Summary
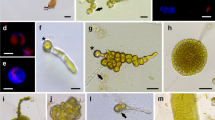
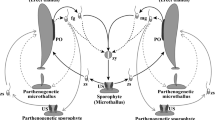
Protoplasts were isolated from four strains of a primitive filamentous brown alga,Pilayella littoralis (L.) Kjellm. (Phaeophyceae) cultured in the same axenic conditions. Protoplast yields were different according to the strain and the concentrations of sodium citrate, a chelator of Ca2+ ions which are known to be involved in the cohesion of the alginate matrix. All protoplasts were able to regenerate and to produce new thalli. Regeneration times varied with the strain, but the modalities were the same. One of the strains, “Pil-Hel”, is always fertile, bearing unilocular and plurilocular zoidangia. After enzymatic digestion of “Pil-Hel”, protoplasts and zoids were recognizable and showed a different pattern of development. Protoplasts developed as did the zoids from unilocular sporangia. Differences observed between strains could be related to differences in the genotype, a hypothesis which seems supported by the existence of differences between the restriction patterns of chloroplastic DNA in two of these strains.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- UA:
-
unit of activity of alginate-lyase
References
Assali NE, Mache R, Loiseaux-de-Goër S (1990) Evidence for a composite phylogenic origin of the plastid genome of the brown algaPylaiella littoralis (L.) Kjellm. Plant Mol Biol 15: 307–315
Boyd PJ, Grimsley NH, Cove DJ (1988) Somatic mutagenesis of moss,Physcomitrella patens. Mol Gen Genet 211: 545–546
Boyen C, Kloareg B, Vreeland V (1988) Comparison of protoplast wall regeneration and native wall deposition in zygotes ofFucus distichus by cell wall labelling with monoclonal antibodies. Plant Physiol Biochem 26: 653–659
—, Bertheau Y, Barbeyron T, Kloareg B (1990 a) Preparation of guluronate-lyase fromPseudomonas alginovora for protoplast isolation inLaminaria. Enzyme Microb Technol 12: 885–890
—, Kloareg B, Polne-Fuller M, Gibor A (1990 b) Preparation of alginate-lyases from marine molluscs for protoplast isolation in brown algae. Phycologia 29: 173–181
Butler DM, Ostgaard K, Boyen C, Evans LV, Jensen A, Kloareg B (1989) Isolation conditions for high yields of protoplasts fromLaminaria saccharina andL. digitata (Phaeophyceae). J Exp Bot 40: 1237–1246
Cardinal A (1964) Etude sur les Ectocarpacées de la Manche. Beih Nova Hedwigia 15: 1–86
Dalmon J, Loiseaux S, Bazetoux S (1983) Heterogeneity of plastid DNA of two species of brown algae. Plant Sci Lett 29: 243–253
Davison IR, Polne-Fuller M (1990) Photosynthesis in protoplasts ofMacrocystis pyrifera (Phaeophyta). J Phycol 26: 384–387
Ducreux G, Kloareg B (1988) Plant regeneration from protoplasts ofSphacelaria (Phaeophyceae). Planta 174: 25–29
— Abdelmoumenaoui G, Mejjad M (1991) Totipotency in brown algae cells and protoplasts. In: Garcia-Reina G, Pedersen M (eds) Seaweed cellular biotechnology, physiology, and intensive cultivation, pp 105–112
Fisher DD, Gibor A (1987) Production of protoplasts from the brown algaSargassum muticum (Yendo) Fensholt (Phaeophyta). Phycologia 26: 488–495
Kajiwara T, Hatanaka A, Fujimura T, Kawai T, Irie M (1988) Isolation of protoplasts from brown algae Dictyotaceae plants. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 547: 1255
Kloareg B, Quatrano RS (1987) Isolation of protoplasts from zygotes ofFucus distichus (L.) Powell. Plant Sci 50: 189–194
— — (1988) Structure of the cell walls of marine algae and ecophysiological functions of the matrix polysaccharides. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 26: 259–315
—, Polne-Fuller M, Gibor A (1989) Mass production and regeneration of protoplasts fromMacrocystis pyrifera. Plant Sci 62: 105–112
Knight CD, Cove DJ, Boyd PJ, Ashton NW (1988) The isolation of biochemical and developmental mutants inPhyscomitrella patens. Methods Biol: 47–58
Knight M (1923) Studies on the Ectocarpaceae: I. The life history and cytology ofPilayella littoralis, Kjellm. Trans R Soc Edinb 53: 343–361
Kropf D, Kloareg B, Quatrano RS (1988) Cell wall is required for fixation of the embryonic axis inFucus zygotes. Science 239: 187–190
Le Gall Y, Braud JP, Kloareg B (1990) Protoplast production inChondrus crispus gametophytes (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta). Plant Cell Rep 8: 582–585
— Brown S, Marie D, Mejjad M, Kloareg B (1991) Quantification of nuclear DNA and GC% in marine macroalgae by flowcytometry of isolated nuclei. J Phycol (in press)
Loiseaux S, Rozier C (1978) Culture axénique dePylaiella littoralis (L.) Kjellm. (Phéophycées). Rev Algol NS 13: 333–340
Loiseaux-de-Goër S, Markowicz Y, Dalmon Y, Audren H (1988) Physical maps of the two circular plastid DNA molecules of the brown algaPylaiella littoralis (L.) Kjellm. Location of the rRNA genes and of several protein coding regions on both molecules. Curr Genet 14: 155–162
Markowicz Y, Loiseaux-de-Goër S, Mache R (1988 a) Presence of a 16S rRNA pseudogene in the bi-molecular plastid genome of the primitive brown algaPylaiella littoralis. Evolutionary implications. Curr Genet 14: 599–608
—, Mache R, Loiseaux-de-Goër S (1988 b) Sequence of the plastid rDNA spacer region of the brown algaPylaella littoralis (L.) Kjellm. Evolutionary significance. Plant Mol Biol 10: 465–469
Müller DG, Stache B (1989) Life history studies onPilaiella littoralis (L.) Kjellm. (Phaeophyceae, Ectocarpales) of different geographical origin. Bot Marina 32: 71–78
Nakada HT, Sweany PC (1967) Alginic acid degradation by eliminases from abalone hepatopancreas. J Biol Chem 242: 845–851
Russell G (1963) A study in populations ofPylaiella littoralis. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 43: 469–483
Russell G (1967) The ecology of some free-living Ectocarpaceae. Helgol Wiss Meeresunters 15: 155–162
Saga N, Sakai Y (1984) Isolation of protoplasts fromLaminaria andPorphyra. Bull Jap Soc Sci Fischeries (Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi) 50: 1085
— Polne-Fuller M, Gibor A (1986) Protoplasts from seaweeds: production and fusion. In: Barclay WR, McIntosh RP (eds) Algal biomass technologies. Nova Hedwigia 83: 37–43
Wang TL, Cove DJ (1989) Mosses—lower plants with high potential. Plants Today March/April 1989: 44–50
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mejjad, M., Loiseaux-de-Goër, S. & Ducreux, G. Protoplast isolation, development, and regeneration in different strains ofPilayella littoralis (L.) Kjellm. (Phaeophyceae). Protoplasma 169, 42–48 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01343368
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01343368