Abstract
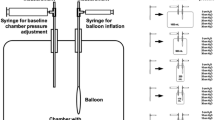
The evaluation of suspected esophageal chest pain is frustrating because of difficulty in clearly implicating the esophagus. Balloon distention was considered as a new provocative test in the esophagus because it has been shown to safely produce pain in other hollow gastrointestinal organs. Studies were performed in 50 chest pain patients (\(\bar X\) age 50 years) with negative coronary arteriograms and 30 healthy volunteers (\(\bar X\) age 41 years). A polyvinyl balloon (length 30 mm; maximum diameter after 10 cc distention 25 mm) was positioned 10 cm above the lower esophageal sphincter and inflated with 1-cc increments of air to a total volume of 10 cc. Using a placebo-controlled design, pain response was recorded along with associated balloon volumes. Pain occurred in 28/50 (56%) patients and 6/30 (20%) volunteers (P<0.005). Symptoms were unassociated with ECG changes, and resolved immediately with decompression of the balloon. Most patients (24/28) experienced their typical chest pain at ≦8 cc distention, while all volunteers with pain noted it at ≧9 cc distention. For this reason, 8 cc was considered a diagnostic cutoff. Chest pain patients were also studied with two other commonly used provocative tests: intraesophageal acid perfusion and intravenous edrophonium (80 μg/kg). These tests reporduced pain in only 12 (24%) patients. Positive balloon studies occurred in 11 of these patients and identified an additional 13 patients, thus increasing the diagnostic yield from 24% to 48%. Only one of 22 (4%) balloon-negative patients had a positive acid-perfusion or edrophonium test.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernstein L, Baker L: A clinical test for esophagitis. Gastroenterology 34:760–781, 1958
Richter JE, Hackshaw BT, Wu WC, Castell DO: Edrophonium: A useful provocative test for esophageal chest pain. Ann Intern Med 103:14–21, 1985
Benjamin SB, Richter JE, Cordova CM, Knuff TE, Castell DO: Prospective manometric evaluation with pharmacologic provocation of patients with suspected esophageal motility dysfunction. Gastroenterology 84:893–901, 1983
Kramer P, Hollander W: Comparison of experimental esophageal pain with clinical pain and angina pectoris and esophageal disease. Gastroenterology 29:719–743, 1955
Baylis JH, Kauntze R, Trounce JR: Observations on distention of the lower end of the esophagus. Q J Med 94:143–154, 1955
Whitehead WE, Engel BT, Schuster MM: Irritable bowel syndrome. Physiological and psychological differences between diarrhea-predominant and constipation-predominant patients. Dig Dis Sci 25:404–413, 1982
Barish CF, Richter JE, Dalton CB, Castell DO: On the mechanism of esophageal chest pain: Evidence for abnormal sensory perception. Clin Res 33:538A, 1985
Dodds WJ, Stef JJ, Hogan WJ: Factors determining pressure measurement accuracy by intraluminal manometry. Gastroenterology 70:117–123, 1976
Benjamin SB, Castell DO: Chest pain of esophageal origin—where are we, and where should we go? Arch Intern Med 143:772–776, 1983
Richter JE, Castell DO: Diffuse esophageal spasm: A reapraisal. Ann Intern Med 100:242–245, 1984
Kemp HG, Vokonas PS, Cohn PF, Gorlin R: The anginal syndrome associated with normal coronary arteriograms. Am J Med 54:735–742, 1973
Kennedy RH, Kennedy MA, Frye RL, Giuliani ER, McGoon DC, Pluth JR, Smith HC, Ritter DG, Nobrega FT, Kurland LT: Cardiac catheterization and cardiac surgical facilities. N Engl J Med 307:986–993, 1982
London RL, Ouyang A, Snape W, Goldberg S, Hirshfield SW, Cohen S: Provocation of esophageal pain by ergonovine or edrophonium. Gastroenterology 81:10–14, 1981
Meyer GW, Castell DO: Human esophageal response during chest pain induced by swallowing cold liquids. JAMA 246:2057–2059, 1981
Mellow M: Symptomatic diffuse esophageal spasm: Manometric follow-up and response to cholinergic stimulation and cholinesterase inhibition. Gastroenterology 73:237–240, 1977
Alban Davis H, Daye MD, Rhoades J, Dart AM, Henderson AH: Diagnosis of esophageal spasm by ergometrine provocation. Gut 23:89–97, 1982
Orlando RC, Bozymski EM: The effects of pentagastrin in achalasia and diffuse esophageal spasm. Gastroenterology 77:472–477, 1979
Respess JC, Inglefinger FJ, Kramer P: Effect of cold on esophageal motor function. Am J Med 20:955, 1952
Catalano CJ, Bozymski EM, Orlando RC: Temperaturedependent symptoms in a patient with esophageal motor disease. Gastroenterology 85:1407–1410, 1983
Dalal JJ, Dart AM, Alban Davis H, Sheridan DJ, Ruttley MST, Henderson AH: Coronary and peripheral arterial responses to ergometrine in patients susceptible to coronary and oesophageal spasm. Br Heart J 45:181–185, 1981
Eastwood GL, Weiner BH, Dickerson WJ, White EM, Ocbene IS, Haffajee CI, Alperts JS: Use of ergonovine to identify esophageal spasm in patients with chest pain. Ann Intern Med 94:768–771, 1981
Koch KL, Curry RC, Feldman RL, Pepine CL, Long A, Mathias JR: Ergonovine-induced esophageal spasm in patients with chest pain resembling angina pectoris. Dig Dis Sci 27:1073–1080, 1982
Cipriano PR, Guthnan DF, Orlick AE, Ricci DR, Wexler L, Silverman JF: The effects of ergonovine maleate on coronary arterial size. Circulation 59:82–89, 1979
Myers D: Ergonovine provocation of coronary artery spasm. Cardiovasc Rev Rep 3(6):855–863, 1982
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barish, C.F., Castell, D.O. & Richter, J.E. Graded esophageal balloon distention. Digest Dis Sci 31, 1292–1298 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01299805
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01299805