Summary
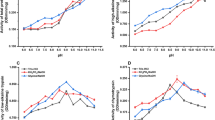
The larval digestive juice of the armyworm,Pseudaletia unipuncta (Harworth), has extremely high alkaline protease activity. No protease or negligible protease activity is present in the hemolymph and in extracts of the body wall. The digestive juice protease is absorbed by the capsules of a granulosis virus under low ionic condition. The protease degrades the capsule matrix proteins at alkaline conditions. The absorption of digestive juice protease by capsules occurs when capsules are obtained by triturating the whole infected larvae. On the other hand, capsules, which have been collected from the triturated body walls of infected larvae whose digestive tracts have been removed, are not degraded when the incubation in an alkaline solution is for less than 24 hours at 25° C. The results suggest that the protease associated with the capsule is derived from the digestive juice of the insect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, D. A.: Two naturally occurring nuclear polyhedrosis virus variants ofNeodiprion sertifer Geoffr. (Hymenoptera; Diprionidae). Appl. environ. Microbiol.43, 65–69 (1982).
Crawford, A. M., Kalmakoff, J.: Effect of alkaline protease on the antigenic nature ofWiseana nuclear polyhedrosis virus polyhedron protein. J. Virol.24, 412–415 (1977).
Eppstein, D. A., Thoma, J. A.: Alkaline protease associated with the matrix protein of a virus infecting the cabbage looper. Biochem. biophys. res. Commun.62, 478–484 (1975).
Eppstein, D. A., Thoma, J. A., Scott, H. A., Young, S. Y., III: Degradation of matrix protein from a nuclear-polyhedrosis virus ofTrichoplusia ni by an endogenous protease. Virology67, 591–594 (1975).
Faulkner, P., Henderson, J. F.: Serial passage of a nuclear polyhedrosis disease virus of the cabbage looper(Trichoplusia ni) in a continuous tissue culture cell line. Virology50, 920–924 (1972).
Kozlov, E. A., Sidorova, N. M., Serebryani, S. B.: Proteolytic cleavage of polyhedral protein during dissolution of inclusion bodies of the nuclear polyhedrosis viruses ofBombyx mori andGalleria mellonella under alkaline conditions. J. invertebr. Pathol.25, 97–101 (1975).
Kozlov, E. A., Levitina, T. L., Gusak, N. M., Larionov, G. V., Veremeichenko, S. N., Serebryanyi, S. B.: Comparative biochemical investigation of polyhedral proteins of nuclear polyhedrosis viruses. Biochemistry (U.S.S.R.)43, 1729–1734 (1978).
Laemmli, U. K.: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature (London)227, 680–685 (1970).
Langridge, W. H. R., Balter, K.: Protease activity associated with the capsule protein ofEstigmene acrea granulosis virus. Virology114, 595–600 (1981).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. biol. Chem.193, 265–275 (1951).
Maruniak, J. E., Summers, M. D., Falcon, L. A., Smith, G. E.:Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus structural proteins compared fromin vivo andin vitro sources. Intervirology11, 82–88 (1979).
McCarthy, W. J., DiCapua, R. A.: Characterization of solubilized proteins from tissue culture- and host-derived nuclear polyhedra ofLymantria dispar andAutographa californica. Intervirology11, 174–181 (1979).
McCarthy, W. J., Liu, S.-Y.: Electrophoretic and serological characterization ofPorthetria dispar polyhedron protein. J. invertebr. Pathol.28, 57–65 (1976).
Payne, C. C., Kalmakoff, J.: Alkaline protease associated with virus particles of a nuclear polyhedrosis virus: assay, purification, and properties. J. Virol.26, 84–92 (1978).
Potter, K. N., Jaques, R. P., Faulkner, P.: Modification ofTrichoplusia ni nuclear polyhedrosis virus passagedvivo. Intervirology9, 76–85 (1978).
Summers, M. D., Smith, G. E.:Trichoplusia ni granulosis virus granulin: a phenolsoluble, phosphorylated protein. J. Virol.16, 1108–1116 (1975).
Tanada, Y., Hukuhara, T., Chang, G. Y.: A strain of nuclear polyhedrosis virus causing extensive cellular hypertrophy. J. invertebr. Pathol.13, 394–409 (1969).
Tweeten, K. A., Bulla, L. A., jr., Consigli, R. A.: Characterization of an alkaline protease associated with a granulosis virus ofPlodia interpunctella. J. Virol.26, 702–711 (1978).
Yamafuji, K., So, K., Soo, K.: Die Wirkung des Seidenraupenpolyedervirus auf die Atmung und Katalase der Hefe. Biochem. Z.311, 203–208 (1941/1942).
Yamafuji, K., Yoshihara, F.: Location of polyhderal pre-viral genome containing protease-synthesizing gene. Enzymologia23, 327–336 (1961).
Yamamoto, T., Tanada, Y., Phospholipid, an enhancing component in the synergistic factor of a granulosis virus of the armyworm,Pseudaletia unipuncta. J. invertebr. Pathol.31, 48–56 (1978a).
Yamamoto, T., Tanada, Y.: Protein components of two strains of granulosis virus of the armyworm,Pseudaletia unipuncta (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae). J. invertebr. Pathol.32, 158–170 (1978b).
Yamamoto, T., Tanada, Y.: Biochemical properties of viral envelopes of insect baculoviruses and their role in infectivity. J. invertebr. Pathol.32, 202–211 (1978c).
Wood, H. A.: Protease degradation ofAutographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus proteins. Virology103, 392–399 (1980).
Zummer, M., Faulkner, P.: Absence of protease in baculovirus polyhedral bodies propagatedin vitro. J. invertebr. Pathol.33, 383–384 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 8 Figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagata, M., Tanada, Y. Origin of an alkaline protease associated with the capsule of a granulosis virus of the armyworm,Pseudaletia unipuncta (Haworth). Archives of Virology 76, 245–256 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01311108
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01311108