Abstract
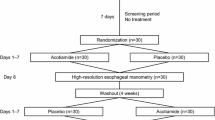
Animal studies have shown that calcium blocking drugs decrease lower esophageal sphincter pressure and inhibit peristaltic amplitude and duration. In a single-dose acute study, we compared the effects of a new oral calcium blocker, diltiazem (90, 120, 150 mg) with placebo in five volunteers and 10 patients with chest pain/dysphagia and high amplitude peristaltic contractions in the distal esophagus-nutcracker esophagus. In volunteers, diltiazem had no effect on esophageal contractions when compared to baseline values or placebo. In contrast, most doses of diltiazem significantly (<0.05) decreased amplitude and duration of peristaltic contractions in patients with nutcracker esophagus. Despite adequate blood levels, interstudy analysis was not statistically significant because placebo also decreased these parameters. During an eight-week open-labeled study, diltiazem 90 mg QID significantly (P<0.01) improved symptoms of chest pain and dysphagia. Side effects were minimal. Although oral diltiazem has minimal effect on baseline esophageal contractions our chronic study suggests it may modify transient increases in neuromuscular tone associated with esophageal chest pain. These observations warrant further placebo-controlled studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stone PH, Antman EM, Muller JE, Braunwold E: Calcium channel blocking agents in the treatment of cardiovascular disorders. Ann Intern Med 93:886–904, 1980
Goyal RK, Rattan S: Effects of sodium nitroprusside and verapamil on lower esophageal sphincter. Am J Physiol 238:40–44, 1980.
Richter JE, Sinar DR, Cordova CM, Castell DO: Verapamil—a potent inhibitor of esophageal contractions in the baboon. Gastroenterology 82:882–886, 1982.
Richter JE, Sinar DR, Cordova CM, Castell DO: Calcium antagonists—potent inhibitors of esophageal function.In Motility of the Digestive Tract. M Wienbeck (ed.). New York, Raven Press, 1982, pp 557–564
Weiser HF, Lepsein G, Golenhofer K, Siewert R: Clinical and experimental studies on the effect of nifedipine on smooth muscle of the esophagus and LES.In Gastrointestinal Motility in Health and Disease. H. Duthie (ed) Lancaster, England, MTP Press, 1978, pp 565–572
Bortolotti M, Labo G: Clinical and manometric effects of nifedipine in patients with esophageal achalasia. Gastroenterology 80:39–44, 1981
Blackwell JN, Holt S, Heading HC: Effect of nifedipine on oesophageal motility and gastric emptying. Digestion 21:50–56, 1981
Berger K, McCallum RW: Nifedipine in the treatment of achalasia. Ann Inter Med 96:61–62, 1982
Benjamin SB, Gerhardt DC, Castell DO: High amplitude, peristaltic esophageal contractions associated with chest pain and/or dysphagia. Gastroenterology 77:478–483, 1979
Brand DL, Martin D, Pope CE II: Esophageal manometrics in patients with angina-like chest pain. Dig Dis Sci 22:300–304, 1977
Herrington JP, Burns TW, Balart LA: Dysphagia in patients with prolonged peristaltic contractile duration—a clinical and manometric analysis. Gastroenterology 80:1173A, 1981
Orr WC, Robinson WG: Hypertensive peristalsis in the pathogenesis of chest pain: Further exploration of the “nut-cracker” esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol 77:604–607, 1982
London RL, Onyang WJ, Snape WJ, Goldberg S Hirshfeld JW, Cohen S: Provocation of esophageal pain by ergonovine or edrophonium. Gastroenterology 81:10–14, 1981
Arndorfer R: Improved infusion system for intraluminal esophageal manometry. Gastroenterology 73:23–27, 1977
Osgood H: A peculiar form of oesophagismus. Boston Med Surg J 120:401–405, 1889
Nagler R, Spiro HM: Serial esophageal motility studies in asymptomatic young subjects. Gastroenterology 41:371–379, 1961
Meyer GW, Castell DO: Human esophageal response during chest pain induced by swallowing cold liquids. JAMA 246:2057–2060, 1981
Kikendoll JW, Mellow MH: Effect of sublingual nitroglycerin and long-acting nitrate preparation on esophageal motility. Gastroenterology 79:703–706, 1980
Gelfond M, Rozen P, Keren S, Gilat T: Effect of nitrates on LOS pressure in achalasia: A potent therapeutic aid. Gut 22:312–318, 1981
Orlando RC, Boyzmski EM: Clinical and manometric effects of nitroglycerine in diffuse esophageal spasm. N Engl J Med 289:23–25, 1973
Mellow MH: Effect of isosorbide and hydralazine in painful esophageal motility disorders. Gastroenterology 83:364–370, 1982
Obrecht WF, Richter JE, Kerr RM, Castell DO, Bradley RA, Young LD: Is the nutcracker esophagus past of the spectrum of irritable bowel syndrome? Gastroenterology 84:1262A, 1983
Benjamin SB, Richter JE, Cordova CM, Knuff TE, Castell DO: Prospective manometric evaluation with pharmacologic provocation of patients with suspected esophageal motility dysfunction. Gastroenterology 84:893–898, 1983
Silverstein BD, Kramer CM, Pope CE II: Treatment of esophageal motor disorders with a calcium-blocker, diltiazem. Gastroenterology 82:1181A, 1982
Zelis R: Calcium-blocker therapy for unstable angina pectoris. N Engl J Med 306:926–928, 1982
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The opinions and assertions contained herein are the private views of the authors and are not construed as official or as reflecting the views of the Department of the Navy or Defense.
The research reported herein was supported by CIP 0-06-1398, USU R08316, and Marion Laboratories, Inc.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richter, J.E., Spurling, T.J., Cordova, C.M. et al. Effects of oral calcium blocker, diltiazem, on esophageal contractions. Digest Dis Sci 29, 649–656 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01347298
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01347298