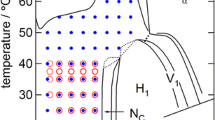
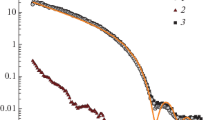
Abstract
A dramatic increase in the viscosity of reverse micellar solutions of lecithin in a variety of organic solvents of up to a factor of 106 upon the addition of a small amount of water can be observed. The formation of viscoelastic solutions can be explained by a water-induced aggregation of lecithin molecules into flexible cylindrical reverse micelles and the subsequent formation of a transient network of entangled micelles. The viscoelastic properties of these solutions are characterized as a function of water content and temperature for different organic solvents by means of dynamic shear viscosity measurements. The results are interpreted by making analogies to the behavior of semidilute polymer solutions and living polymers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scartazzini R, Luisi PL (1988) J Phys Chem 92:829
Schurtenberger P, Scartazzini R, Magid LJ, Leser ME, Luisi PL (1989) submitted to J Phys Chem
De Gennes PG (1979) Scaling Concepts in Polymer Physics. Cornell Univ Press, Ithaca, NY
Ferry JD (1980) Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers. J Wiley & Sons, New York
Candau SJ, Hirsh E, Zana R, Adam M (1988) J Colloid Interface Sci 122:430
Daoud M, Cotton JP, Farnoux B, Jannink G, Sarma G, Benoit H, Duplessix R, Picot C, De Gennes PG (1975) Macromolecules 8:804
Brown W, Mortensen K (1988) Macromolecules 21:420
Wiltzius P, Haller HR, Cannell DS, Schaefer DW (1983) Phys Rev Lett 51:1183
Adam M, Delsanti M (1977) Macromolecules 10:1229
Wiltzius P, Haller HR, Cannell DS, Schaefer DW (1984) Phys Rev Lett 53:834
Cates ME (1988) J Phys France 49:1593
Israelachvili JN (1985) In: Degiorgio V, Corti M (eds) Proceedings of the International School of Physics “Enrico Fermi”. Physics of Amphiphiles, Micelles, Vesicles and Microemulsions. North Holland, Amsterdam, p 24
Blankshtein D, Thurston G, Benedek GB (1986) J Chem Phys 85:7268
Safran S, Turkevitch LA, Pincus P (1984) J Phys Lett 45:L-69
Missel PJ, Mazer NA, Benedek GB, Young CY, Carey MC (1980) J Phys Chem 84:1044
Sheu EY, Chen S-H (1988) J Phys Chem 92:4466
Tausk RJM, Oudshoom C, Overbeek J Th G (1974) Biophys Chem 2:53
Messager R, Ott A, Chatenay D, Urbach W, Langevin D (1988) Phys Rev Lett 60:1410
Ying Q, Chu B (1987) Macromolecules 20:362
Cates ME (1987) Macromolecules 20:2289
Rehage H, Hoffmann H (1988) J Phys Chem 92:4712
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. Dr. J. Meissner on the occasion of his 60th birthday.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schurtenberger, P., Scartazzini, R. & Luisi, P.L. Viscoelastic properties of polymerlike reverse micelles. Rheol Acta 28, 372–381 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01336804
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01336804