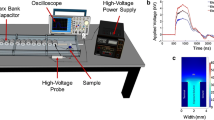
Summary
The lethal effects of high-voltage capacitor-discharges in suspensions of E. coli K12 with varying electrolytes have been examined. A reduction of more than 99.9% of living cells, dependent on the applied voltage could be proved. The bactericidal action is assumed to be due to direct effects of high electric fields. Electrolytically produced chlorine was shown to act as an additional toxic agent, when chloride is present in the treated medium. The relative survival rate of bacteria has been found to depend also on the concentration of cells during pulse treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prochownick, L., Spaeth, F.: Über die keimtötende Wirkung des galvanischen Stromes. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr.26, 564–565 (1890)
Krüger, S.: Über den Einfluß des constanten elektrischen Stromes auf Wachsthum und Virulenz der Bakterien. Z. Klin. Med.22, 191–207 (1893)
Thiele, H., Wolf, K.: Über die Einwirkung des elektrischen Stromes auf Bakterien. Centralbl. Bakt. Parasitenk. Abt. I Orig.25, 650–655 (1899)
Lehmann, K. B., Zierler, F.: Untersuchung über die Abtötung von Bakterien durch schwache therapeutisch verwertbare Ströme. Arch. Hyg.46, 221–250 (1903)
Pareilleux, A., Sicard, N.: Lethal effects of electric current on Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol.19, 421–424 (1970)
Sale, A. J. H., Hamilton, W. A.: Effects of high electric fields on microorganisms I. and II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta.148, 781–800 (1967)
Sale, A. J. H., Hamilton, W. A.: Effects of high electric fields on microorganisms III. Biochim. Biophys. Acta163, 37–43 (1968)
Stolte, W.: Einfluß elektrischer Felder auf Bakteriensuspensionen. Diplomarbeit am Institut für Biophysik der Universität Hannover (1976)
Zimmermann, U., Schulz, J., Pilwat, G.: Transcellular ion flow in Escherichia coli B and electrical sizing of bacterias. Biophys. J.13, 1005–1013 (1973)
Coster, H. G. L., Zimmermann, U.: Dielectric breakdown in the membranes of Valonia utricularis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta382, 410–418 (1975)
Zimmermann, U., Pilwat, G., Riemann, F.: Dielectric breakdown of cell membranes. Biophys. J.14, 881–899 (1974)
Zimmermann, U., Pilwat, G., Holzapfel, C., Rosenheck, K.: Electrical hemolysis of human and bovine red blood cells. J. Membrane Biol.30, 135–152 (1976)
Kinosita, K., Tsong, T. Y.: Voltage-induced pore formation and hemolysis of human erythrocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta.471, 227–242 (1977)
Schwan, H.P.: Field interaction with biological matter. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.303, 198–231 (1977)
Benz, R., Beckers, F., Zimmermann, U.: Reversible electrical breakdown of lipid bilayer membranes: a charge-pulse relaxation study. J. Membrane Biol.48, 181–204 (1979)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hülsheger, H., Niemann, E.G. Lethal effects of high-voltage pulses on E. coli K12. Radiat Environ Biophys 18, 281–288 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01324271
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01324271