Summary
The influence of divalent cations on the stability of human rotavirus was investigated using the indirect immunofluorescence (FA) technique in LLC-MK2 cells to titrate infectivity.
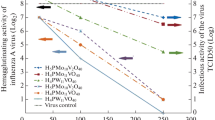
Rotavirus infectivity was stabilized by calcium and strontium ions in solution but not by magnesium ions. Rotavirus isolates were found to be much less stable at 37° C than at +4° C or 20° C. A study of virus morphology at intervals during the course of the experiment and treatment with the chelating agents EDTA and EGTA suggests that loss of infectivity coincides with the removal of the outer capsid layer and that calcium may be required to maintain virus integrity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bridger, J. C., Woode, G. N.: Characterisation of two particle types of calf rotavirus. J. gen. Virol.31, 245–250 (1976).
Bryden, A. S., Davies, Heather A., Thouless, M. E., Flewett, T. H.: Diagnosis of rotavirus infection by cell culture. J. med. Microbiol.10, 121–125 (1977).
Cohen, J.: Ribonucleic acid polymerase activity associated with purified calf rotavirus. J. gen. Virol.36, 395–402 (1977).
Cohen, J., Laporte, J., Charpillienne, A., Scherrer, R.: Activation of rotavirus RNA polymerase by calcium chelation. Arch. Virol.60, 177–186 (1979).
Elias, M. M.: Separation and infectivity of two particle types of human rotavirus. J. gen. Virol.37, 191–194 (1977).
Estes, Mary K., Graham, D. Y., Smith, E. M., Gerba, C. P.: Rotavirus stability and inactivation. J. gen. Virol.43, 403–409 (1979).
Flewett, T. H., Bryden, A. S., Davies, H., Woode, G. N., Bridger, J. C., Derrick, J. M.: Relation between viruses from acute gastroenteritis of children and newborn calves. Lancetii, 61 (1974).
Flewett, T. H., Davies, Heather A., Bryden, A. S., Robertson, M. J.: Acute gastroenteritis associated with reovirus-like particles. J. clin. Pathol.27, 608–614 (1974).
Thouless, M. E., Bryden, A. S., Flewett, T. H., Woode, G. N., Bridger, J. C., Snodgrass, D. R., Herring, J. A.: Serological relationships between rotaviruses from different species as studied by complement fixation and neutralisation. Arch. Virol.53, 287–294 (1977).
Zak, B., Epstein, E., Baginski, E.: Review of calcium methodologies. Ann. clin. Lab. Sci.5, (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 2 Figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shirley, J.A., Beards, G.M., Thouless, M.E. et al. The influence of divalent cations on the stability of human rotavirus. Archives of Virology 67, 1–9 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01314596
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01314596