtungen über die Entstehung des angeborenen Zwerchfellbruches. Als Beitrag zur pathologischen Anatomic der Henien. Wochenschr Prakt Heilk 18: 89–94
Bohn DJ (1989) Ventilatory management of blood gas changes in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. In: Puri P (ed) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Karger, Basel, pp 76–89
Bohn DJ, James I, Filler RM, Ein SH, Wesson DE, Shandling B, Barker GA (1984) The relationship between PaCO2 and ventilation parameters in predicting survival in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 19: 666–671
Boix-Ochoa J, Peguero G, Seijo G, Natal A, Canals J (1974) Acid base balance and blood gases in prognosis and therapy of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 19: 49–57
Bonetus T (1679) Sepulchretum sive anatomia proctei et cadaverieius morbo denatus (Geneva). In: Gray SW, Skandalakis JE (eds) Embryology for surgeons (1972). Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 359–374
Boros SJ, Mammel MC, Coleman JM, Lewallen PK, Gordon MJ, Bing DR, Ophoven JP (1985) Neonatal high-frequency jet ventilation: four years' experience. Pediatrics 75: 657–663
Bos AP, Tibboel D, Hazebroek FWJ, Lachmann B, Gommers D (1991) Surfactant replacement therapy in high-risk congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Letter to the editor. Lancet 338: 1279
Bowditch HI (1853) Peculiar care of diaphragmatic hernia. Buffalo Med J 9: 65–95
Broman I (1902) Über die Entwicklung des Zwerchfells beim Menschen. Verh Anat Gres 21: 9–17
Butt W, Taylor B, Shann FG (1992) Mortality prediction in infants with congenital diaphragmatic hernia: potential criteria for ECMO. Anesth Intensive Care 20: 439–442
Campanale RP, Rowland RH (1955) Hypoplasia of the lung associated with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Ann Surg 142: 176–189
Cartlidge PHT, Mann NP, Kapila L (1986) Preoperative stabilisation in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Arch Dis Child 61: 1226–1228
Charlton AJ, Bruce J, Davenport M (1991) Timing of surgery in congenital diaphragmatic hernia: low mortality after preoperative stabilisation. Anaesthesia 46: 820–823
Cooper AP (1827) The anatomy and surgical treatment of abdominal hernia. Longmen Recs Orme Brown & Green, London
Di Fiore JW, Wilson JM (1995) Lung liquid, fetal lung growth, and congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatr Surg Int 10: 2–9
Di Fiore JW, Fauza DO, Slavin R, Peters CA, Fackler JC, Wilson JM (1994) Experimental fetal tracheal ligation reverses the structural and physiological effects of pulmonary hypoplasia in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 29: 248–257
Di Fiore JW, Fauza DO, Slavin R, Wilson JM (1995) Experimental fetal tracheal ligation and congenital diaphragmatic hernia: a pulmonary vascular morphometric analysis. J Pediatr Surg 30: 917–924
Estes JM, MacGillivray TE, Hedrick MH, Adzick NS, Harrison MR (1992) Fetoscopic surgery for the treatment of congenital anomalies. J Pediatr Surg 27: 950–954
Fitzgerald RJ (1977) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: a study of mortality factors. Ir J Med Sci 146: 280–284
Frostell C, Fratacci MD, Wain JC, Jones R, Zapol WM (1991) Inhaled nitric oxide: a selective pulmonary vasodilator reversing hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Circulation 83: 2038–2047
Geisler F, Grotlieb A, Fried D (1977) Agenesis of the diaphragm repaired with Marlex. J Pediatr Surg 12: 587–588
Gibson C, Fonkalsrud EW (1983) Iatrogenic pneumothorax and mortality in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 18: 555–559
Glick PL, Stannard VA, Leach CL, Rossman J, Hosada Y, Morin FC, Cooney DR, Allen JE, Holm B (1992) Pathophysiology of congenital diaphragmatic hernia II: the fetal lamb CDH model is surfactant deficient. J Pediatr Surg 27: 382–388
Glick PL, Leach CL, Besner GE, Egan EA, Morin FC, Malanowska-Kantoch A, Robinson LK, Brody A, Lele AS, McDonnell M, Holm B, Rodgers BT, Msall ME, Courey NG, Karp MP, Allen JE, Jewett TC, Cooney DR (1992) Pathophysiology of congenital diaphragmatic hernia III: exogenous surfactant therapy for the high-risk neonate with CDH. J Pediatr Surg 27: 866–869
Goetzman BW, Sunshine P, Johnson JD, Wennberg RP, Hackel A, Merten DF, Bartoletti AL, Silverman NH (1976) Neonatal hypoxia and pulmonary vasospasm: response to tolazoline. J Pediatr Surg 89: 617–621
Gray SW, Skandalakis JE (1972) The diaphragm. In: Gray SW, Skandalakis JE (eds) Embryology for surgeons. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 357–385
Greenwald HM, Steiner M (1929) Diaphragmatic hernia in infancy and childhood. Am J Dis Child 38: 361–392
Gross RE (1946) Congenital hernia of the diaphragm. Am J Dis Child 71: 579–592
Haller JA Jr, Sroner RD, Grolladay ES, Inon AE, Harrington DP, Shermata DW (1976) Pulmonary and ductal hemodynamics in studies of simulated diaphragmatic hernia of fetal and newborn lambs. J Pediatr Surg 11: 675–680
Hardy KJ, Auldist AW, Shulkes A (1982) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: intrauterine repair in fetal sheep. Med J Aust 26: 223–225
Harrison MR, Jester JA, Ross NA (1980) Correction of congenital diaphragmatic hernia in utero I. The model: intrathoracic balloon produced fetal pulmonary hypoplasia. Surgery 88: 174–182
Harrison MR, Ross NA, de Lorimier AA (1981) Correction of congenital diaphragmatic hernia in utero III. Development of a successful surgical technique using abdominoplasty to avoid compromise of umbilical blood flow. J Pediatr Surg 16: 934–942
Harrison MR, Filly RA, Golbus MS, Berkowitz RL, Callen PW, Canty TG, Catz C, Clewell WH, Depp R, Edwards MS, Fletcher JL, Frigoletto FD, Garrett WJ, Johnson ML, Jonsen A, de Lorimier AA, Liley WA, Mahoney MJ, Manning FD, Meier PR, Michejda M, Nakayama DK, Nelson L, Newkirk JB, Pringle K, Rodech C, Rosen MA, Shulman JD (1982) Fetal treatment 1982. N Engl J Med 307: 1651–1652
Harrison MR, Adzick NS, Longaker MT, Goldberg JD, Rosen MA, Filly RA, Evans MI, Golbus MS (1990) Successful repair in utero of a fetal diaphragmatic hernia after removal of viscera from the left thorax. N Engl J Med 322: 1522–1524
Harrison MR, Langer JC, Adzick NS, Golbus MS, Filly RA, Anderson RL, Rosen MA, Callen PW, Goldstein RB, deLorimier AA (1990) Correction of congenital diaphragmatic hernia in utero V Initial clinical experience. J Pediatr Surg 25: 47–57
Harrison MR, Adzick NS, Flake AW, Jennings RW, Estes JM, McGillivray TE, Chuch JT, Goldberg JD, Filly RA, Goldstein RB, Rosen MA, Cauldwell C, Levine AH, Howell LJ (1993) Correction of congenital diaphragmatic hernia in utero VI. Hard-earned lessons. J Pediatr Surg 28: 1411–1418
Harrison MR, Adzick NS, Flake AW, Jennings RW (1993) The CDH two-step: a dance of necessity. J Pediatr Surg 28: 813–816
Hedblom CA (1925) Diaphragmatic hernia: a study of three hundred and seventy eight cases in which operation was performed. JAMA 85: 547–553
Hedrick HL, Kaban JM, Pacheco BA, Losty PD, Doody DP, Ryan DP, Manganaro TF, Donahoe PK, Schnitzer JJ (1996) Prenatal glucocorticoids improve pulmonary morphometrics in fetal sheep with CDH. Presented at the 277th annual meeting of the American Pediatric Surgical Association, San Diego, California, 19–22 May 1996
Heidenhain L (1905) Geschichte eines Falles von chronischer Incarceration des Magens in einer angeborenen Zwerchfellhemie welcher durch Laparotomie geheilt wurde mit anschliessenden Bemerkungen über die Möglichkeit das Kardiacarcinom der Speiseröhre zu resesziren. Deutsch Z Chir 76: 394–403
Holcomb GW Jr (1962) A new technique for repair of congenital diaphragmatic hernia with the absence of the left hemidiaphragm. Surgery 51: 534–540
Holt C (1701) Child that lived two months with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Phil Trans 22: 992
Henneberg SW, Jepsen S, Andersen PK, Pedersen SA (1995) Inhalation of nitric oxide as a treatment of pulmonary hypertension in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 30: 853–855
Kaapa P, Koivisto M, Ylikorkala O, Kouvalainen K (1985) Prostacyclin in the treatment of neonatal pulmonary hypertension. J Pediatr 107: 951–953
Karamanoukian HL, Glick PL, Zayek M, Steinhorn RH, Zwass MS, Fineman JR, Morin FC (1994) Inhaled nitric oxide in congenital hypoplasia of the lungs due to diaphragmatic hernia or oligohydramnios. Pediatris 94: 715–718
Karl SR, Balantine TVN, Snider MT (1983) High-frequency ventilation at rates of 375 to 1800 cycles per minute in four neonates with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 18: 822–828
Kerr S, Crawford M, Currie B, Pracy E, Stacey R, Duffy B (1992) ECMO in newborn infants: the New South Wales experience. J Pediatr Child Health 28: 421–431
Kluth D, Tenbrinek R, von Ekesparre M, Kangah R, Reich P, Brandsma A, Tibboel D, Lambrecht W (1993) The natural history of congenital diaphragmatic hernia and pulmonary hypoplasia in the embryo. J Pediatr Surg 28: 456–463
Kluth D, Tander B, von Ekesparre M, Tibboel D, Lambrecht W (1995) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: the impact of embryological studies. Pediatr Surg Int 10: 16–22
Korns HM (1921) The diagnosis of eventration of the diaphragm. Arch Intern Med 28: 192–212
Ladd WE, Gross RE (1940) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia. N Engl J Med 223: 917–925
Laennec RTH (1834) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia. In: Nyhus, Harkins (eds) (1964). Hernia. Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 602–619
Lally KP, Paranka MS, Roden J, Georgeson KE, Wilson JM, Lillehei CW, Breaux CW, Poon M, Clark RH, Atkinson JB (1992) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: stabilisation and repair on ECMO. Ann Surg 216: 569–573
de Lorimier AA, Tierney DF, Parker HR (1967) Hypoplastic lungs in fetal lambs with surgically produced diaphragmatic hernia. Surgery 62: 12–17
Losty PD, Suen HC, Manganaro TF, Donahoe PK, Schnitzer JJ (1995) Prenatal hormonal therapy improves pulmonary compliance in the nitrofen-induced CDH rat model. J Pediatr Surg 30: 420–426
Lotze A, Knight GR, Anderson KD, Hull WM, Whitsett JA, O'Donnell RM, Martin G, Bulas DI, Short BL (1994) Surfactant (Beractant) therapy for infants with congenital diaphragmatic hernia on ECMO: evidence of persistent surfactant deficiency. J Pediatr Surg 29: 407–412
Luks FI, Deprest JA, Vandenberghe K, Brosens IA, Lerut T (1994) A model for fetal surgery through intrauterine endoscopy. J Pediatr Surg 29: 1007–1009
Metkus AP, Filly RA, Stringer MD, Harrison MR, Adzick NS (1996) Sonographic predictors of survival in fetal diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 31: 148–152
Morgagni GB (1769) Seats and causes of disease investigated by anatomy. Miller and Cadell, London, p 205
Murdock AI, Burrington JB, Swyer PR (1971) Alveolar to arterial oxygenation difference and venous admixture in newly born infants with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Biol Neonate 17: 161–172
Nagaya M, Tsuda M, Murahashi O, Kishida Y (1991) Management of congenital diaphragmatic hernia by extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). Eur J Pediatr Surg 1: 10–14
Nair UR, Entress A, Walker DR (1983) Management of neonatal posterolateral diaphragmatic hernia. Thorax 38: 254–257
Naumann G (1888) Hernia diaphragmatica. Laparotomi Dod Hygeia 50: 524
Neville WE, Clowes GWA (1954) Congenital abscence of hemidiaphragm and the use of a lobe of liver in its surgical correction. Arch Surg 69: 282–290
Newman BM, Jewett TC, Lewis A, Cerny F, Khan A, Karp M, Cooney DR (1985) Prosthetic materials and muscle flaps in the repair of extensive diaphragmatic defects: an experimental study. J Pediatr Surg 20: 362–367
O'Dwyer J (1890) Operation for relief of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Ann Surg 11: 124
O'Toole SJ, Karamanoukian HL, Morin FC, Holm BA, Egan EA, Azizkhan RG, Glick PL (1996) Surfactant decreases pulmonary vascular resistance and increases pulmonary blood flow in the fetal lamb model of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 31: 507–511
O'Toole SJ, Sharma A, Karamanoukian HL, Holm B, Azizkhan RG, Glick PL (1996) Tracheal ligation does not correct the surfactant deficiency associated with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 31: 546–550
Paranka MMS, Clark RH, Yoder CBA, Null DM (1995) Predictors of failure of high-frequency oscillatory ventilation in term infants with severe respiratory failure. Pediatrics 95: 400–404
Pare A (1575) Les oeuvres. Buon, Paris
Peckham GJ, Fox WW (1978) Physiologic factors affecting pulmonary artery pressure in infants with persistent pulmonary hypertension. J Pediatr 93: 1005
Pranikoff T, Gauger PG, Hirschl RB (1996) Partial liquid ventilation in newborn patients with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 31: 613–618
Price MR, Galantowicz ME, Stolar CJ (1991) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and death: a spectrum of etiologies. J Pediatr Surg 26: 1023–1027
Pringle KC, Turner JW, Schofield JC, Soper RT (1984) Creation and repair of diaphragmatic hernia in the fetal lamb: lung development and morphology. J Pediatr Surg 19: 131–140
Puri P, Gorman F (1984) Lethal non-pulmonary anomalies associated with congenital diaphragmatic hernia: implications for early intrauterine surgery. J Pediatr Surg 19: 29–32
Puri P, Gorman WA (1987) Natural history of congenital diaphragmatic hernia: implications for management. Pediatr Surg Int 2: 327–330
Puri P, Dewan P (1989) Historical review. In: Puri P (ed) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Karger, Basel, pp 1–6
Raephaely RC, Downes JJ (1973) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: prediction of survival. J Pediatr Surg 8: 815–823
Rosenkranz JG, Cotton EK (1964) Replacement of left hemidiaphragm by a pedicled abdominal muscle flap. J horac Cardiovasc Surg 48: 912–920
Rowe MI, Uribe FL (1971) Diaphragmatic hernia in the newborn infant: blood gas and pH considerations. Surgery 70: 758–761
Schranz D, Huth R, Michel-Behnke I, Wippermann C-F (1995) Norepinephrine, enoximone, and nitric oxide for treatment of myocardial stunning and pulmonary hypertension in a newborn with diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 30: 801–804
Shah N, Jacob T, Exler R, Morrow S, Ford H, Albanese C, Wiener E, Rowe M, Billiar T, Simmons R, Motoyama E, Nakayama D (1994) Inhaled nitric oxide in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 29: 1010–1015
Simpson JS, Gassage JD (1971) Use of abdominal wall muscle flap in repair of large congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 6: 42–44
Singleton A,Stehauwer OW (1945) Fascia patch transplant in repair of hernia. Surg Gynecol Obstet 80: 243–251
Stone LC, Manson JM (1981) Effects of the herbicide 2,4 dichlorophenyl-p-nitrophenyl ether (nitrofen) on fetal lung development in rats. Toxicology 20: 195–207
Sweed Y, Puri P (1993) The impact of associated malformations on the survival of neonates with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Arch Dis Child 69: 68–70
Tovar JA, Nogues A, Echeverria K, Giribet M (1979) Antenatal diagnosis of posterolateral diaphragmatic hernia. Z Kinderchir 26: 202–204
Towokian RJ, Markowitz RI (1984) A preoperative scoring system for risk assessment of newborns with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 19: 252–257
Valente A, Brereton RJ (1987) Unilateral agenesis of the diaphragm. J Pediatr Surg 22: 848–850
Weinberg J (1938) Diaphragmatic hernia in infants: surgical treatment with use of renal fascia. Surgery 3: 78–86
White JJ, Suzuki M (1972) Hernia through the foramen of Bochdalek: a misnomer. J Pediatr Surg 7: 60–61
Wiener ES (1982) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: new dimensions in management. Surgery 92: 669–681
Wilcox DT, Glick PL, Karamanoukian H, Rossman J, Morin FC, Holm BA (1994) Pathophysiology of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. V Effect of exogenous surfactant therapy on gas ex change and lung mechanics in the lamb congenital diaphragmatic hernia model. J Pediatr 124: 289–293
Wilson JM, Luna DP, Lillehei AW, O'Rourke PP, Vacanti JP (1992) Delayed repair and postoperative ECMO does not improve survival in high risk congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg: 368–375
Wilson JM, DiFiorc JW, Peters CA (1993) Experimental fetal tracheal ligation prevents the pulmonary hypoplasia associated with fetal nephrectomy: possible application for congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 28: 1433–1440
Wilson JM, Lund DP, Lillehei CW Fauza DO, Vacanti JP (1996) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia - a tale of two cities: the Boston experience. Presented at the XLIII Annual International Congress of the British Association of Paediatric Surgeons, Jersey, Channel Islands, 16–19 July 1996
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Puri, P., Wester, T. Historical aspects of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatr Surg Int 12, 95–100 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01349971
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01349971