Abstract
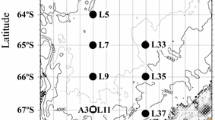
Large (>64 µm) protozooplankton (radiolarians, thecate dinoflagellates, foraminiferans, and tintinnid ciliates) and copepod nauplii were sampled at six stations located in sea-ice-covered waters, using a multinet at five depth intervals between the surface and 1000 m depth during a late winter expedition of R.V. ‘Polarstern’ on a west-east transect across the Weddell Sea in 1989. Large (>400 µm) phaeodarian radiolarians contributed more than 98% of the carbon in the large protozooplankton fraction; large protozooplankton represented ca. 38% of the total protozooplankton carbon during late winter under the close pack ice in the upper 250 m. Large protozooplankton may therefore be an important food source for small particle-feeding zooplankton in the upper 250 m, and a modest food source down to 1000 m. Phaeodarian species distributions showed a distinct vertical pattern. Except for spumellarian and nassellarian radiolarians all other protozooplankton (foraminiferans, thecate dinoflagellates, tintinnids) were most abundant in the upper 250 m. The horizontal variation showed a western, central and eastern pattern most probably due to the differing regional hydrography. Feeding ecology of the dominant species of phaeodarians was examined using transmission electron microscopy of contents of feeding vacuoles. The 58 specimens were trophic generalists. The predominance of silica fragments and amorphous material in vacuoles and the similarity of vacuole contents of specimens from three depth zones suggest that phaeodarians in late winter may have fed on organic aggregates.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Augstein, E., Bagriantsev, N., Schenke, H. W. (1991). Die Expedition Antarktis VIII/1-2 des FS „Polarstern“ mit der Winter Weddell Gyre Study 1989 gemeinsam mit dem FS „Akademic Federov“. Ber. Polarforsch. (Bremerhaven) 84: 1–124
Beers, J. R., Stewart G. L. (1970). Numerical abundance and estimated biomass of microzooplankton. In: Strickland, J. D. H. (ed.) The ecology of the plankton off La Jolla, California in the period April through September, 1967. Bull. Scripps Instn Oceanogr. 17: 67–87
Boltovskoy, D., Alder, V. A., Spinelli, F. (1989). Summer Weddell Sea microplankton: assemblage structure, distribution and abundance, with special emphasis on the Tintinnina. Polar Biol. 9: 447–456
Cachon-Enjumet, M. (1961). Contribution a l'etude des radiolaires phaeodaires. Archs Zool. exp. gén. 100: 151–238
Coleman, A. (1980). Enhanced detection of bacteria in natural environments by fluorochrome staining of DNA. Limnol. Oceanogr. 25: 948–951
Dieckmann, G. S., Spindler, M., Lange, M. A., Ackley, S. F., Eicken, H. (in press). Antarctic sea ice: a habitat for the foraminiferNeogloboquadrina pachyderma. J. foraml Res.
Evans, C. A., O'Reilly, J. E. (1983). A handbook for the measurement of chlorophyll a in netplankton and nanoplankton. S.C.A.R. Biomass handbook 9: 1–44
Fischer, G., Fütterer, D. K., Gersonde, R., Honjo, S., Ostermann, D., Wefer, G. (1988). Seasonal variability of particle flux in the Weddell Sea and its relation to ice cover. Nature, Lond. 335: 426–428
Garrison, D. L. (in press). an overview of the abundance and role of protozooplankton in Antarctic waters. J mar. Systems
Garrison, D. L., Buck, K. R. (1989). Protozooplankton in the Weddell Sea, Antarctica: abundance and distribution in the ice-edge zone. Polar Biol. 9: 341–351
Garrison, D. L., Buck, K. R., Gowing, M. M. (in press). Plankton assemblages in the ice edge zone of the Weddell Sea during the austral winter. J. mar. Systems
Garrison, D. L., Gowing, M. M. (in press). Protozooplankton. In: Friedmann, E. I. (ed.) Antarctic microbiology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Gowing, M. M. (1986). Trophic biology of phaeodarian radiolarians and flux of living radiolarians in the upper 2000 m of the North Pacific central gyre. Deep-Sea Res. 33: 665–674
Gowing, M. M. (1989). Abundance and feeding ecology of Antarctic phaeodarian radiolarians. Mar. Biol. 103: 107–118
Gowing, M. M., Garrison, D. L. (in press a). Austral winter distributions of large tintinnid and large sarcodinid protozooplankton in the ice-edge zone of the Weddell/Scotia Seas. J. mar. Systems
Gowing, M. M., Garrison, D. L. (in press b). Abundance and feeding ecology of larger protozooplankton in the ice edge zone of the Weddell and Scotia Seas during the austral winter. Deep-Sea Res.
Haeckel, E. (1887). Report on the Radiolaria collected by H. M. S. Challenger during the years 1873–1876. In: Thompson, C. W., Murray, J. (eds.) The voyage of HMS Challenger, Vol. 18. Her Majesty's Stationery Office, London, p. 1–1803
Haecker, V. (1908). Tiefsee-Radiolarien. Wiss. Ergebn. dt. Tiefsee-Exped. ‘Validivia’ 14: 1–706
Hopkins, T. L. (1985). Food web of an Antarctic midwater ecosystem. Mar. Biol. 89: 197–212
Hopkins, T. L. (1987). Midwater food web in McMurdo Sound, Ross Sea, Antarctica. Mar. Biol. 96: 93–106
Hopkins, T. L., Torres, J. J. (1989). Midwater food web in the vicinity of a marginal ice zone in the Western Weddell Sea. Deep-Sea Res. 36: 543–560
Morley, J. J., Stepien, J. C. (1985). Antarctic radiolaria in late winter/early spring Weddell Sea waters. Micropaleontology 31: 365–371
Nöthig, E.-M., von Bodungen, B. (1989). Occurrence and vertical flux of faecal pellets of probable protozoan origin in the southeast Weddell Sea (Antarctica). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 56: 281–289
Nöthig, E.-M., Bathmann, U., Fahrbach, E., Gordon, L., Gradinger, R., Jennings, J., Makarov, R. (in press). Regional relationship between biological and hydrographical properties in the Weddell Gyre in late austral winter 1989. Mar. Chem.
Nöthig, E.-M., von Bodungen, B., Sui, Q. (1991). Phyto- and protozooplankton biomass during austral summer in surface waters of the Weddell Sea and vicinity. Polar Biol. 11: 293–304
Peinert, R., von Bodungen, B., Smetacek, V. S. (1989). Food web structure and loss rates. In: Berger, W. H., Smetacek, V. S., Wefer, G. (eds.) Productivity of the ocean: present and past. Dahlem Konferenzen, John Wiley & Sons, New York, p. 35–48
Peters, N. (1929). Beiträge zur Planktonbevölkerung der Weddell-See. 4. Die Tripyleen Radiolarien der Weddell-Sea. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. Hydrogr. 21: 383–401
Popofsky, A. (1908). Die Radiolarien der Antarktis. Dt. Südpol.-Exped. 1901–1903. 10(3): 185–308
Porter, K. G., Feig, Y. S. (1980). The use of DAPI for identifying and counting aquatic microflora. Limnol. Oceanogr. 25: 943–948
Scharek, R. (1990). Die Entwicklung des Phytoplanktons im östlichen Weddellmeer (Antarktis) beim Übergang vom Spätwinter zum Frühjahr. Ph.D. thesis, University of Bremen
Smetacek, V. (1975). Die Sukzession des Phytoplankton der westlichen Kieler Bucht. Ph. D. thesis, University of Kiel
Smetacek, V., Scharek, R., Nöthig E.-M. (1990). Seasonal and regional variation in the pelagial and its relationship to the life history cycle of krill. In: Kerry, K. R., Hempel, G. (eds.) Antarctic ecosystems. Ecological change and conservation. Springer Verlag, New York, p. 103–114
Spindler, M., Dieckmann, G. (1986). Distribution and abundance of the planktic foraminiferaNeogloboquadrina pachyderma in sea ice of the Weddell Sea (Antarctica). Polar Biol. 5: 185–191
Spurr, A. R. (1969). A low viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 26: 31–43
Tibbs, J. F., Tibbs, S. D. (1986). Further studies on the Phaeodaria (Protozoa: Radiolaria) of the Antarctic Seas. Antarctic Res. Ser. 41: 167–202
Wefer, G., Fischer, G., Fütterer, D. K., Gersonde, R., Honjo, S., Ostermann, D. (1990). Particle sedimentation and productivity in antarctic waters of the Antlantic Sector. In: Bleil, U., Thiede, J. (eds.) Geological history of the polar oceans: Arctic versus Antarctic. Kluwer Academic Publications, The Netherlands, p. 363–379
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by O. Kinne, Oldendorf/Luhe
Publication no. 469 of the Alfred-Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nöthig, E.M., Gowing, M.M. Late winter abundance and distribution of phaeodarian radiolarians, other large protozooplankton and copepod nauplii in the Weddell Sea, Antarctica. Mar. Biol. 111, 473–484 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01319421
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01319421