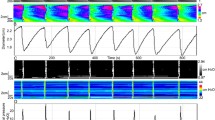
Abstract
Using real-time ultrasonic imaging, and a test meal of 500 ml of dilute orange juice, we have studied the temporal relationships among contractions of the terminal antrum, pylorus, and proximal duodenum of 22 normal subjects. A total of 259 cyclical periods of motor activity were observed. Individual mean gastroduodenal cycle times ranged from 17.9 to 29.6 seconds (2.0–3.3 cycles/min). Terminal antral contractions (TACs) were observed 98% of cycles and pyloric closure invariably occurred at the midpoint of these contractions. The pylorus then opened as the terminal antrum relaxed and remained open until the next TAC. Only 67% of TACs were associated with contractions of the proximal duodenum (DC), but 94% of these occurred about 1 sec (range 1 sec before to 2 sec after) after pyloric closure. Only 6% of DCs were ectopic, in that their occurrence was apparently uncoordinated with the TACs. Our observations demonstrate that after ingestion of a test meal, the human terminal antrum, pylorus, and proximal duodenum usually contract in sequential coordinated manner, presumably under the control of the gastric slow wave. No evidence of independent pyloric closure was obtained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith AWM, Code CF, Schlegel JF: Simultaneous cineradiographic and kymographic studies of human gastric antral motility. J Appl Physiol 11:12–16, 1957
Smith WM, Code CF: The effect of an ordinary and of an excessively fatty breakfast on human gastric antral motility. Gastroenterology 35:398–405, 1958
Johnson AG: The action of metoclopramide on human gastroduodenal motility. Gut 12:421–426, 1971
Fisher R, Cohen S: Physiological characteristics of the human pyloric sphincter. Gastroenterology 64:67–75, 1973
Kaye MD, Mehta SJ, Showalter JP: Manometric studies of the human pylorus. Gastroenterology 70:477–480, 1976
Bateman DN, Leeman S, Metreweli C, Wilson K: A noninvasive technique for gastric motility measurement. Br J Radiol 50:526–527, 1977
Rees WDW, Go VLW, Malagelada JR: Simultaneous measurement of antroduodenal motility, gastric emptying, and duodenogastric reflux in man. Gut 20:963–970, 1979
Rees WDW, Go VLW, Malagelada JR: Antroduodenal motor response to solid-liquid and homogenized meals. Gastroenterology 76:1438–1442, 1979
White CM, Poxon V, Alexander-Williams J: A study of motility of normal human gastroduodenal region. Dig Dis Sci 26:609–617, 1981
Lederer PC, Lauterbach H, Schmitt W, Domschke W, Lux G: Coordination of gastric and duodenal interdigestive motility and the effect of metoclopramide.In Gastrointestinal Motility. G Labo, M Bortolotti (eds). Verona, Cortina International, 1983, pp 109–116
Johnson AG, Eyre-Brook IA, Linhardt GE, Smallwood RH: Does the human pylorus close in response to an isolated duodenal cap contraction? Studies with a new technique.In Gastrointestinal Motility. G Labo, M Bortolotti (eds). Verona, Cortina International, 1983, pp 251–254
Heading RC: Gastric motility. Front Gastrointest Res 6:35–56, 1980
Davenport HW: Physiology of the Digestive Tract, 4th ed. Chicago, year Book Medical Publishers, 1977
Cooke AR: Control of gastric emptying and motility. Gastroenterology 68:804–816, 1975
McShane AJ, O'Moraine C, Lennon JR, Coakley JB, Alton BG: Atraumatic nondistorting pyloric sphincter pressure studies. Gut 21:826–828, 1980
Edwards DAW: Physiological concepts of the pylorus. Proc R Soc Med 54:930–933, 1961
Atkinson M, Edwards DAW, Honour AJ, Rowlands EN: Comparison of cardiac and pyloric sphincters. Lancet 2:918–922, 1957
Valenzuela JE, Defilippi C, Csendes A: Manometric studies on the human pyloric sphincter. Effects of cigarette smoking, metoclopramide, and atropine. Gastroenterology 70:481–483, 1976
White CM, Poxon V, Alexander-Williams J: Effects of nutrient liquids on human gastroduodenal motor activity. Gut 24:1109–1116, 1983
Daniel EE: The electrical and contractile activity of the pyloric region in dogs and the effects of drugs. Gastroenterology 49:405–418, 1965
Weisbrodt NW, Wiley JN, Overholt BF, Bass P: A relationship between gastroduodenal muscle contractions and gastric emptying. Gut 10:543–548, 1969
Lipshutz W, Cohen S: Interaction of gastrin I and secretin on gastrointestinal circular muscle. Am J Physiol 222:775–781, 1972
Wilbur BG, Kelly KA: Effect of proximal gastric, complete gastric, and truncal vagotomy on canine gastric electric activity, motility and emptying. Ann Surg 178:295–303, 1973
Dubois A: Pathophysiology of gastric emptying: Methods of measurement and clinical significance. J Clin Gastroenterol 1:259–266, 1979
Rock E, Malmud L, Fisher RS: Motor disorders of the stomach. Med Clin North Am 65:1269–1289, 1981
King PM, Adam RD, Pryde A, McDicken WN, Heading RC: Relationships of human antroduodenal motility and transpyloric fluid movement: Noninvasive observations with realtime ultrasound. Gut25:1384–1391, 1984
Bateman DN, Whittingham TA: Measurement of gastric emptying by real-time ultrasound. Gut 23:524–527, 1982
Holt S, McDicken WN, Anderson T, Stewart IC, Heading RC: Dynamic imaging of the stomach by real-time ultrasound—a method for the study of gastric motility. Gut 21:597–601, 1980
Rees WDW, Malagelada JR, Go VLW: Human interdigestive motor activity: Effect of saline and liquid nutrient meals. Gastroenterology 74:1083, 1978
Rees WDW, Go VLW, Malagelada JR: The antroduodenal motor response to solid, liquid and homogenized meals in man. Gastroenterology 74:1083, 1978
Friedman G, Wolf BS, Waye JD, Janowitz HD: Correlation of cineradiographic and intraluminal pressure changes in the human duodenum: An analysis of the functional significance of monophasic waves. Gastroenterology 49:37–49, 1965
Duthie HL, Kwong NK, Brown BH, Whittacker GE: Pacesetter potential of the human gastroduodenal junction. Gut 12:250–256, 1971
Stoddard CJ, Waterfall WE, Brown BH, Duthie HL: The effects of varying the extent of the vagotomy on the myoelectrical and motor activity of the stomach. Gut 14:657–664, 1973
Gibb WT: A theory concerning the manner in which the stomach empties itself. Ann Intern Med 16:94–103, 1942
Lerman SH, Mason GR, Bathon EM, Ormsbee HS: Pyloric motor response to sympathetic nerve stimulation in dogs. Surgery 89:460–465, 1981
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by Scottish Home and Health Department grant K/MRS/50/C423.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
King, P.M., Heading, R.C. & Pryde, A. Coordinated motor activity of the human gastroduodenal region. Digest Dis Sci 30, 219–224 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01347887
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01347887